Fusing point cloud with image for object detection using convolutional neural networks
-
摘要
针对自动驾驶场景中目标检测存在尺度变化、光照变化和缺少距离信息等问题,提出一种极具鲁棒性的多模态数据融合目标检测方法,其主要思想是利用激光雷达提供的深度信息作为附加的特征来训练卷积神经网络(CNN)。首先利用滑动窗对输入数据进行切分匹配网络输入,然后采用两个CNN特征提取器提取RGB图像和点云深度图的特征,将其级联得到融合后的特征图,送入目标检测网络进行候选框的位置回归与分类,最后进行非极大值抑制(NMS)处理输出检测结果,包含目标的位置、类别、置信度和距离信息。在KITTI数据集上的实验结果表明,本文方法通过多模态数据的优势互补提高了在不同光照场景下的检测鲁棒性,附加滑动窗处理改善了小目标的检测效果。对比其他多种检测方法,本文方法具有检测精度与检测速度上的综合优势。

Abstract
Addressing on the issues like varying object scale, complicated illumination conditions, and lack of reliable distance information in driverless applications, this paper proposes a multi-modal fusion method for object detection by using convolutional neural networks. The depth map is generated by mapping LiDAR point cloud onto the image plane and taken as input data together with the RGB image. The input data is also processed by the sliding window to reduce information loss. Two feature extracting networks are used to extract features of the image and the depth map respectively. The generated feature maps are fused through a connection layer. The objects are detected by processing the fused feature map through position regression and object classification. Non-maximal suppression is used to optimize the detection results. The experimental results on the KITTI dataset show that the proposed method is robust in various illumination conditions and especially effective on detecting small objects. Compared with other methods, the proposed method exhibits integrated advantages in terms of detection accuracy and speed.
-
Key words:
- data fusion /
- object detection /
- convolutional neural networks /
- sliding window
-
Overview

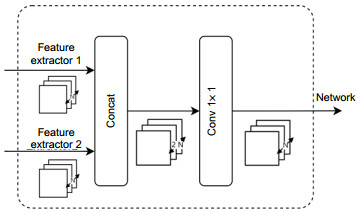
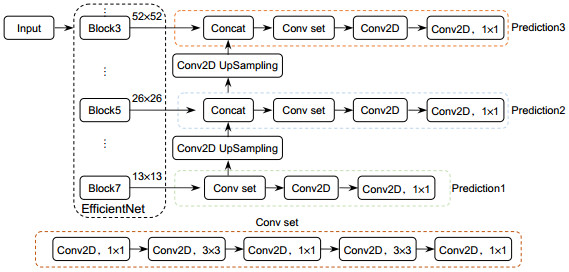
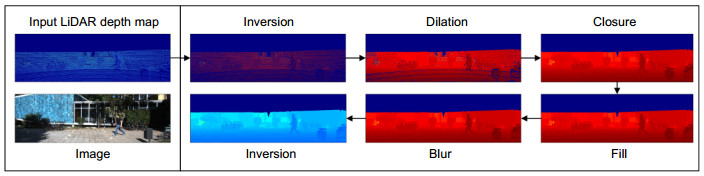
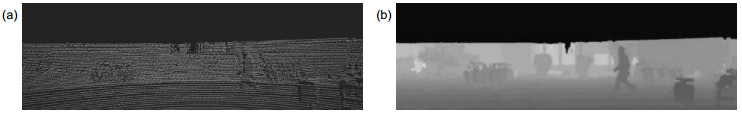
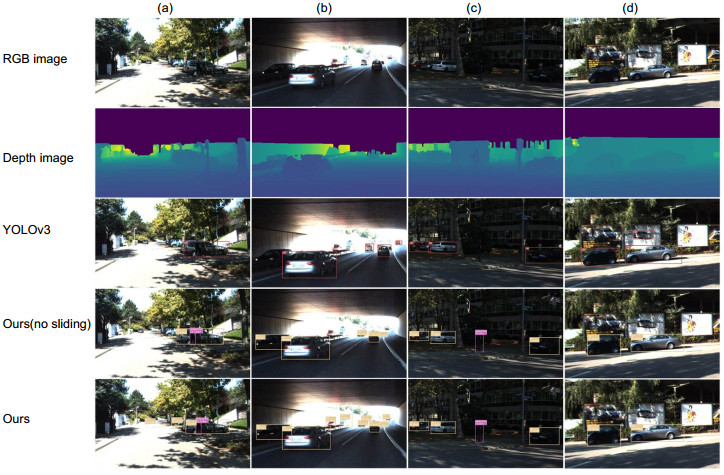
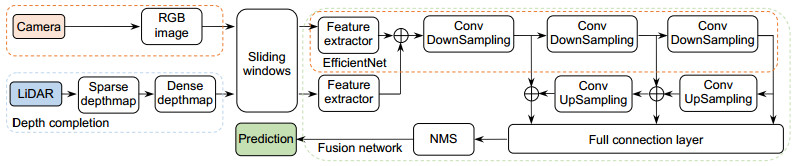
Overview: Autonomous vehicles are equipped with cameras and light detection and ranging (LiDAR) for obstacle detection. Cameras can provide dense texture and color information, but the nature of the passive sensor makes it vulnerable to variations in ambient lighting. LiDAR can get accurate spatial information and is not affected by seasons and lighting conditions, but the point cloud data is sparse and distributed non-uniformly. Single sensor cannot provide satisfactory solution for task of environment perception. Fusion of the two sensors can take advantage of the two modalities of data, improving the robustness and accuracy. In recent years, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have achieved great success in vision-based object detection and also provide an efficient tool for multi-modal data fusion. This paper proposes a novel multi-modal fusion method for object detection by using CNNs. The depth information provided by LiDAR is used as additional features to train CNNs. Disordered and sparse point cloud is projected onto the image plane to generate the depth map which is processed by a depth completion algorithm. The dense depth map and the RGB image are taken as the input of the network. The input data is also processed by sliding the window to reduce information loss caused by resolution mismatch and inappropriate aspect ratio. We adopt EfficientNet-B2 as backbone network of feature extraction, data fusion, and detection. The network extracts respectively the features of the RGB image and the depth map and then fuses the feature maps together through a connection layer. Followed by 1×1 convolution operation, the detection network uses feature pyramid to generate three scales of feature maps and estimates objects through position regression and object classification. Non-maximum suppression is used to optimize the detection results for all sliding windows. The output of the network contains information about location, class, confidence and distance of the target. The experiments were conducted on the KITTI benchmark dataset by using a workstation equipped with 4-core processor and 11 GB NVIDIA 1080Ti GPU and Pytorch neural network framework. By quantitatively analyzing the single-frame inference time and average precision (mAP) of different data modality detection methods, the experimental results show that our method achieves a balance between detection accuracy and detection speed. By qualitatively analyzing the performance of different detection methods under various scenarios, the results show that the proposed method is robust in various illumination conditions and especially effective on detecting small objects.
-

-
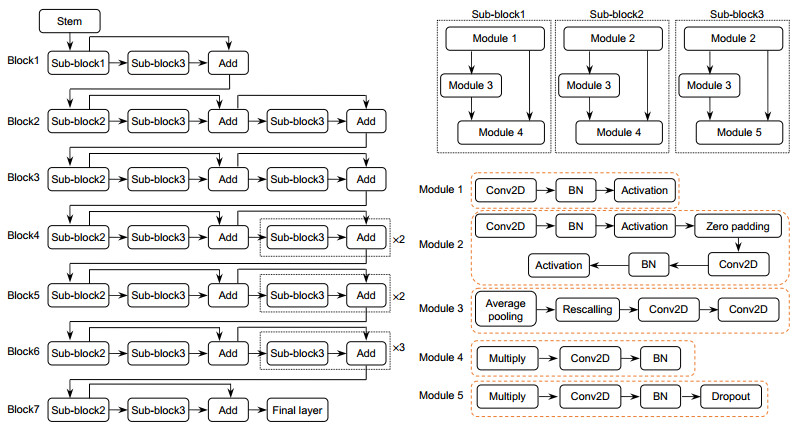
表 1 特征提取网络参数
Table 1. The parameters of the feature extraction network
Stage Kernel Resolution Channel 1(Stem) Conv, 3×3 416×416- > 208×208 32 2(Block1) Conv, 3×3 208×208- > 208×208 16 3(Block2) Conv, 3×3 208×208- > 104×104 24 4(Block3) Conv, 5×5 104×104- > 52×52 48 5(Block4) Conv, 3×3 52×52- > 26×26 88 6(Block5) Conv, 5×5 26×26- > 26×26 120 7(Block6) Conv, 5×5 26×26- > 13×13 208 8(Block7) Conv, 3×3 13×13- > 13×13 352 表 2 与其他方法在KITTI数据集上的性能对比
Table 2. Performance comparison of different algorithms on the KITTI dataset
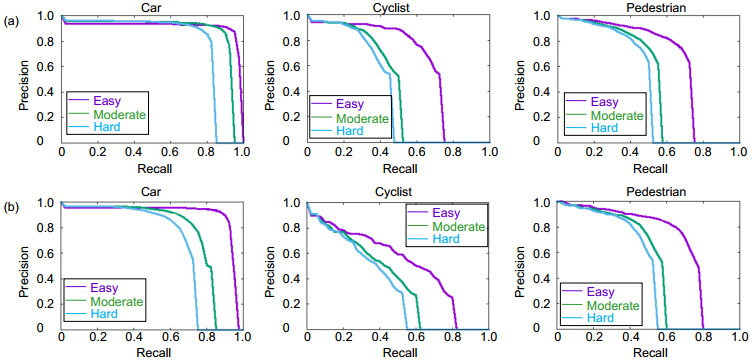
Methods Data mAP/% Car Pedestrian Cyclist Times/(s/F) Easy Moderate Hard Easy Moderate Hard Easy Moderate Hard Faster-RCNN Image 70.26 87.9 79.11 70.19 71.41 62.81 55.44 78.35 65.91 61.19 0.23 YOLOv3 Image 56.75 88.71 74.4 65.58 67.23 49.47 44.99 50.88 36.89 32.64 0.027 VoxelNet LiDAR 50.99 77.47 65.11 57.73 39.48 33.69 31.51 61.22 48.36 44.37 0.23 MV3D Image+
LiDAR62.85 71.09 62.35 55.12 - - - - - - 0.36 F-PointNet Image+
LiDAR82.94 95.85 95.17 85.42 89.83 80.13 75.05 86.86 73.16 65.21 0.16 AVOD Image+
LiDAR62.15 95.17 89.88 82.83 50.9 39.43 35.75 66.45 52.6 46.39 0.08 Ours
(No sliding)Image+
LiDAR60.29 90.01 82.4 73.58 69.23 48.45 44.95 55.18 41.59 37.32 0.017 Ours Image+
LiDAR70.12 92.51 86.9 79.52 81.91 66.37 48.45 73.22 58.93 43.3 0.087 -
参考文献
[1] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 2014: 580-587.
[2] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2015, 37(9): 1904-1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824
[3] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440-1448.
[4] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031
[5] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 779-788.
[6] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLO9000: better, faster, stronger[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 7263-7271.
[7] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: single shot MultiBox detector[C]//Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21-37.
[8] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YoLOv3: an incremental improvement[Z]. arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018.
[9] Qi C R, Su H, Mo K C, et al. PointNet: deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 652-660.
[10] Qi C R, Yi L, Su H, et al. PointNet++: deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2017: 5099-5108.
[11] Zhou Y, Tuzel O. VoxelNet: end-to-end learning for point cloud based 3D object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2018: 4490-4499.
[12] Simon M, Milz S, Amende K, et al. Complex-YOLO: Real-time 3D object detection on point clouds[Z]. arXiv: 1803.06199, 2018.
[13] Beltrán J, Guindel C, Moreno F M, et al. BirdNet: a 3D object detection framework from LiDAR information[C]//Proceedings of 2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Maui, HI, USA, 2018: 3517-3523.
[14] Minemura K, Liau H, Monrroy A, et al. LMNet: real-time multiclass object detection on CPU using 3D LiDAR[C]//Proceedings of 2018 3rd Asia-Pacific Conference on Intelligent Robot Systems, Singapore, 2018: 28-34.
[15] Li B, Zhang T L, Xia T. Vehicle detection from 3D lidar using fully convolutional network[Z]. arXiv: 1608.07916, 2016.
[16] Qi C R, Liu W, Wu C X, et al. Frustum PointNets for 3D object detection from RGB-D data[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2018: 918-927.
[17] Du X X, Ang M H, Karaman S, et al. A general pipeline for 3D detection of vehicles[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2018: 3194-3200.
[18] Du X X, Ang M H, Rus D. Car detection for autonomous vehicle: LIDAR and vision fusion approach through deep learning framework[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2017: 749-754.
[19] Chen X Z, Ma H M, Wan J, et al. Multi-view 3D object detection network for autonomous driving[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 1907-1915.
[20] Ku J, Mozifian M, Lee J, et al. Joint 3D proposal generation and object detection from view aggregation[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Madrid, Spain, 2018: 1-8.
[21] Tan M X, Le Q V. EfficientNet: rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[Z]. arXiv: 1905.11946, 2020.
[22] Lin T Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 2117-2125.
[23] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 770-778.
[24] Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 4700-4708.
[25] Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 2818-2826.
[26] Huang Y P, Cheng Y L, Bapna A, et al. GPipe: efficient training of giant neural networks using pipeline parallelism[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 103-112.
[27] 常昕, 陈晓冬, 张佳琛, 等. 基于激光雷达和相机信息融合的目标检测及跟踪[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(7): 180420. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180420
Chang X, Chen X D, Zhang J C, et al. An object detection and tracking algorithm based on LiDAR and camera information fusion[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2019, 46(7): 180420. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180420
[28] Chattopadhay A, Sarkar A, Howlader P, et al. Grad-CAM++: generalized gradient-based visual explanations for deep convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 2018: 839-847.
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: