-
摘要
本文对过去50年中光全息数据存储技术的发展进行了综述。随着关键器件和材料的不断发展,光全息数据存储技术也日臻成熟。当下正值大数据时代,对数据存储密度和数据存取速度的需求比以往任何时候都要大,光全息数据存储以其超大存储容量、超快读取速度、超长保存寿命等优势,成为下一代数据存储技术的有力候选者。其中同轴全息存储系统以其结构紧凑、操作简单、兼容性强等特点将成为全息存储技术进一步实用化的基石。同时新型的相位调制光全息数据存储系统正成为研究热点,新一轮的飞速发展时机已至。
Abstract
The development of optical holographic data storage technology in the past 50 years is reviewed in this paper. With the continuous development of key devices and materials, optical holographic data storage technology is becoming more and more mature. At present, in the era of Big Data, the demands for data storage density and data transfer rate are greater than ever before. Optical holographic data storage has become a potential candidate for the next generation of data storage technology because of its advantages of superhigh storage capacity, superfast data transfer rate, and superlong storage life. The coaxial holographic storage system will become the cornerstone of further practicality of holographic storage technology because of its compact structure, simple operation and strong compatibility. Meanwhile, new phase modulated holographic data storage system is becoming the research hotspot. The new round of rapid development has arrived.
-
Key words:
- optical holography /
- data storage /
- big data /
- phase modulation
-
Overview

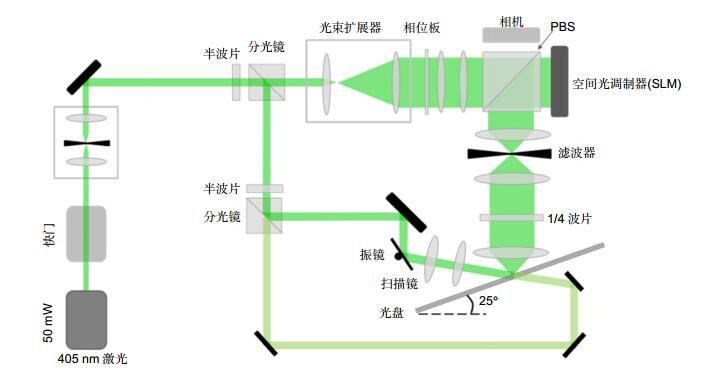
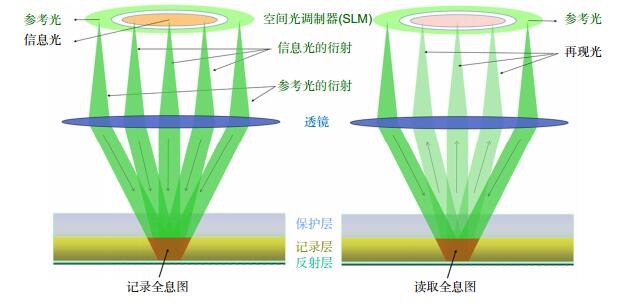
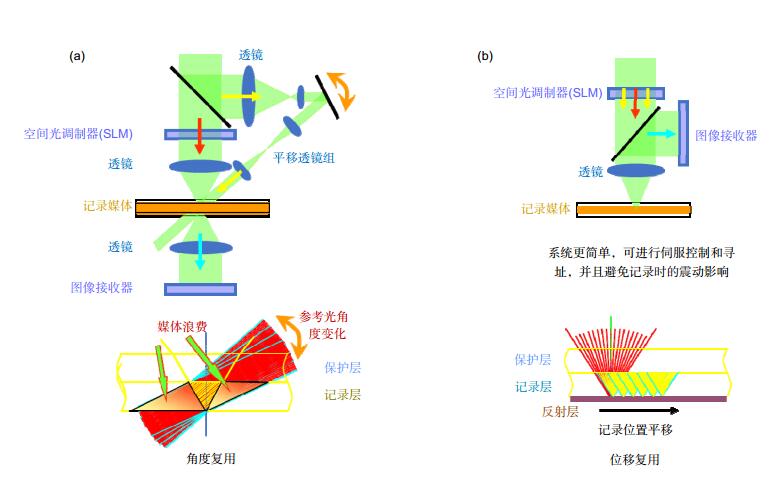
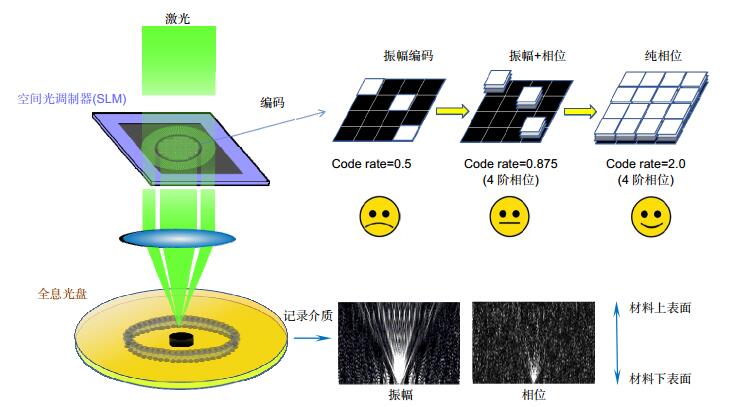
Overview: The development of optical holographic data storage technology in the past 50 years is reviewed briefly according to time line in this paper. With the continuous development of key devices and materials, optical holographic data storage technology is becoming more and more mature. At present, in the era of Big Data, the demands for data storage density and data transfer rate are greater than ever before. Optical holographic data storage has become a potential candidate for the next generation of data storage technology because of its advantages of high storage capacity, fast data transfer rate, and long storage life. The theoretical researches of holographic data storage were done mainly in 1970s~1980s including some multiplexing technologies. The developments of key devices such as spatial light modulator and detector and recording material such as lithium niobate crystal and photopolymer pushed holographic data storage technology into practicability quickly in 1990s~2000s. In the aspect of system, there are two kinds of holographic data storage systems on-axis and off-axis. For instance, collinear holographic data storage system (CHDSS) by Optware corporation and 2-axis HDSS by InPhase corporation. 2-axis HDSS can provide sensitive Bragg selectivity to achieve high storage density by using angular multiplexing. CHDSS owns more compact structure, simpler operation and stronger compatibility by combining with servo system and by faster recording shifting multiplexing. In this paper, a comparison between two systems was given. We believe CHDSS may be the cornerstone of further practicality of holographic storage technology. In the aspect of code, conventional HDSS owns low code rate because it uses amplitude modulation which meanwhile gets low signal noise ratio (SNR) due to the overconsumption of dynamic range of recording material. To solve this problem, phase modulation is used in the HDSS to increase code rate and SNR. One challenge of phase modulation is that phase cannot be detected by the camera which can be solved by using interferometric and non-interferometric methods. Several phase retrieval methods are also mentioned in this paper.
-

-
-
参考文献
[1] Gabor D. A new microscopic principle[J]. Nature, 1948, 161(4098): 777-779. doi: 10.1038/161777a0
[2] Gabor D. Microscopy by reconstructed wave-fronts[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1949, 197(1051): 454-487.
[3] Gabor D. Microscopy by reconstructed wave fronts: Ⅱ[J]. Proceedings of the Physical Society: Section B, 1951, 64(6): 449-469. doi: 10.1088/0370-1301/64/6/301
[4] Kirkpatrick P, El-Sum H M A. Image formation by reconstructed wave fronts. Ⅰ. Physical principles and methods of refinement[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1956, 46(10): 825-830. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.46.000825
[5] El-Sum H M A. Reconstructed wave-front microscopy[D]. Stanford: Stanford University, 1953.
[6] Baez A V. Resolving power in diffraction microscopy with special reference to X-rays[J]. Nature, 1952, 169(4310): 963-964.
[7] Rogers G L. Gabor diffraction microscopy: the hologram as a generalized zone-plate[J]. Nature, 1950, 166(4214): 237.
[8] Leith E N, Upatnieks J. Reconstructed wavefronts and communication theory[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1962, 52(10): 1123-1130. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.52.001123
[9] Leith E N, Upatnieks J. Wavefront reconstruction with diffused illumination and three-dimensional objects[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1964, 54(11): 1295-1301. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.54.001295
[10] Van Heerden P J. Theory of optical information storage in solids[J]. Applied Optics, 1963, 2(4): 393-400. doi: 10.1364/AO.2.000393
[11] Leith E N, Kozma A, Upatnieks J, et al. Holographic data storage in three-dimensional media[J]. Applied Optics, 1966, 5(8): 1303-1311. doi: 10.1364/AO.5.001303
[12] Ashkin A, Boyd G D, Dziedzic J M, et al. Optically-induced refractive index inhomogeneities in LiNbO3 and LiTaO3[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1966, 9(1): 72-74. doi: 10.1063/1.1754607
[13] Staebler D L, Amodei J J. Coupled-wave analysis of holographic storage in LiNbO3[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1972, 43(3): 1042-1049. doi: 10.1063/1.1661215
[14] Staebler D L, Burke W J, Phillips W, et al. Multiple storage and erasure of fixed holograms in Fe-doped LiNbO3[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1975, 26(4): 182-184. doi: 10.1063/1.88108
[15] Ishida A, Mikami O, Miyazawa S, et al. Rh-doped LiNbO3 as an improved new material for reversible holographic storage[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1972, 21(5): 192-193. doi: 10.1063/1.1654339
[16] Shah P, Rabson T A, Tittel F K, et al. Volume holographic recording and storage in Fe-doped LiNbO3 using optical pulses[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1974, 24(3): 130-131. doi: 10.1063/1.1655122
[17] Stewart W C, Mezrich R S, Cosentino L S, et al. An experimental read-write holographic memory[J]. RCA Review, 1973, 34: 3-44.
[18] Nishida N, Sakaguchi M, Saito F. Holographic coding plate: a new application of holographic memory[J]. Applied Optics, 1973, 12(7): 1663-1674. doi: 10.1364/AO.12.001663
[19] D'Auria L, Huignard J, Spitz E. Holographic read-write memory and capacity enhancement by 3-D storage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1973, 9(2): 83-94. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.1973.1067578
[20] D'Auria L, Huignard J P, Slezak V C, et al. Experimental holographic read-write memory using 3-D storage[J]. Applied Optics, 1974, 13(4): 808-818. doi: 10.1364/AO.13.000808
[21] Amodei J J, Staebler D L. Holographic pattern fixing in electro-optic crystals[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1971, 18(12): 540-542. doi: 10.1063/1.1653530
[22] Mikaeliane A L. Holographic bulk memories using lithium niobate crystals for data recording[M]//Barrekette E S, Stroke G W, Nesterikhin Y E, et al. Optical Information Processing. Boston, MA: Springer, 1978: 217-233.
[23] Tsunoda Y, Tatsuno K, Kataoka K, et al. Holographic video disk: an alternative approach to optical video disks[J]. Applied Optics, 1976, 15(6): 1398-1403. doi: 10.1364/AO.15.001398
[24] Kubota K, Ono Y, Kondo M, et al. Holographic disk with high data transfer rate: its application to an audio response memory[J]. Applied Optics, 1980, 19(6): 944-951. doi: 10.1364/AO.19.000944
[25] Mok F H, Tackitt M C, Stoll H M. Storage of 500 high-resolution holograms in a LiNbO3 crystal[J]. Optics Letters, 1991, 16(8): 605-607. doi: 10.1364/OL.16.000605
[26] Mok F H. Angle-multiplexed storage of 5000 holograms in lithium niobate[J]. Optics Letters, 1993, 18(11): 915-917. doi: 10.1364/OL.18.000915
[27] Heanue J F, Bashaw M C, Hesselink L. Volume holographic storage and retrieval of digital data[J]. Science, 1994, 265(5173): 749-752. doi: 10.1126/science.265.5173.749
[28] Bernal M P, Coufal H, Grygier R K, et al. A precision tester for studies of holographic optical storage materials and recording physics[J]. Applied Optics, 1996, 35(14): 2360-2374. doi: 10.1364/AO.35.002360
[29] Shelby R M, Hoffnagle J A, Burr G W, et al. Pixel-matched holographic data storage with megabit pages[J]. Optics Letters, 1997, 22(19): 1509-1511. doi: 10.1364/OL.22.001509
[30] Hong J H, McMichael I C, Chang T Y, et al. Volume holographic memory systems: techniques and architectures[J]. Optical Engineering, 1995, 34(8): 2193-2203. doi: 10.1117/12.213214
[31] Curtis K. Digital holographic data storage prototype[C]//Proceedings of 2000 Optical Data Storage. Conference Digest, Whisler, BC, Canada, 2000: 164-166.
[32] Pu A, Psaltis D. Holographic data storage with 100 bits/μm2 density[C]//Proceedings of 1997 Optical Data Storage Topical Meeting ODS Conference Digest, Tucson, AZ, USA, 1997: 48-49.
[33] Dhar L, Curtis K, Tackitt M, et al. Holographic storage of multiple high-capacity digital data pages in thick photopolymer systems[J]. Optics Letters, 1998, 23(21): 1710-1722. doi: 10.1364/OL.23.001710
[34] Thaxter J B, Kestigian M. Unique properties of SBN and their use in a layered optical memory[J]. Applied Optics, 1974, 13(4): 913-924. doi: 10.1364/AO.13.000913
[35] Zhou H J, Morozov V, Neff J. Characterization of dupont photopolymers in infrared light for free-space optical interconnects[J]. Applied Optics, 1995, 34(32): 7457-7459. doi: 10.1364/AO.34.007457
[36] Pu A, Psaltis D. High-density recording in photopolymer-based holographic three-dimensional disks[J]. Applied Optics, 1996, 35(14): 2389-2398. doi: 10.1364/AO.35.002389
[37] Bieringer T. Photoaddressable polymers[M]//Coufal H J, Psaltis D, Sincerbox G T. Holographic Data Storage. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2000: 209-228.
[38] Orlov S S, Bjornson E, Phillips W, et al. High transfer rate (1 Gbit/sec) high-capacity holographic disk digital data storage system[C]//Proceedings of 2000 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2000: 190-191.
[39] Waldman D A, Li H Y S, Horner M G. Volume shrinkage in slant fringe gratings of a cationic ring-opening holographic recording material[J]. Journal of Imaging Science and Technology, 1997, 41(5): 497-514.
[40] Waldman D A, Butler C J, Raguin D H. CROP holographic storage media for optical data storage greater than 100 bits/μm2[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 5216, doi: 10.1117/12.513614.
[41] Suzuki N, Tomita Y, Kojima T. Holographic recording in TiO2 nanoparticle-dispersed methacrylate photopolymer films[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2002, 81(22): 4121-4123. doi: 10.1063/1.1525391
[42] Goldenberg L M, Sakhno O V, Smirnova T N, et al. Holographic composites with gold nanoparticles: nanoparticles promote polymer segregation[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2008, 20(14): 4619-4627. doi: 10.1021/cm8005315
[43] Omura K, Tomita Y. Photopolymerization kinetics and volume holographic recording in ZrO2 nanoparticle-polymer composites at 404 nm[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 107(2): 023107. doi: 10.1063/1.3289729
[44] Hata E, Mitsube K, Momose K, et al. Holographic nanoparticle-polymer composites based on step-growth thiol-ene photopolymerization[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2011, 1(2): 207-222. doi: 10.1364/OME.1.000207
[45] Li C M Y, Cao L C, He Q S, et al. Holographic kinetics for mixed volume gratings in gold nanoparticles doped photopolymer[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(5): 5017-5028. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.005017
[46] Li C M Y, Cao L C, Wang Z, et al. Hybrid polarization-angle multiplexing for volume holography in gold nanoparticle-doped photopolymer[J]. Optics Letters, 2014, 39(24): 6891-6894. doi: 10.1364/OL.39.006891
[47] Tomita Y, Urano H, Fukamizu T A, et al. Nanoparticle-polymer composite volume holographic gratings dispersed with ultrahigh-refractive-index hyperbranched polymer as organic nanoparticles[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(6): 1281-1284. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.001281
[48] Liu P, Zhao Y, Li Z R, et al. Improvement of ultrafast holographic performance in silver nanoprisms dispersed photopolymer[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(6): 6993-7004. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.006993
[49] Ortuño M, Gallego S, Márquez A, et al. Biophotopol: a sustainable photopolymer for holographic data storage applications[J]. Materials, 2012, 5(5): 772-783. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLHY/NSTL_HYCC0210170587/
[50] Ortuño M, Fernández E, Fuentes R, et al. Improving the performance of PVA/AA photopolymers for holographic recording[J]. Optical Materials, 2013, 35(3): 668-673. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2012.11.001
[51] Cody D, Gribbin S, Mihaylova E, et al. Low-toxicity photopolymer for reflection holography[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(28): 18481-18487. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a3b57b99f5c83a94313a0dd9e9835a30
[52] Fan F L, Liu Y, Hong Y F, et al. Improving the polarization-holography performance of PQ/PMMA photopolymer by doping with THMFA[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(14): 17794-17803. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.017794
[53] Liu P, Wang L L, Zhao Y, et al. Holographic memory performances of titanocene dispersed poly (methyl methacrylate) photopolymer with different preparation conditions[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2018, 8(6): 1441-1453. doi: 10.1364/OME.8.001441
[54] Mok F H, Psaltis D, Burr G W. Spatially and angle-multiplexed holographic random access memory[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1993, 1773: 334-345. doi: 10.1117/12.141544
[55] Orlov S S, Phillips W, Bjornson E, et al. High data rate (10 Gbit/sec) demonstration in holographic disk digital data storage system[C]//Proceedings of the Summaries of Papers Presented at the Lasers and Electro-Optics. CLEO '02. Technical Diges, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2002: 70-71.
[56] Rakuljic G A, Leyva V, Yariv A. Optical data storage by using orthogonal wavelength-multiplexed volume holograms[J]. Optics Letters, 1992, 17(20): 1471-1473. doi: 10.1364/OL.17.001471
[57] Denz C, Pauliat G, Roosen G, et al. Volume hologram multiplexing using a deterministic phase encoding method[J]. Optics Communications, 1991, 85(2-3): 171-176. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(91)90389-U
[58] John R, Joseph J, Singh K. Holographic digital data storage using phase-modulated pixels[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2005, 43(2): 183-194. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2004.06.008
[59] Psaltis D, Levene M, Pu A, et al. Holographic storage using shift multiplexing[J]. Optics Letters, 1995, 20(7): 782-784. doi: 10.1364/OL.20.000782
[60] Steckman G J, Pu A, Psaltis D. Storage density of shift-multiplexed holographic memory[J]. Applied Optics, 2001, 40(20): 3387-3394. doi: 10.1364/AO.40.003387
[61] Pu A, Psaltis D. Holographic 3-D disks using shift multiplexing[C]//Summaries of papers presented at the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, Anaheim, CA, USA, 1996: 165.
[62] Darsky A M, Markov V B. Angular sensitivity of holograms with a reference speckle wave[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1991, 1238: 54-62. doi: 10.1117/12.19425
[63] Barbastathis G, Levene M, Psaltis D. Shift multiplexing with spherical reference waves[J]. Applied Optics, 1996, 35(14): 2403-2417. doi: 10.1364/AO.35.002403
[64] Markov V, Millerd J, Trolinger J, et al. Multilayer volume holographic optical memory[J]. Optics Letters, 1999, 24(4): 265-267. doi: 10.1364/OL.24.000265
[65] Orlov S S, Phillips W, Bjornson E, et al. High-transfer-rate high-capacity holographic disk data-storage system[J]. Applied Optics, 2004, 43(25): 4902-4914. doi: 10.1364/AO.43.004902
[66] Horimai H, Tan X D. Collinear technology for a holographic versatile disk[J]. Applied Optics, 2006, 45(5): 910-914. doi: 10.1364/AO.45.000910
[67] Horimai H, Tan X D, Li J. Collinear holography[J]. Applied Optics, 2005, 44(13): 2575-2579. doi: 10.1364/AO.44.002575
[68] Horimai H, Tan X D. Advanced collinear holography[J]. Optical Review, 2005, 12(2): 90-92. doi: 10.1007/s10043-004-0090-7
[69] Horimai H, Tan X D. Holographic information storage system: today and future[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2007, 43(2): 943-947. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2006.888528
[70] Shih H F. Integrated optical unit design for the collinear holographic storage system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2007, 43(2): 948-950. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2006.888530
[71] Wilson W L, Curtis K R, Anderson K E, et al. Realization of high-performance holographic data storage: the InPhase technologies demonstration platform[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 5216: 178-191. doi: 10.1117/12.506055
[72] Dhar L, Curtis K, Fäcke T. Holographic data storage: coming of age[J]. Nature Photonics, 2008, 2(7): 403-405. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2008.120
[73] Wilson W L. Toward the commercial realization of high performance holographic data storage[C]//Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics/International Quantum Electronics Conference and Photonic Applications Systems Technologies, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2004: 4.
[74] Schnoes M, Ihas B, Dhar L, et al. Photopolymer use for holographic data storage[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 4988: 68-76. doi: 10.1117/12.474791
[75] Anderson K, Curtis K. Polytopic multiplexing[J]. Optics Letters, 2004, 29(12): 1402-1404. doi: 10.1364/OL.29.001402
[76] 陶世荃, 徐敏.采用空间-角度复用的盘式三维全息存储[J].光学学报, 1997, 17(8): 1015-1020. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.1997.08.012
Tao S Q, Xu M. Spatioangularly-multiplexed three-dimensional holographic disks[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 1997, 17(8): 1015-1020. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.1997.08.012
[77] 袁泉, 陶世荃, 宋雪华, 等.光折变晶体中的盘式三维全息存储[J].中国激光, 1999, 26(12): 1097-1102. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.1999.12.009
Yuan Q, Tao S Q, Song X H, et al. Disk-type 3-D holographic storage in a photorefractive crystal[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 1999, 26(12): 1097-1102. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.1999.12.009
[78] 宋雪华, 陶世荃, 江竹青, 等.光折变晶体中全息图的热固定过程研究[J].中国激光, 2001, 28(1): 59-62. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgjg200101017
Song X H, Tao S Q, Jiang Z Q, et al. Study on thermal fixing process of holograms in photorefractive crystals[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2001, 28(1): 59-62. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgjg200101017
[79] 万玉红, 袁韡, 刘国庆, 等.光折变晶体全息存储中散射噪声特性的研究[J].中国激光, 2003, 30(6): 529-532. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2003.06.014
Wan Y H, Yuan W, Liu G Q, et al. Study on the characteristics of scattering noise in photorefractive holographic storage[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2003, 30(6): 529-532. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2003.06.014
[80] 郭亚军, 张建, 刘彩霞, 等. Zn:Fe:LiNbO3晶体全息存储性能研究[J].光子学报, 2004, 33(5): 570-572. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xyjsclygc201103009
Guo Y J, Zhang J, Liu C X, et al. Holographic storage properties of Zn:Fe:LiNbO3 crystals[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2004, 33(5): 570-572. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xyjsclygc201103009
[81] 刘友文, 刘立人, 周常河, 等.双掺杂和三掺杂铌酸锂晶体稳定全息存储的实验研究[J].中国激光, 2001, 28(2): 165-168. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgjg200102019
Liu Y W, Liu L R, Zhou C H, et al. Experimental study of non-volatile holographic storage of doubly- and triply-doped lithium niobate crystals[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2001, 28(2): 165-168. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgjg200102019
[82] 姚华文, 黄明举, 陈仲裕, 等.光致聚合物材料中引发剂浓度的优化和全息存储性能研究[J].中国激光, 2002, 29(11): 972-974. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2002.11.004
Yao H W, Huang M J, Chen Z Y, et al. Optimization of acrylamide-based photopolymer and its holographic character investigation[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2002, 29(11): 972-974. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2002.11.004
[83] 黄明举, 姚华文, 陈仲裕, 等.导致光聚物全息存储布喇格偏移因素的研究[J].光子学报, 2002, 31(7): 855-859. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzxb200207016
Huang M J, Yao H W, Chen Z Y, et al. The factor of introducing the bragg-mismatch during the photopolymer holographic exposure[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2002, 31(7): 855-859. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzxb200207016
[84] 黄明举, 姚华文, 陈仲裕, 等.新型绿光敏感光致聚合物高密度全息存储特性[J].物理学报, 2002, 51(11): 2536-2541. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wlxb200211024
Huang M J, Yao H W, Chen Z Y, et al. Study on the character of novel green light sensitive high-density digital holographic photopolymer[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2002, 51(11): 2536-2541. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wlxb200211024
[85] 黄明举, 姚华文, 陈仲裕, 等.厚度对光聚物高密度全息存储记录参量的影响[J].光子学报, 2002, 31(2): 246-249. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzxb200202027
Huang M J, Yao H W, Chen Z Y, et al. The effect of the thickness of photopolymer on high-density holographic recording parameters[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2002, 31(2): 246-249. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzxb200202027
[86] 鲍鹏, 何树荣, 何庆声, 等.像素1: 1匹配的晶体全息存储系统中像素位置偏移的补偿算法[J].光学技术, 2005, 31(2): 297-298, 301. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.2005.02.042
Bao P, He S R, He Q S, et al. Compensation method for misregistration in pixel-matched holographic data storage system[J]. Optical Technique, 2005, 31(2): 297-298, 301. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.2005.02.042
[87] 曹良才, 何庆声, 尉昊赟, 等. 10 Gb/cm3小型化体全息数据存储及相关识别系统[J].科学通报, 2004, 49(23): 2495-2500. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.23.022
Cao L C, He Q S, Wei H Y, et al. Miniaturized volume holographic optical data storage and correlation system with a storage density of 10 Gb/cm3[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(23): 2495-2500. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.23.022
[88] 黄雄斌, 何庆声, 王建岗, 等.体全息存储中SLM和CCD的性能对页内噪声的影响[J].光学技术, 2002, 28(6): 543-544. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.2002.06.032
Huang X B, He Q S, Wang J G, et al. Effect of performance of SLM and CCD on intrapage noise in volume[J]. Optical Technique, 2002, 28(6): 543-544. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.2002.06.032
[89] Jin G F, Cao L C, He Q S, et al. Random modulation in high-density holographic data storage and correlation recognition system[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 5206: 125-134. doi: 10.1117/12.505137
[90] Li J H, Cao L C, Gu H R, et al. Orthogonal-reference- pattern-modulated shift multiplexing for collinear holographic data storage[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(5): 936-938. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.000936
[91] Gu H R, Yin S F, Tan Q F, et al. Optimization of the geometrical shape of the aperture in holographic data storage system[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2007, 6827: 68271I. doi: 10.1117/12.755757
[92] Wei H Y, Luo S J, He Q S, et al. Novel holographic storage system with two data channels[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 5908: 59081F. doi: 10.1117/12.617189
[93] Yu Y W, Chen C Y, Sun C C. Increase of signal-to-noise ratio of a collinear holographic storage system with reference modulated by a ring lens array[J]. Optics Letters, 2010, 35(8): 1130-1132. doi: 10.1364/OL.35.001130
[94] Yu Y W, Yang C H, Yang T H, et al. Analysis of a lens-array modulated coaxial holographic data storage system with considering recording dynamics of material[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(19): 22947-22958. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.022947
[95] Sun C C, Yu Y W, Hsieh S C, et al. Point spread function of a collinear holographic storage system[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(26): 18111-18118. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.018111
[96] Lin X, Huang Y, Shimura T, et al. Fast non-interferometric iterative phase retrieval for holographic data storage[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(25): 30905-30915. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.030905
[97] Lin X, Huang Y, Li Y, et al. Four-level phase pair encoding and decoding with single interferometric phase retrieval for holographic data storage[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2018, 16(3): 032101. doi: 10.3788/COL
[98] Tan X D, Horimai H, Arai R, et al. Phase modulated collinear holographic data storage system[C]//International Workshop on Holography and Related Technologies, 2016.
[99] Lin X, Huang Y, Cheng Y B, et al. Inter-page-crosstalk reduction in holographic data storage system through phase modulation in signal region[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2016, 55(9S): 09SA07. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=IOP_9285210
[100] Lin X, Ke J, Wu A A, et al. An effective phase modulation in the collinear holographic storage[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9006: 900607. doi: 10.1117/12.2035171
[101] Das B, Joseph J, Singh K. Performance analysis of content-addressable search and bit-error rate characteristics of a defocused volume holographic data storage system[J]. Applied Optics, 2007, 46(22): 5461-5470. doi: 10.1364/AO.46.005461
[102] Das B, Joseph J, Singh K. Improved data search by zero-order (dc) peak filtering in a defocused volume holographic content-addressable memory[J]. Applied Optics, 2009, 48(1): 55-63. doi: 10.1364/AO.48.000055
[103] Sun C C, Tsou R H, Chang W C, et al. Random phase-coded multiplexing of hologram volumes using ground glass[J]. Optical and Quantum Electronics, 1996, 28(10): 1551-1561. doi: 10.1007/BF00326225
[104] Gao Q, Kostuk R. Improvement to holographic digital data-storage systems with random and pseudorandom phase masks[J]. Applied Optics, 1997, 36(20): 4853-4861. doi: 10.1364/AO.36.004853
[105] Sun C C, Su W C, Wang B, et al. Diffraction selectivity of holograms with random phase encoding[J]. Optics Communications, 2000, 175(1-3): 67-74. doi: 10.1016/S0030-4018(99)00769-5
[106] Xu X F, Cai L Z, Wang Y R, et al. Blind phase shift extraction and wavefront retrieval by two-frame phase-shifting interferometry with an unknown phase shift[J]. Optics Communications, 2007, 273(1): 54-59. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2006.12.033
[107] Jeon S H, Gil S K. 2-step phase-shifting digital holographic optical encryption and error analysis[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of Korea, 2011, 15(3): 244-251. doi: 10.3807/JOSK.2011.15.3.244
[108] Hariharan P, Oreb B F, Eiju T. Digital phase-shifting interferometry: a simple error-compensating phase calculation algorithm[J]. Applied Optics, 1987, 26(13): 2504-2506. doi: 10.1364/AO.26.002504
[109] Horimai H. Multi-level data write/retrieve by phase-locked collinear holography[C]//Asia Communications and Photonics Conference, Wuhan, 2016: AF1J.2.
[110] Xu K, Huang Y, Lin X, et al. Unequally spaced four levels phase encoding in holographic data storage[J]. Optical Review, 2016, 23(6): 1004-1009. doi: 10.1007/s10043-016-0263-1
[111] Fienup J R. Reconstruction of a complex-valued object from the modulus of its Fourier transform using a support constraint[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1987, 4(1): 118-123. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.4.000118
[112] Fienup J R. Phase retrieval algorithms: a comparison[J]. Applied Optics, 1982, 21(15): 2758-2769. doi: 10.1364/AO.21.002758
[113] Fienup J R, Wackerman C C. Phase-retrieval stagnation problems and solutions[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1986, 3(11): 1897-1907. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.3.001897
[114] Maiden A M, Rodenburg J M. An improved ptychographical phase retrieval algorithm for diffractive imaging[J]. Ultramicroscopy, 2009, 109(10): 1256-1262. doi: 10.1016/j.ultramic.2009.05.012
[115] Pan X C, Liu C, Lin Q, et al. Ptycholographic iterative engine with self-positioned scanning illumination[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(5): 6162-6168. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.006162
[116] Gureyev T E, Roberts A, Nugent K A. Phase retrieval with the transport-of-intensity equation: matrix solution with use of Zernike polynomials[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1995, 12(9): 1932-1942. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.12.001932
[117] Gureyev T E, Nugent K A. Rapid quantitative phase imaging using the transport of intensity equation[J]. Optics Communications, 1997, 133(1-6): 339-346. doi: 10.1016/S0030-4018(96)00454-3
[118] Volkov V V, Zhu Y, De Graef M. A new symmetrized solution for phase retrieval using the transport of intensity equation[J]. Micron, 2002, 33(5): 411-416. doi: 10.1016/S0968-4328(02)00017-3
[119] Lin X, Fujimura R, Umegaki S, et al. Single-shot phase reconstruction by iterative Fourier transform algorithm in the holographic data storage system[C]//International Symposium on Optical Memory 2016, Kyoto, Japan, 2016.
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: