Application of two step sensitivity matrix method in Cassegrain telescope alignment
-
摘要
为了调节视场较大的卡塞格林望远镜的次镜位置,提出了两步式灵敏度矩阵模型的计算机辅助装调方法。在分析了传统的二次模型灵敏度矩阵法的缺陷的基础上,根据灵敏度矩阵的特点加入了精调步骤,对传统的灵敏度矩阵法进行了改进。针对卡塞格林系统,分析了各项泽尼克系数与失调量之间的关系,并对300 mm口径,0.6°视场的卡塞格林系统进行了校正仿真。仿真结果显示,传统的灵敏度矩阵法校正后沿x、y、z轴偏移及绕x、y轴倾斜的失调量的均值分别为:-0.0684 mm、-0.0892 mm、0.0015 mm、0.0498°和-0.0444°,全视场波像差RMS均小于0.1λ(λ=632.8 nm);两步式灵敏度矩阵法校正后的均值分别为-0.0018 mm、-0.0012 mm、0.0002 mm、0.0008°和-0.0012°,全视场RMS均小于0.03λ,明显优于传统的灵敏度矩阵法。

Abstract
In order to adjust the position of the secondary mirror of Cassegrain telescope with large field of view, a computer aided adjustment method of two-step sensitivity matrix model was proposed. Based on the analysis of the shortcomings of the traditional sensitivity matrix method of the two order model, a fine tuning step was added based on the characteristics of the sensitivity matrix and the traditional sensitivity matrix method was improved. For the Cassegrain system, the relationship between the Zernike coefficients and the misalignment was analyzed, and the calibration simulation of Cassegrain system with 300 mm aperture and 0.6° field of view was carried out. The simulation results show that after correction by traditional sensitivity matrix method, the mean values of offset along x, y, z axes and tilt around x, y axes are -0.0684 mm, -0.0892 mm, 0.0015 mm, 0.0498° and -0.0444°, respectively, and the full field wavefront aberration RMS is less than 0.1λ(λ=632.8 nm). After correction by two step sensitivity matrix correction method, the mean values are -0.0018 mm, -0.0012 mm, 0.0002 mm, 0.0008° and -0.0012°, respectively, and the full field wavefront aberration RMS is less than 0.03λ, which is obviously superior to the traditional sensitivity matrix method.
-
Overview

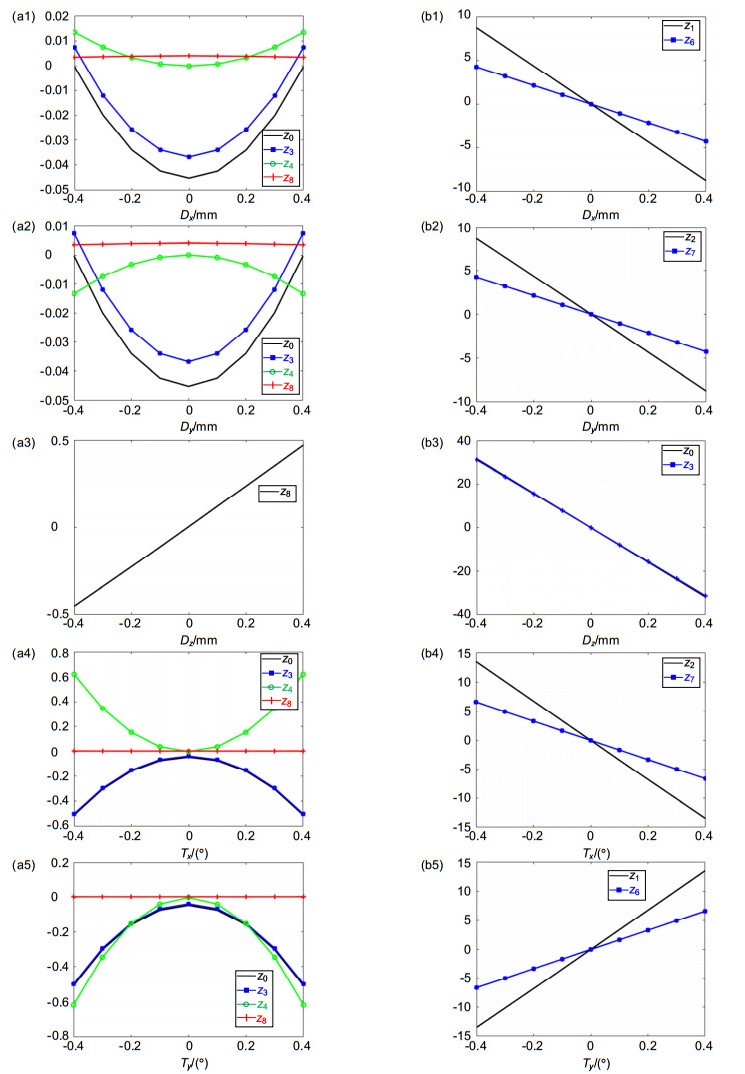
Overview: With the development of telescope technology, the aperture and field of view of telescope are becoming larger and larger, the structure of optical system is becoming more and more complex, and the difficulty of fabrication and assembly is also increasing. The speckle pattern of the focal plane of the optical system can be measured by interferometer and other testing equipment, and the Zernike coefficients can be calculated by the speckle pattern. For Cassegrain telescope, in order to obtain good imaging quality, it is necessary to correct the position of its secondary mirror. By using computer-aided alignment technology, the optical system can be real-time detected and compared with the theoretical results. By establishing a mathematical model between Zernike coefficient and misalignment, the misalignment of the components can be corrected accurately. The most widely used computer-aided alignment method is the sensitivity matrix method. Sensitivity matrix method is a method of correcting aberration by establishing mathematical model of misalignment and Zernike coefficient on the basis of analyzing aberration characteristics. The traditional sensitivity matrix method only carries out single correction. According to the meaning of Zernike coefficient, z3、z4、z5、z6、z7 and z8 are chosen to construct the sensitivity matrix. Based on the analysis of the shortcomings of the traditional sensitivity matrix method of the two order model, a fine tuning step was added based on the characteristics of the sensitivity matrix. The calculation method of sensitivity is improved. According to the relationship between misalignment and Zernike coefficient, the selection principle of Zernike coefficient for constructing sensitivity matrix is proposed. The traditional sensitivity matrix method is improved. For the Cassegrain system, the relationship between the Zernike coefficients and the misadjustment was analyzed, and the calibration simulation of Cassegrain system with 300 mm aperture and 0.6° field of view was carried out. The simulation results show that after correction by traditional sensitivity matrix method, the mean values of offset along x, y, z axes and tilt around x, y axes are -0.0684 mm, -0.0892 mm, 0.0015 mm, 0.0498° and -0.0444°, respectively, and the full field wavefront aberration RMS is less than 0.1λ (λ=632.8 nm). After correction by two step sensitivity matrix correction method, the mean values are -0.0018 mm, -0.0012 mm, 0.0002 mm, 0.0008° and -0.0012°, respectively, and the full field wavefront aberration RMS is less than 0.03λ. The corrected optical system reaches the diffraction limit and approaches the design position, which is obviously superior to the traditional sensitivity matrix method.
-

-
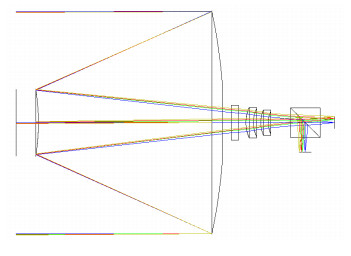
表 1 卡塞格林望远镜光学系统参数
Table 1. Optical system parameters of Cassegrain telescope
光学面 曲率半径/mm 间隔/mm 半径/mm 非球面系数 主镜 -699.512 -250 150 -1.06 次镜 -269.876 260 45 -3.45 校正镜1(前) 3722.167 10 20 0 校正镜1(后) 5147.631 10 20 0 校正镜2(前) 51.141 10 20 0 校正镜2(后) 43.322 10 20 0 校正镜3(前) 43.345 10 20 0 校正镜3(后) 34.065 30 20 0 分光棱镜 - 40 20 0 像面 - - - - 表 2 粗调后的各自由度失调量
Table 2. The degree of misalignment of each degree of freedom after coarse tuning
Dx=0.9058 mm
Dy=0.127 mm
Dz=0.8147 mm
Tx=0.9134°
Ty=0.6324°Dx=0.3689 mm
Dy=0.5178 mm
Dz=0.2311 mm
Tx=-0.1538°
Ty=0.8126°Dx=0.8491 mm
Dy=0.934 mm
Dz=0.0357 mm
Tx=0.6787°
Ty=0.7577°Dx=0.4318 mm
Dy=0.5625 mm
Dz=0.1324 mm
Tx=0.7419°
Ty=0.8828°Dx/mm -0.0602 -0.0111 -0.0509 -0.1282 Dy/mm -0.102 -0.1722 0.024 0.0125 Dz/mm 0.0027 0.0011 -0.0043 0.0024 Tx/(°) 0.0984 0.1362 -0.0213 -0.0081 Ty/(°) -0.0426 -0.0074 -0.0323 -0.0872 表 3 初始状态的灵敏度矩阵
Table 3. Sensitivity matrix of initial state
Dx/mm Dy/mm Dz/mm Tx/(°) Ty/(°) z0 0.23;-0.56 0.22;-0.36 0;-79.55 -4.5;5.3 -4.1;5.6 z1 0;21.82 0;0.054 0.64;-0.44 0;0.082 0;-33.42 z2 0;0.054 0;21.84 -0.84;1.01 0;33.34 0;-0.083 z3 0.24;-0.54 0.24;-0.4 0;-78.53 -4.3;5.2 -4.1;5.54 z6 0;10.69 0;0.011 0.28;-0.02 0;0.017 0;-16.35 z7 0;0.011 0;10.75 -0.34;0.48 0;16.38 0;-0.017 表 4 精调后的各自由度失调量
Table 4. The degree of misalignment of each degree of freedom after fine tuning
Dx=0.9058 mm
Dy=0.127 mm
Dz=0.8147 mm
Tx=0.9134°
Ty=0.6324°Dx=0.3689 mm
Dy=0.5178 mm
Dz=0.2311 mm
Tx=-0.1538°
Ty=0.8126°Dx=0.8491 mm
Dy=0.934 mm
Dz=0.0357 mm
Tx=0.6787°
Ty=0.7577°Dx=0.4318 mm
Dy=0.5625 mm
Dz=0.1324 mm
Tx=0.7419°
Ty=0.8828°Dx/mm -0.0003 -0.0034 -0.0025 -0.001 Dy/mm 0.0016 -0.005 0.0003 -0.0017 Dz/mm 0.0002 0.0002 0.0002 0.0002 Tx/(°) -0.0011 0.0032 -0.0002 0.0011 Ty/(°) -0.0002 -0.0022 -0.0017 -0.0006 表 5 粗调后的灵敏度矩阵
Table 5. First-order sensitivity matrix after coarse tuning
Dx/mm Dy/mm Dz/mm Tx/(°) Ty/(°) z0 0.0083 -0.0028 -79.4587 -0.0650 -0.1012 z1 21.8904 0.0000 -0.0008 0.0001 35.2296 z2 0.0000 21.8904 0.0014 33.7626 -0.0001 z3 0.0086 -0.0030 -78.2894 -0.0646 -0.1004 z6 10.7042 0.0000 -0.0004 0.0000 -16.4869 z7 0.0000 10.7042 0.0007 16.4869 -0.0000 表 6 精调采用的一阶灵敏度矩阵
Table 6. First-order sensitivity matrix for fine tuning
Dx/mm Dy/mm Dz/mm Tx/(°) Ty/(°) z0 -0.0085 -0.0482 -79.4451 0.2625 0.3028 z1 21.882 0.0002 0.0013 0.0016 -33.7492 z2 -0.0002 21.8823 -0.0166 33.7494 -0.0016 z3 -0.0091 -0.0468 -78.2814 0.2629 0.3012 z6 10.7025 -0.0001 -0.0002 0.0006 -16.4836 z7 -0.0004 10.7027 -0.0037 16.4839 -0.0008 表 7 传统的灵敏度矩阵法校正后的失调量
Table 7. Misalignment after correction by traditional sensitivity matrix method
Dx=0.9058 mm
Dy=0.127 mm
Dz=0.8147 mm
Tx=0.9134°
Ty=0.6324°Dx=0.3689 mm
Dy=0.5178 mm
Dz=0.2311 mm
Tx=-0.1538°
Ty=0.8126°Dx=0.8491 mm
Dy=0.934 mm
Dz=0.0357 mm
Tx=0.6787°
Ty=0.7577°Dx=0.4318 mm
Dy=0.5625 mm
Dz=0.1324 mm
Tx=0.7419°
Ty=0.8828°Dx/mm -0.0782 0.0669 -0.1189 -0.1432 Dy/mm -0.024 -0.2072 -0.087 -0.0385 Dz/mm 0.0067 0.0031 -0.0043 0.0004 Tx/(°) 0.0094 0.1192 0.0627 0.0079 Ty/(°) -0.0426 0.0406 -0.0783 -0.0972 表 8 校正前后的泽尼克系数
Table 8. Zernike coefficient before and after correction
z0 z1 z2 z3 z6 z7 第一组 初始 61.1902 1.7441 -34.3459 60.3361 0.8321 -16.7761 粗调后 0.1165 -0.1204 -0.2506 0.122 -0.0579 -0.1194 精调后 -0.0293 -0.0002 0.0021 -0.0212 -0.0001 0.001 传统校正后 -0.5817 0.2735 0.208 -0.5655 0.1347 0.1019 第二组 初始 16.3064 19.3113 -6.1533 16.1609 9.4315 -3.0148 粗调后 -0.0343 -0.0068 0.0101 -0.0268 -0.0032 0.0089 精调后 -0.0294 -0.0007 -0.0012 -0.0134 -0.0004 -0.0006 传统校正后 -0.3284 -0.0937 0.5113 -0.3161 -0.0467 0.2527 第三组 初始 -0.2186 6.8088 -43.1554 -0.2127 3.3268 -21.1387 粗调后 -0.3907 -0.0406 0.0328 -0.4455 -0.0181 0.0195 精调后 -0.0293 -0.0027 0.0002 -0.0212 -0.0013 0.0001 传统校正后 0.2712 -0.0407 -0.2123 0.2747 -0.0181 -0.1024 第四组 初始 6.0277 20.1141 -37.1608 5.9514 9.8478 -18.2063 粗调后 0.1262 -0.1376 -0.0001 0.1319 -0.0653 -0.0003 精调后 -0.0293 0.0016 0.0001 -0.0212 0.0008 0.0001 传统校正后 -0.1005 -0.1469 0.576 -0.0915 -0.0696 0.2818 -
参考文献
[1] 周龙峰.大口径反射式望远镜在线调整技术研究[D].成都: 中国科学院研究生院(光电技术研究所), 2016.
Zhou L F. Study on the alignment technique of large aperture reflecting telescope on-line[D]. Chengdu: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Optics and Electronics), 2016.
http://ir.ioe.ac.cn/handle/181551/7990 [2] Figoski J W, Shrode T E, Moore G F. Computer-aided alignment of a wide-field, three-mirror, unobscured, high-resolution sensor[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1989, 1049: 166. doi: 10.1117/12.951421
[3] Egdall I M. Manufacture of a three-mirror wide-field optical system[J]. Optical Engineering, 1985, 24(2): 242285. doi: 10.1117/12.7973470
[4] 巩盾, 田铁印, 王红.利用Zernike系数对离轴三反射系统进行计算机辅助装调[J].光学精密工程, 2010, 18(8): 1754–1759. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201008009
Gong D, Tian T Y, Wang H. Computer-aided alignment of off-axis three-mirror system by using Zernike coefficients[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2010, 18(8): 1754–1759. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201008009
[5] 杨晓飞.三反射镜光学系统的计算机辅助装调技术研究[D].长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2005.
Yang X F. Study on the computer-aided alignment of three-mirror optical system[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005.
[6] Kim S, Yang H S, Lee Y W, et al. Merit function regression method for efficient alignment control of two-mirror optical systems.[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(8): 5059–5068. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.005059
[7] 王彬, 蒋世磊.卡塞格林系统计算机辅助装调技术研究[J].光学仪器, 2008, 30(1): 50–54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5630.2008.01.011
Wang B, Jiang S L. Study on computer-aided alignment method of Cassegrain system[J]. Optical Instruments, 2008, 30(1): 50–54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5630.2008.01.011
[8] 孙敬伟, 吕天宇, 姚丽双, 等.发射望远镜的设计与装调[J].光学精密工程, 2014, 22(2): 369–375. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201402018
Sun J W, Lv T Y, Yao L S, et al. Design and assembly of transmitter-telescope[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2014, 22(2): 369–375. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201402018
[9] 张向明, 姜峰, 孔龙阳, 等.卡塞格林系统光学装调技术研究[J].应用光学, 2015, 36(4): 526–530. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yygx201504006
Zhang X M, Jiang F, Kong L Y, et al. Research on optical alignment technology for Cassegrain system[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2015, 36(4): 526–530. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yygx201504006
[10] 顾志远, 颜昌翔, 李晓冰, 等.改进的灵敏度矩阵法在离轴望远镜装调中的应用[J].光学精密工程, 2015, 23(9): 2595–2604. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201509022
Gu Z Y, Yan C X, Li X B, et al. Application of modified sensitivity matrix method in alignment of off-axis telescope[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(9): 2595–2604. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201509022
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: