Electrons dynamics control micro-hole drilling using temporally/spatially shaped femtosecond laser
-
摘要
微孔作为一种常见结构,被广泛应用于生物医疗、航空航天、三维封装等领域。飞秒激光具有的超短脉冲持续时间和超高峰值功率特性使其在高质量微孔加工方面具有独特优势。本文综述了近年来飞秒激光时空整形微孔加工方法及其应用,包括飞秒激光时空整形方法、时域/空域整形的电子动态调控微孔加工以及微孔在增透减反、切割以及油水分离、雾气收集、气体收集等方面的应用,并讨论了时空整形飞秒激光微孔加工目前所面临的挑战和未来研究方向。
Abstract
As a common structure, microholes are widely used in various fields, including biomedical, aerospace, 3D packaging and so on. Femtosecond laser has unique advantages in drilling high-quality microhole due to its ultra-short pulse duration and ultra-high peak power. This review covers temporally/spatially shaped femtosecond laser microhole drilling methods and their applications over the past decade, including femtosecond laser temporally/spatially shaped methods, temporally/spatially shaped femtosecond laser microhole drilling based on electrons dynamics control, and the applications of microhole in transmittance enhancement and anti-reflection, material cutting, oil/water separation, fog collection and gas collection. Furthermore, present challenges and future research opportunities in this field are analyzed.
-
Overview
Overview: As a common structure, microholes are widely used in biomedical, microfluidic devices, aerospace and 3D packaging fields. As the performance requirements of various functional devices are more and more strict in practical applications, the requirements for the quality and depth-diameter ratio of microhole processing also become much higher, which makes the microhole processing in manufacturing extremely challenging. In view of the increasingly strict requirements of microhole indicators, selecting a suitable microhole processing method is the key.
At present, the commonly used microhole drilling methods are mechanical drilling, electric spark drilling, electron beam drilling, focused ion beam drilling, laser drilling and electro discharge machining (EDM). Mechanical drilling is easy to operate, but it is difficult to process microholes with small diameters and high depth-diameter ratios. EDM drilling is only suitable for conductive materials and is difficult to process. Electron beam and focused ion beam drilling can achieve micro holes with nanometer to submicron precision, but the conditions are harsh. The equipment is expensive, and the processing efficiency is slow. Laser drilling has the characteristics of non-contact, wide material adaptability and high processing efficiency, but the microholes processed by continuous laser and long pulse laser have a certain heat affected zone.
Femtosecond laser is different from the continuous laser and long pulse laser. It has characteristics of ultra-short pulse duration and ultra-high peak power, enabling high-quality processing capacity and wide material adaptability. Compared with traditional processing methods, femtosecond laser has the following three significant advantages: (1) Small thermal effect and high processing quality; (2) Strong nonlinear effect, wide range of material processing and higher processing resolution; (3) The "true" 3D processing. When the femtosecond laser is focused inside the transparent medium, only the material near the focal point can be modified or removed, so the "true" 3D machining of arbitrary complex structures can be achieved with femtosecond laser. Therefore, femtosecond laser provides a new possibility for high-quality microhole drilling. Unshaped Gaussian laser microhole drilling has the contradiction between small diameters and high depth-diameter ratios. Due to the precise and adjustable properties of femtosecond laser, its light field distribution can be controlled in terms of transient local electronic dynamic and subsequent phase transitions by temporally/spatially shaping. In this way, the microhole can be drilled to satisfy the requirements of both small diameter and high depth-diameter ratio.
In this paper, the processing methods regarding electrons dynamics control micro-hole drilling using temporally/spatially shaped femtosecond laser and the applications of microholes in transmittance enhancement and anti-reflection, material cutting, oil and water separation, fog collection and gas transportation are reviewed.
-

-
-
参考文献
[1] Fei Z Z, Hu X, Choi H W, et al. Micronozzle array enhanced sandwich electroporation of embryonic stem cells[J]. Anal Chem, 2010, 82(1): 353−358.
[2] An R, Hoffman M D, Donoghue M A, et al. Water-assisted femtosecond laser machining of electrospray nozzles on glass microfluidic devices[J]. Opt Express, 2008, 16(19): 15206−15211. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.015206
[3] Vong T H, Schoffelen S, van Dongen S F M, et al. A DNA-based strategy for dynamic positional enzyme immobilization inside fused silica microchannels[J]. Chem Sci, 2011, 2(7): 1278−1285. doi: 10.1039/c1sc00146a
[4] Baheri S, Tabrizi S P A, Jubran B A. Film cooling effectiveness from trenched shaped and compound holes[J]. Heat Mass Transfer, 2008, 44(8): 989−998. doi: 10.1007/s00231-007-0341-9
[5] Landgraf R, Rieske R, Danilewsky A N, et al. Laser drilled through silicon vias: crystal defect analysis by synchrotron x-ray topography[C]//Proceedings of the 2nd Electronics System-Integration Technology Conference, 2008: 1023–1028.
[6] Salah K. TGV versus TSV: a comparative analysis[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Advances in Computational Tools for Engineering Applications (ACTEA), 2016: 49–53.
[7] Lai M F, Li S W, Shih J Y, et al. Wafer-level three-dimensional integrated circuits (3D IC): Schemes and key technologies[J]. Microelectron Eng, 2011, 88(11): 3282−3286. doi: 10.1016/j.mee.2011.05.036
[8] Egashira K, Mizutani K. Micro drilling of monocrystalline silicon using a cutting tool[J]. Precis Eng, 2002, 26(3): 263−268. doi: 10.1016/S0141-6359(01)00113-1
[9] Cao X D, Kim B H, Chu C N. Micro-structuring of glass with features less than 100 μm by electrochemical discharge machining[J]. Precis Eng, 2009, 33(4): 459−465. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2009.01.001
[10] Spinney P S, Howitt D G, Smith R L, et al. Nanopore formation by low energy focused electron beam machining[J]. Nanotechnology, 2010, 21(37): 375301. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/21/37/375301
[11] Sebastiani M, Eberl C, Bemporad E, et al. Depth resolved residual stress analysis of thin coatings by a new FIB-DIC method[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2011, 528(27): 7901−7908. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2011.07.001
[12] Zhang Y, Li S C, Chen G Y, et al. Experimental observation and simulation of keyhole dynamics during laser drilling[J]. Opt Laser Technol, 2013, 48: 405−414. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2012.10.039
[13] 王国彪. 光制造科学与技术的现状和展望[J]. 机械工程学报, 2011, 47(21): 157−169.
Wang G B. Photonic manufacturing science & technology: overview and outlook[J]. J Mechan Eng, 2011, 47(21): 157−169.
[14] Ultrafast laser processing: from micro-to nanoscale[M]. CRC Press, 2013.
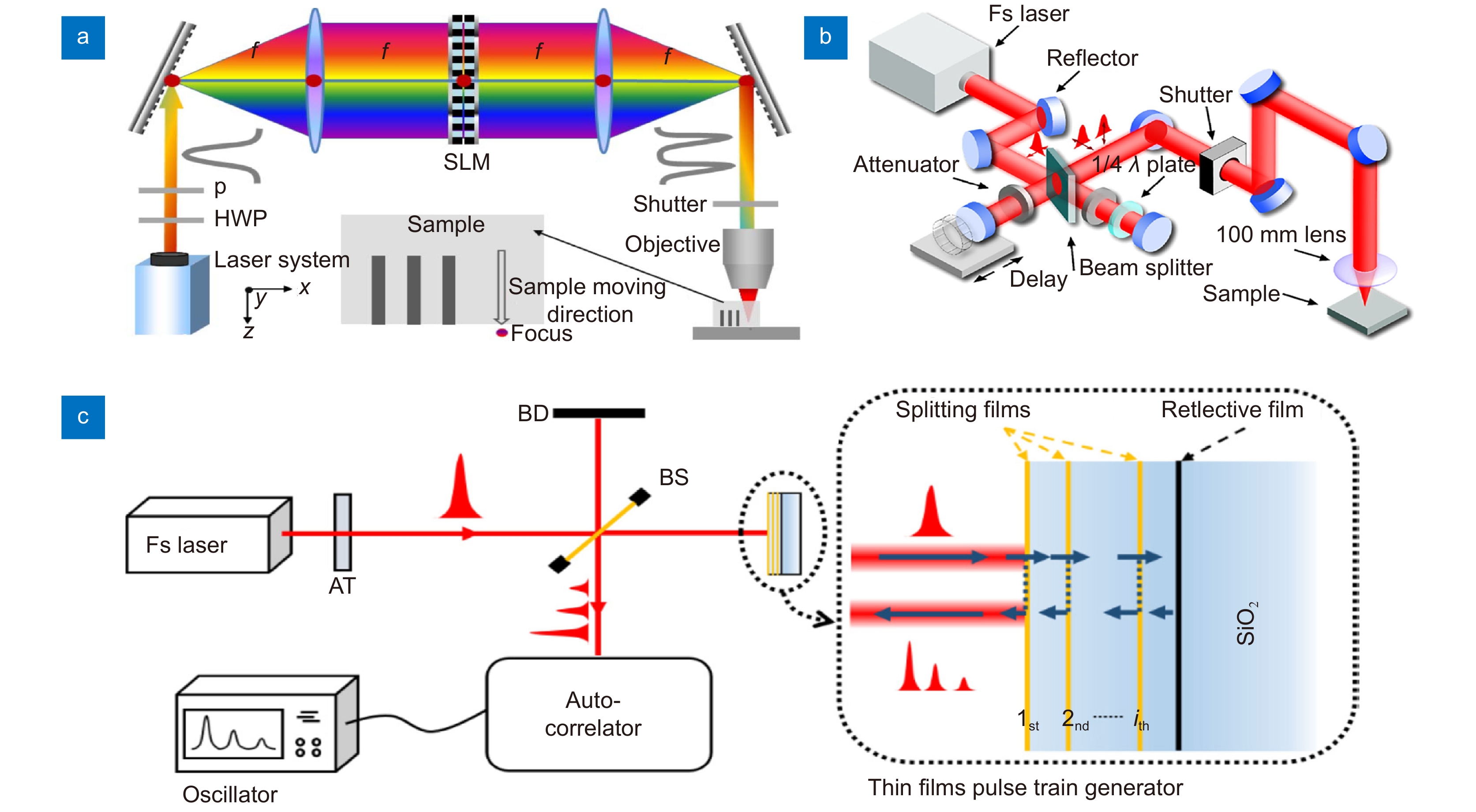
[15] Sugioka K, Cheng Y. Ultrafast lasers-reliable tools for advanced materials processing[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2014, 3(4): e149.
[16] Malinauskas M, Žukauskas A, Hasegawa S, et al. Ultrafast laser processing of materials: from science to industry[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2016, 5(8): e16133. doi: 10.1038/lsa.2016.133
[17] Yang Q X, Liu H L, He S, et al. Circular cladding waveguides in Pr: YAG fabricated by femtosecond laser inscription: Raman, luminescence properties and guiding performance[J]. Opto-Electron Adv, 2021, 4(2): 200005.
[18] Chen L, Cao K Q, Li Y L, et al. Large-area straight, regular periodic surface structures produced on fused silica by the interference of two femtosecond laser beams through cylindrical lens[J]. Opto-Electron Adv, 2021, 4(12): 200036. doi: 10.29026/oea.2021.200036
[19] Livakas N, Skoulas E, Stratakis E. Omnidirectional iridescence via cylindrically-polarized femtosecond laser processing[J]. Opto-Electron Adv, 2020, 3(5): 190035. doi: 10.29026/oea.2020.190035
[20] Jia Y C, Wang S X, Chen F. Femtosecond laser direct writing of flexibly configured waveguide geometries in optical crystals: fabrication and application[J]. Opto-Electron Adv, 2020, 3(10): 190042. doi: 10.29026/oea.2020.190042
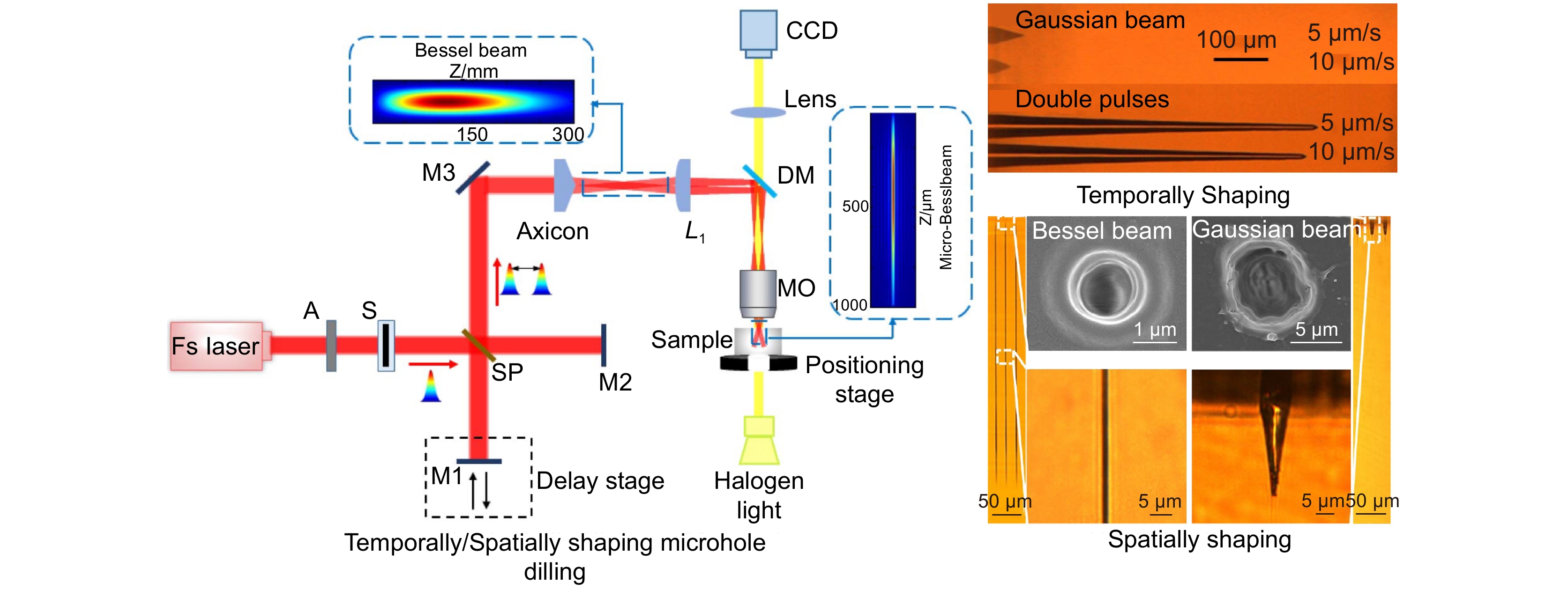
[21] Jiang L, Wang A D, Li B, et al. Electrons dynamics control by shaping femtosecond laser pulses in micro/nanofabrication: modeling, method, measurement and application[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2018, 7(2): 17134. doi: 10.1038/lsa.2017.134
[22] Sundaram S K, Mazur E. Inducing and probing non-thermal transitions in semiconductors using femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Nat Mater, 2002, 1(4): 217−224. doi: 10.1038/nmat767
[23] Gattass R R, Mazur E. Femtosecond laser micromachining in transparent materials[J]. Nat Photonics, 2008, 2(4): 219−225. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2008.47
[24] Chichkov B N, Momma C, Nolte S, et al. Femtosecond, picosecond and nanosecond laser ablation of solids[J]. Appl Phys A, 1996, 63(2): 109−115. doi: 10.1007/BF01567637
[25] Gamaly E G. Femtosecond Laser-Matter Interaction: Theory, Experiments and Applications[M]. London: Pan Stanford, 2011.
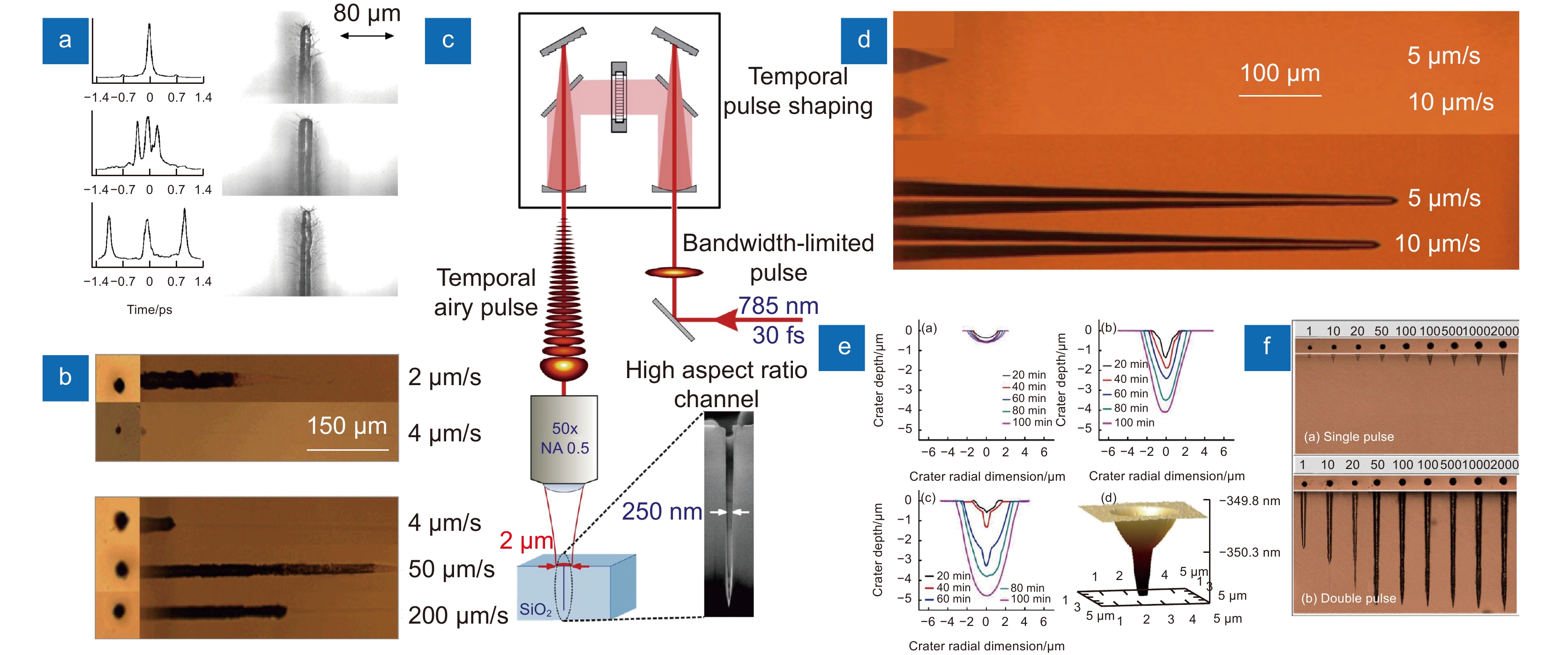
[26] Wu D, Wu S Z, Xu J, et al. Hybrid femtosecond laser microfabrication to achieve true 3D glass/polymer composite biochips with multiscale features and high performance: the concept of ship-in-a-bottle biochip[J]. Laser Photonics Rev, 2014, 8(3): 458−467. doi: 10.1002/lpor.201400005
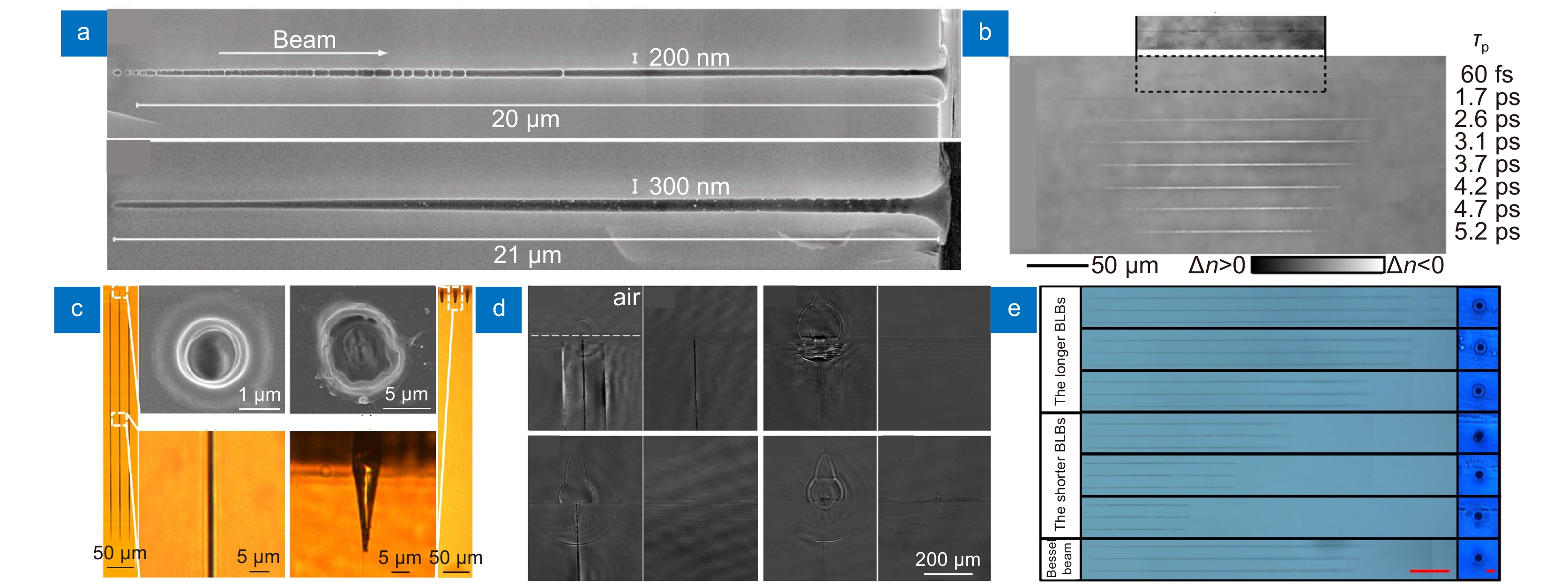
[27] Liu P J, Jiang L, Hu J, et al. Etching rate enhancement by shaped femtosecond pulse train electron dynamics control for microchannels fabrication in fused silica glass[J]. Opt Lett, 2013, 38(22): 4613−4616. doi: 10.1364/OL.38.004613
[28] Liu W, Hu J, Jiang L, et al. Formation of laser-induced periodic surface nanometric concentric ring structures on silicon surfaces through single-spot irradiation with orthogonally polarized femtosecond laser double-pulse sequences[J]. Nanophotonics, 2021, 10(4): 1273−1283. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2020-0568
[29] Du K, Li X W, Zhang H, et al. Controllable photon energy deposition efficiency in laser processing of fused silica by temporally shaped femtosecond pulse: experimental and theoretical study[J]. Opt Laser Technol, 2020, 128: 106265. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106265
[30] Dromey B, Zepf M, Landreman M, et al. Generation of a train of ultrashort pulses from a compact birefringent crystal array[J]. Appl Opt, 2007, 46(22): 5142−5146. doi: 10.1364/AO.46.005142
[31] Wang A D, Jiang L, Li X W, et al. Simple and robust generation of ultrafast laser pulse trains using polarization-independent parallel-aligned thin films[J]. Opt Laser Technol, 2018, 101: 298−303. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2017.11.003
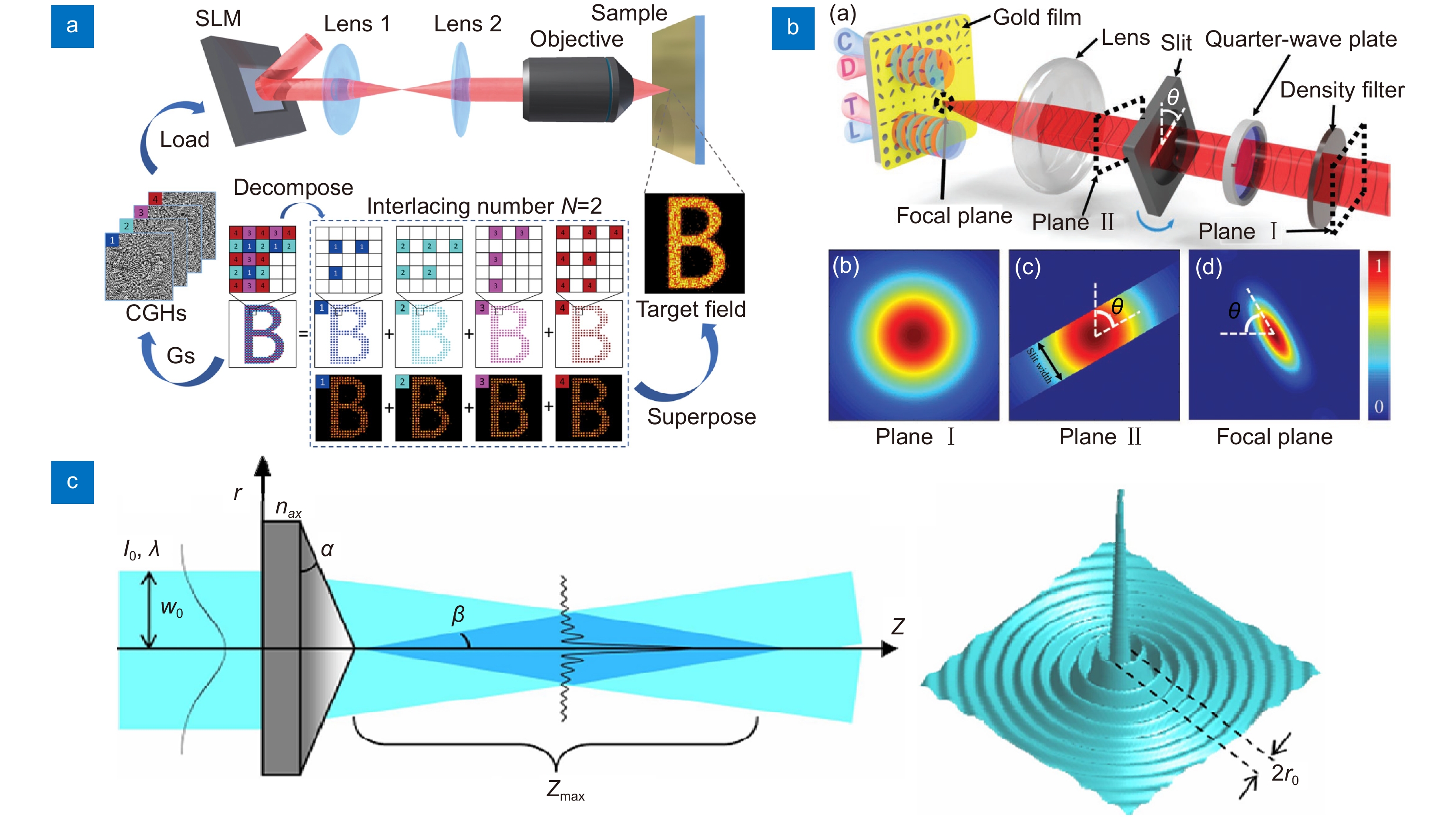
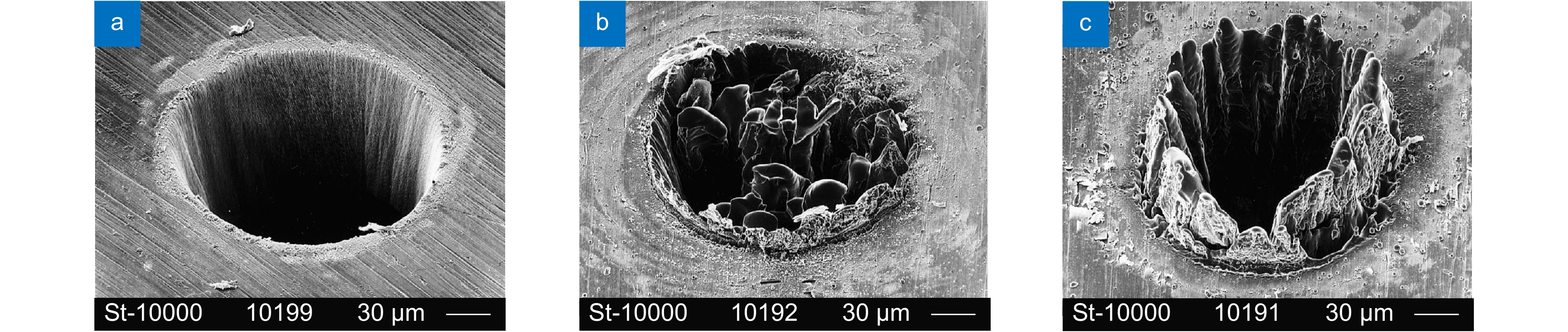
[32] Wang Z P, Li X W, Jiang L, et al. High-quality micropattern printing by interlacing-pattern holographic femtosecond pulses[J]. Nanophotonics, 2020, 9(9): 2895−2904. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2020-0138
[33] Li B H, Li X W, Zhao R Z, et al. Polarization multiplexing terahertz metasurfaces through spatial femtosecond laser‐shaping fabrication[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2020, 8(12): 2000136. doi: 10.1002/adom.202000136
[34] Zambon V, McCarthy N, Piché M. Fabrication of photonic devices directly written in glass using ultrafast Bessel beams[C]//Photonics North 2008. SPIE, 2008, 7099: 720-724.
[35] Durnin J, Miceli Jr J J, Eberly J H. Diffraction-free beams[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1987, 58(15): 1499−1501. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.58.1499
[36] Gori F, Guattari G, Padovani C. Bessel-gauss beams[J]. Opt Commun, 1987, 64(6): 491−495. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(87)90276-8
[37] Herman R M, Wiggins T A. High-efficiency diffractionless beams of constant size and intensity[J]. Appl Opt, 1994, 33(31): 7297−7306. doi: 10.1364/AO.33.007297
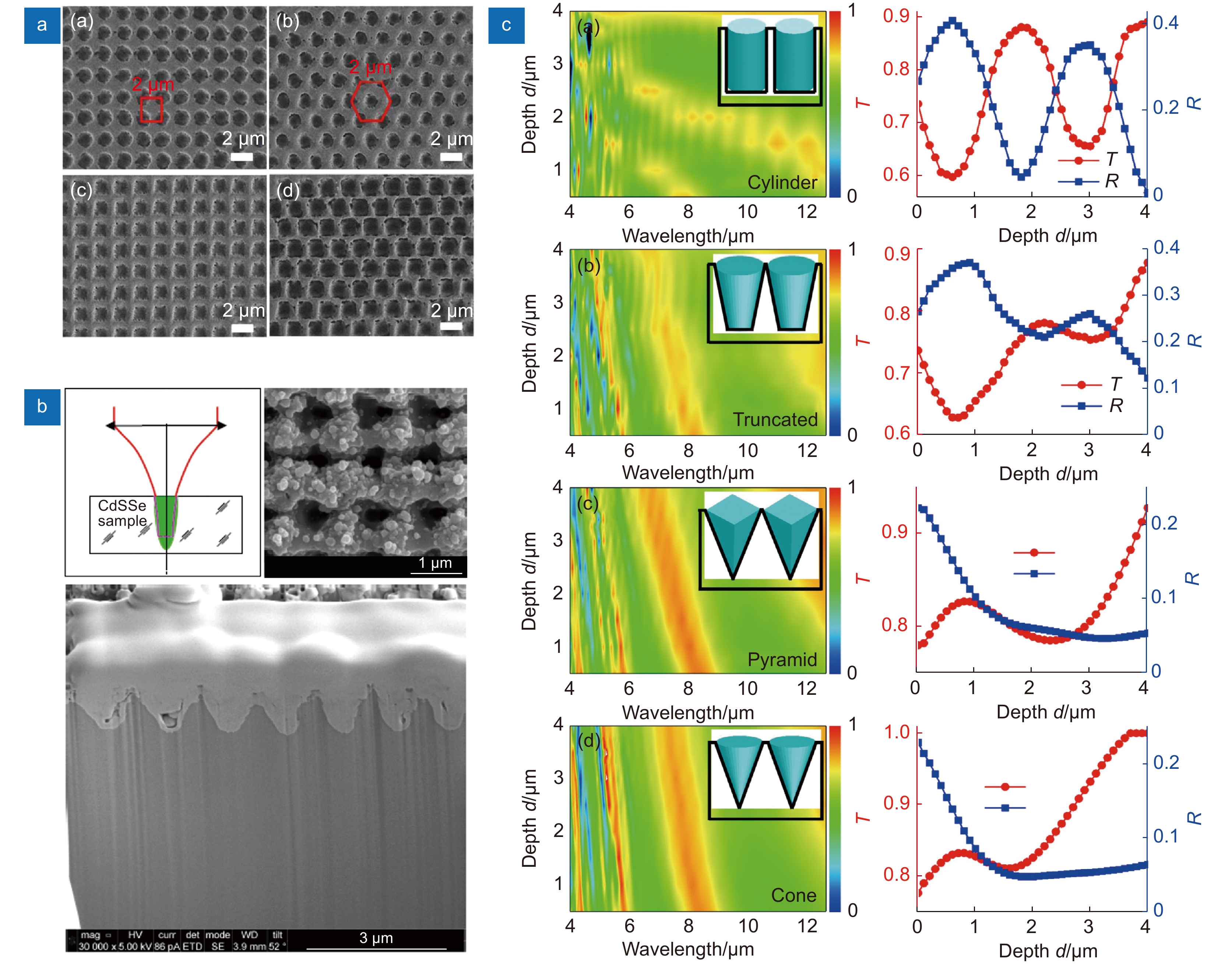
[38] Duocastella M, Arnold C B. Bessel and annular beams for materials processing[J]. Laser Photonics Rev, 2012, 6(5): 607−621. doi: 10.1002/lpor.201100031
[39] Stoian R, Boyle M, Thoss A, et al. Laser ablation of dielectrics with temporally shaped femtosecond pulses[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2002, 80(3): 353−355. doi: 10.1063/1.1432747
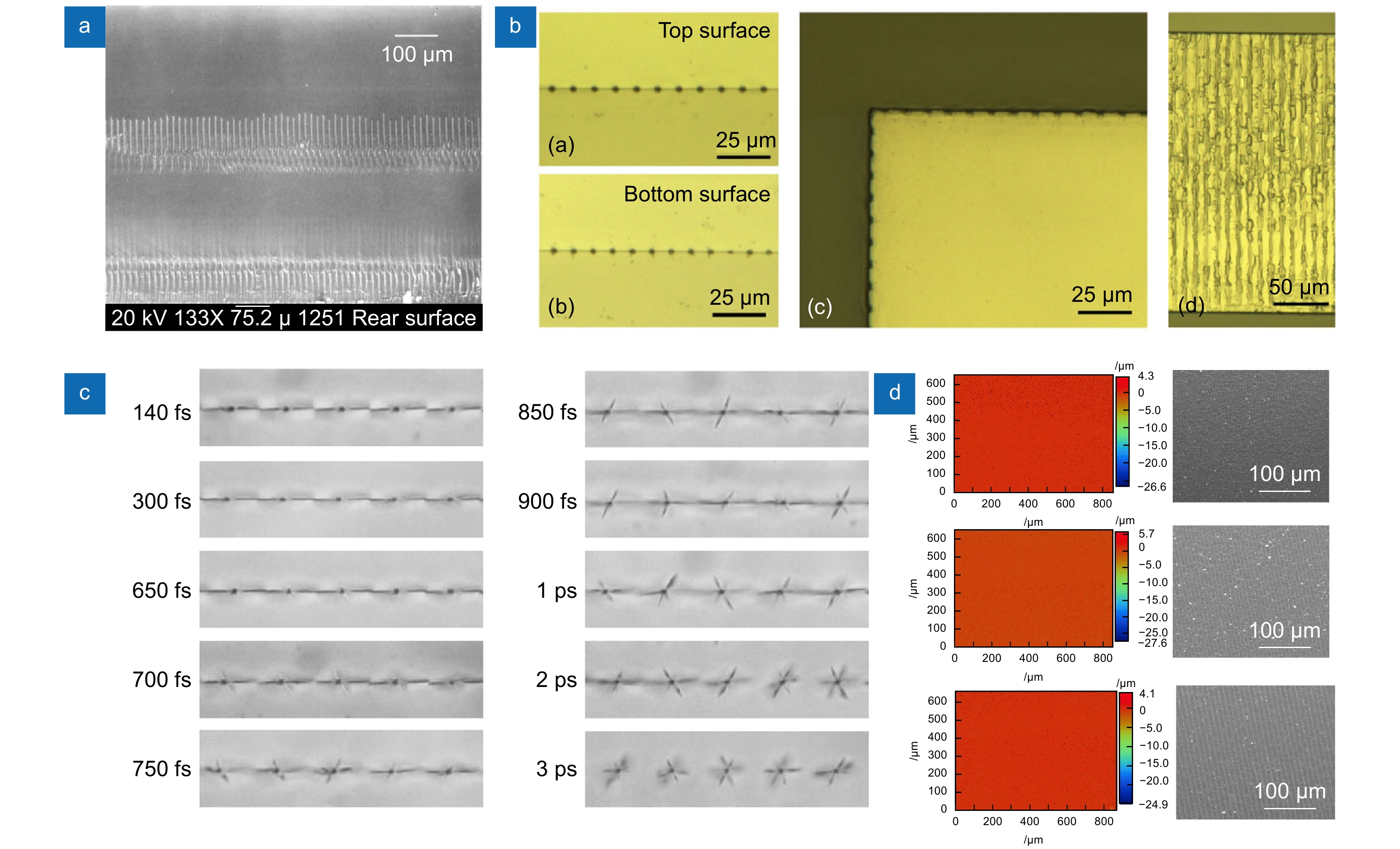
[40] Jiang L, Liu P J, Yan X L, et al. High-throughput rear-surface drilling of microchannels in glass based on electron dynamics control using femtosecond pulse trains[J]. Opt Lett, 2012, 37(14): 2781−2783. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.002781
[41] Jiang L, Fang J Q, Cao Q, et al. Femtosecond laser high-efficiency drilling of high-aspect-ratio microholes based on free-electron-density adjustments[J]. Appl Opt, 2014, 53(31): 7290−7295. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.007290
[42] Götte N, Winkler T, Meinl T, et al. Temporal Airy pulses for controlled high aspect ratio nanomachining of dielectrics[J]. Optica, 2016, 3(4): 389−395. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.3.000389
[43] Del Hoyo J, Meyer R, Furfaro L, et al. Nanoscale confinement of energy deposition in glass by double ultrafast Bessel pulses[J]. Nanophotonics, 2021, 10(3): 1089−1097. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2020-0457
[44] Wang Z, Jiang L, Li X W, et al. High-throughput microchannel fabrication in fused silica by temporally shaped femtosecond laser Bessel-beam-assisted chemical etching[J]. Opt Lett, 2018, 43(1): 98−101. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.000098
[45] Courvoisier F, Lacourt P A, Jacquot M, et al. Surface nanoprocessing with nondiffracting femtosecond Bessel beams[J]. Opt Lett, 2009, 34(20): 3163−3165. doi: 10.1364/OL.34.003163
[46] Bhuyan M K, Courvoisier F, Lacourt P A, et al. High aspect ratio nanochannel machining using single shot femtosecond Bessel beams[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 97(8): 081102. doi: 10.1063/1.3479419
[47] Bhuyan M K, Velpula P K, Colombier J P, et al. Single-shot high aspect ratio bulk nanostructuring of fused silica using chirp-controlled ultrafast laser bessel beams[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2014, 104(2): 021107. doi: 10.1063/1.4861899
[48] Zhao W W, Li X W, Xia B, et al. Single-pulse femtosecond laser Bessel beams drilling of high-aspect-ratio microholes based on electron dynamics control[J]. Proc SPIE, 2014, 9296: 92960Q.
[49] He F, Yu J J, Tan Y X, et al. Tailoring femtosecond 1.5-μm Bessel beams for manufacturing high-aspect-ratio through-silicon vias[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 40785. doi: 10.1038/srep40785
[50] Wang G Y, Yu Y W, Jiang L, et al. Cylindrical shockwave-induced compression mechanism in femtosecond laser Bessel pulse micro-drilling of PMMA[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2017, 110(16): 161907. doi: 10.1063/1.4981248
[51] Yao Z L, Jiang L, Li X W, et al. Non-diffraction-length, tunable, Bessel-like beams generation by spatially shaping a femtosecond laser beam for high-aspect-ratio micro-hole drilling[J]. Opt Exp, 2018, 26(17): 21960−21968. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.021960
[52] Wang H R, Zhang F, Ding K W, et al. Non-diffraction-length Bessel-beam femtosecond laser drilling of high-aspect-ratio microholes in PMMA[J]. Optik, 2021, 229: 166295. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.166295
[53] Yashunin D A, Malkov Y A, Mochalov L A, et al. Fabrication of microchannels in fused silica using femtosecond Bessel beams[J]. J Appl Phys, 2015, 118(9): 093106. doi: 10.1063/1.4929649
[54] Park M S, Lee Y, Kim J K. One-step preparation of antireflection film by spin-coating of polymer/solvent/nonsolvent ternary system[J]. Chem Mater, 2005, 17(15): 3944−3950. doi: 10.1021/cm0500758
[55] Raut H K, Ganesh V A, Nair A S, et al. Anti-reflective coatings: a critical, in-depth review[J]. Energy Environ Sci, 2011, 4(10): 3779−3804. doi: 10.1039/c1ee01297e
[56] Tarabrin M K, Bushunov A A, Lazarev V A, et al. Fabrication of anti-reflection microstructures on ZnSe single crystal by using femtosecond laser pulses[C]//Laser Science 2017, 2017: JTu2A. 20.
[57] Li Q K, Cao J J, Yu Y H, et al. Fabrication of an anti-reflective microstructure on sapphire by femtosecond laser direct writing[J]. Opt Lett, 2017, 42(3): 543−546. doi: 10.1364/OL.42.000543
[58] Bushunov A A, Tarabrin M K, Lazarev V A, et al. Fabrication of anti-reflective microstructures on chalcogenide crystals by femtosecond laser ablation[J]. Opt Mater Express, 2019, 9(4): 1689−1697. doi: 10.1364/OME.9.001689
[59] Zhang F, Wang H R, Wang C, et al. Direct femtosecond laser writing of inverted array for broadband antireflection in the far-infrared[J]. Opt Lasers Eng, 2020, 129: 106062. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2020.106062
[60] Li X, Li M, Liu H J, et al. Fabrication of an anti-reflective microstructure on ZnS by femtosecond laser Bessel beams[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(14): 4278. doi: 10.3390/molecules26144278
[61] Matsumaru K, Takata A, Ishizaki K. Advanced thin dicing blade for sapphire substrate[J]. Sci Technol Adv Mater, 2005, 6(2): 120−122. doi: 10.1016/j.stam.2004.11.002
[62] Borowiec A, Haugen H K. Femtosecond laser micromachining of grooves in indium phosphide[J]. Appl Phys A, 2004, 79(3): 521−529. doi: 10.1007/s00339-003-2377-0
[63] Shin H, Kim D. Cutting thin glass by femtosecond laser ablation[J]. Opt Laser Technol, 2018, 102: 1−11.
[64] Li J Z, Ertorer E, Herman P R. Ultrafast laser burst-train filamentation for non-contact scribing of optical glasses[J]. Opt Express, 2019, 27(18): 25078−25090. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.025078
[65] Dogan Y, Madsen C K. Optimization of ultrafast laser parameters for 3D micromachining of fused silica[J]. Opt Laser Technol, 2020, 123: 105933. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.105933
[66] Ahmed F, Lee M S, Sekita H, et al. Display glass cutting by femtosecond laser induced single shot periodic void array[J]. Appl Phys A, 2008, 93(1): 189−192. doi: 10.1007/s00339-008-4672-2
[67] Mishchik K, Beuton R, Caulier O D, et al. Improved laser glass cutting by spatio-temporal control of energy deposition using bursts of femtosecond pulses[J]. Opt Express, 2017, 25(26): 33271−33282. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.033271
[68] Rapp L, Meyer R, Furfaro L, et al. High speed cleaving of crystals with ultrafast Bessel beams[J]. Opt Express, 2017, 25(8): 9312−9317. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.009312
[69] Shin H, Kim D. Strength of ultra-thin glass cut by internal scribing using a femtosecond Bessel beam[J]. Opt Laser Technol, 2020, 129: 106307. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106307
[70] Li Z Q, Wang X F, Wang J L, et al. Stealth dicing of sapphire sheets with low surface roughness, zero kerf width, debris/crack-free and zero taper using a femtosecond Bessel beam[J]. Opt Laser Technol, 2021, 135: 106713. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106713
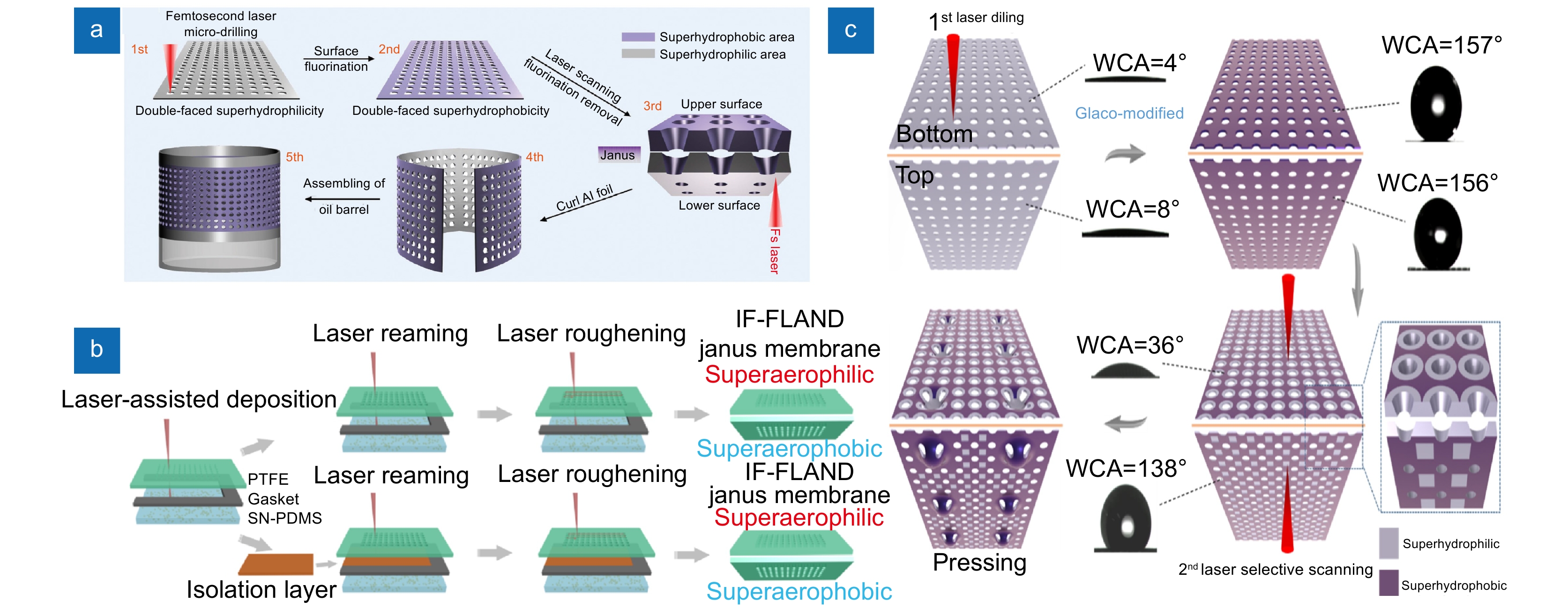
[71] Zhang Z, Zhang Y H, Fan H, et al. A Janus oil barrel with tapered microhole arrays for spontaneous high-flux spilled oil absorption and storage[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(41): 15796−15803. doi: 10.1039/C7NR03829A
[72] Ren F F, Li G Q, Zhang Z, et al. A single-layer Janus membrane with dual gradient conical micropore arrays for self-driving fog collection[J]. J Mater Chem A, 2017, 5(35): 18403−18408. doi: 10.1039/C7TA04392A
[73] Chen C, Shi L A, Huang Z C, et al. Microhole‐arrayed PDMS with controllable wettability gradient by one‐step femtosecond laser drilling for ultrafast underwater bubble unidirectional self‐transport[J]. Adv Mater Interfaces, 2019, 6(12): 1900297. doi: 10.1002/admi.201900297
[74] Hu Y L, Qiu W X, Zhang Y Y, et al. Channel-controlled Janus membrane fabricated by simultaneous laser ablation and nanoparticles deposition for underwater bubbles manipulation[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2019, 114(17): 173701. doi: 10.1063/1.5095615
[75] Ibrahim M H, El-Naas M H, Zhang Z E, et al. CO2 capture using hollow fiber membranes: a review of membrane wetting[J]. Energy Fuels, 2018, 32(2): 963−978. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b03493
[76] Su Y H, Chen L, Jiao Y L, et al. Hierarchical hydrophilic/hydrophobic/bumpy Janus membrane fabricated by femtosecond laser ablation for highly efficient fog harvesting[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2021, 13(22): 26542−26550. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c02121
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: