-
摘要
为解决超声乳腺肿瘤分级检测问题,从超声射频(RF)信号的角度提出了一种有效的乳腺肿瘤分级检测方法。首先,采用Shearlet变换提取乳腺超声RF信号的多尺度、多方向特征;其次,考虑Shearlet特征的高维冗余性,采用多尺度方向二值模式(MDBP)对其进行编码,在不损失特征信息的条件下降低特征维度;最后,依据医生阅片经验以及不同分级乳腺肿瘤的特征差异性,设计出适合乳腺病变分级检测的层级二叉树SVM分类器(CBT-SVM)。在928个乳腺肿瘤患者的超声RF信号上进行验证,大量结果表明,提出方法可以有效实现3级、4A级~4C级、5级乳腺肿瘤的分级检测,准确度、敏感度、特异度、PPV、NPV以及MCC分别达到89.29%、75.62%、94.54%、97%、98.3%和81.01%。
-
关键词:
- 计算机辅助诊断 /
- 超声RF信号 /
- 支持向量机 /
- Shearlet变换
Abstract
A novel efficient method based on the ultrasound radio frequency (RF) signals is proposed to distinguish the breast tumors grades. First, we utilize the multi-scale geometric characteristic of Shearlet transformation to extract the multi-scale and multi-directional features of ultrasound RF signal, and then reduce the high-dimensional Shearlet features by multi-scale directional binary pattern which can effectively preserve the sufficient discriminated information. At last, we draw on the feature difference between different grades of breast tumors to design a cascade binary tree SVM classifier which not only overcome the problem of sample quantity disequilibrium but also conform to the subjective diagnosis rule of sonographer. Extensive experiments on 928 breast ultrasound RF signals collected from the hospital demonstrate the effectiveness of the new proposed method and its precision, sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV and MCC are 89.29%, 75.62%, 94.54%, 97%, 98.3% and 81.01%, respectively.
-
Key words:
- CAD /
- ultrasound RF signal /
- support vector machine /
- Shearlet transformation
-
Overview

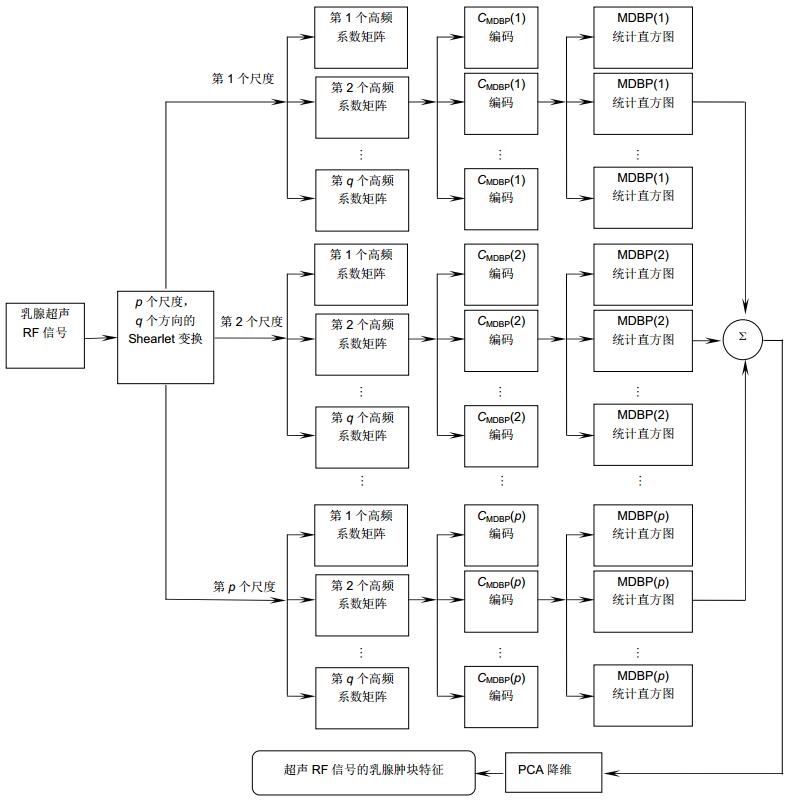
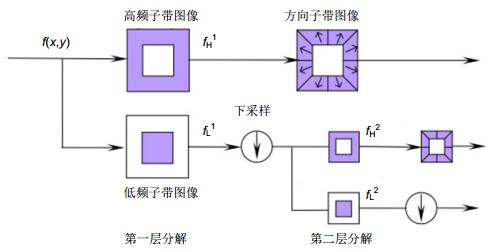
Overview: According to the statistics published by the American Cancer Society (ACS) in 2015, it is estimated that breast cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in women' patients accounting for 29% of all cancer cases. Early detection and better diagnosis methods play a significant role in reducing the number of fatalities induced by breast cancer. Current sonography has become one of the common methods for early screening breast cancer which are widely used to evaluate doubtful masses based on breast imaging-reporting and data system (BI-RADS). However, this method is limited by low contrast of B-mode images and high subjectivity of sonographers which may make the diagnosis results inaccurate and inconsistent. To address these limitations, ultrasound-based computer aided diagnosis (CAD) system is proposed to assist sonographers in breast tumor diagnosis for achieving higher accuracy and consistency. Since most of the existing CAD systems only can distinguish benign tumors and malignant tumors, and their processing data are all B-mode images which are obtained by ultrasound radio frequency signals, the existing CAD systems still need further researches and improvements. In view of this, we present a new method for distinguishing the grades of breast tumors based on the original ultrasound radio frequency signals which have richer tumor lesion information compared to B-mode images. First, we utilize the multi-scale geometric characteristic of Shearlet transformation to extract the multi-scale and multi-directional features of ultrasound RF signal. Second, multi-scale directional binary pattern (MDBP) is designed to code the texture information of high-frequency Shearlet features in different directions and different scales, which can not only reduce the dimension of Shearlet features but also preserve the sufficient discriminated information of breast tumors for the subsequent grade detection. At last, we draw on the feature difference between different grades of breast tumors to put forward a cascade binary tree SVM classifier, which not only overcome the problem of unbalance samples but also conform to the diagnosis rule of sonographer. Extensive experiments on 928 breast ultrasound RF signals collected from the hospital demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method and its precision, sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV and MCC are 89.29%, 75.62%, 94.54%, 97%, 98.3% and 81.01%, respectively. A point worth emphasizing that the higher values of PPV and NPV further show that the diagnosis results of the proposed method are close to the biopsy gold standard.
-

-
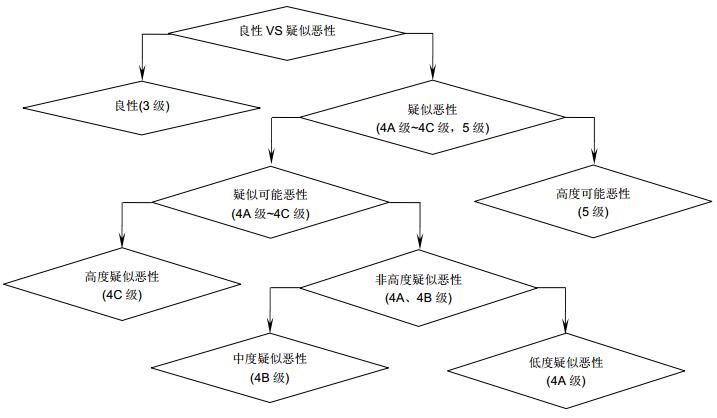
表 1 BI-RADS-US分级标准及特征描述
Table 1. BI-RADS-US standard and characteristic description
分级 评价 常见判别特征 0 需要附加的影像评价 - 1 阴性 - 2 良性(发现物) 圆形或者椭圆形,边缘光整,无回声,后方回声增强 3 可能良性(发现物),建议短期间隔继续检查 椭圆或稍不规则,边界清晰,边缘光整,平行皮肤方向,后方回声增强或无变化 4A 低度疑似恶性 不规则形状,边缘不光整、分叶毛刺、模糊、成角中一到两项模糊,边界不清楚,不确定方向,低回声,后方回声衰减或部分衰减 4B 中度疑似恶性 4C 高度疑似恶性 5 高度提示恶性,需要采取适当措施 不规则形状,边缘不光整、分叶、毛刺、模糊、成角中两项以上,边界模糊,与皮肤不平行,强回声晕征,后方衰减或部分衰减 6 已行活检, 并有恶性病理诊断 - 表 2 不同方向与尺度参数下的识别结果
Table 2. Performance comparison of different parameters of Shearlet transformation
Shearlet参数 Shearlet特征维数 MDBP特征维数 识别率/(%) 3个尺度4个方向 10692864 470016 79.02 3个尺度8个方向 21385728 940032 81.25 4个尺度4个方向 14257152 626688 79.91 4个尺度8个方向 28514304 1253376 89.29 5个尺度4个方向 17821440 783360 79.46 5个尺度8个方向 35642880 1566720 83.93 表 3 不同分块尺寸下的识别率
Table 3. Performance comparison of different block sizes of MDBP
分块尺寸/pixels 14×13 28×26 42×39 识别率/(%) 81.25 89.29 73.66 表 4 不同特征提取算法下的识别率
Table 4. Recognition rates of different feature extraction algorithms
表 5 不同分类器下的识别率和时间
Table 5. Recognition rate and classification time of different classifiers
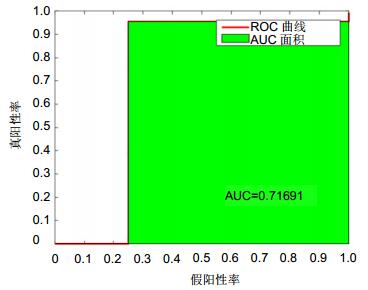
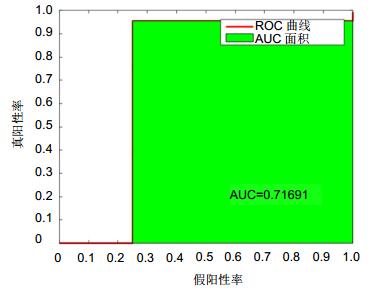
识别率/(%) 训练时间/s 测试时间/s DAG-SVM 58.03 58.93 1.79 OAO-SVM 58.03 58.93 3.93 KNN 79.91 1.81 0.44 RF 79.46 37.69 8.09 CBT-SVM 89.29 206.89 0.37 表 6 四种分类器性能比较
Table 6. Performance comparison of four classifiers
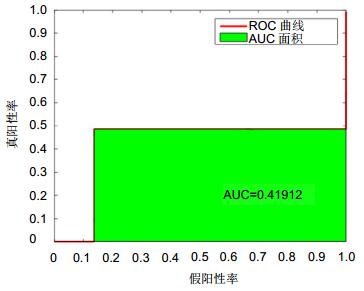
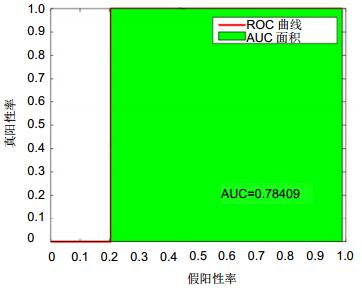
分类器 准确度/(%) 敏感度/(%) 特异性/(%) PPV/(%) NPV/(%) MCC/(%) DAG-SVM 58.03 64.71 88.97 72.56 88.03 54.28 KNN 79.91 63.84 92.69 79.53 88.03 64.31 RF 79.46 63.07 92.59 77.88 86.73 63.14 CBT-SVM 89.29 75.62 94.54 97.00 98.30 81.01 表 7 有向无环图SVM分类器的混淆矩阵
Table 7. The confusion matrix of DAG-SVM classifier
输入 3级 4A级 4B级 4C级 5级 3级 66 29 0 0 41 4A级 0 24 0 0 8 4B级 0 0 8 0 4 4C级 12 0 0 6 0 5级 0 0 0 0 26 表 8 KNN分类器的混淆矩阵
Table 8. The confusion matrix of KNN classifier
输入 3级 4A级 4B级 4C级 5级 3级 130 0 0 0 6 4A级 4 20 0 0 8 4B级 2 0 8 0 2 4C级 6 0 0 8 4 5级 10 0 0 3 13 表 9 随机森林分类器的混淆矩阵
Table 9. The confusion matrix of random forest classifier
输入 3级 4A级 4B级 4C级 5级 3级 130 0 0 0 6 4A级 4 20 0 0 8 4B级 2 0 8 0 2 4C级 6 0 0 8 4 5级 10 0 0 4 12 表 10 层级二叉树分类器的混淆矩阵
Table 10. The confusion matrix of CBT-SVM classifier
输入 3级 4A级 4B级 4C级 5级 3级 136 0 0 0 0 4A级 8 24 0 0 0 4B级 4 0 8 0 0 4C级 10 0 0 8 0 5级 2 0 0 0 24 -
参考文献
[1] 周世崇, 曾炜, 范亦武, 等.乳腺超声分级方法应用的初步探讨[J].中国超声医学杂志, 2008, 24(6): 19-23. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200802697560
Zhou S C, Zeng W, Fan Y W, et al. Discussing of using breast grades in ultrasound[J]. Chinese Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine, 2008, 24(6): 19-23. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200802697560
[2] 侯新燕, 高宇, 黄晓玲, 等.乳腺影像报告数据系统在乳腺超声中的应用价值[J].中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2011, 8(6): 1227-1233. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2011.06.008
Hou X Y, Gao Y, Huang X L, et al. Application value of breast image report data system for ultrasonography in mamary gland[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Ultrasound (Electronic Edition), 2011, 8(6): 1227-1233. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2011.06.008
[3] Suzuki K. A review of computer-aided diagnosis in thoracic and colonic imaging[J]. Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery, 2012, 2(3): 163-176. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23256078
[4] He J T, Chen M H, Jia W Y, et al. Segmentation of diabetic macular edema in Oct retinal images[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2018, 45(7): 170605. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170605
[5] 吕卫, 翟庆伟, 褚晶辉, 等.彩色眼底图像糖网渗出物的自动检测[J].光电工程, 2016, 43(12): 183-192, 199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.12.028
Lv W, Zhai Q W, Chu J H, et al. Automated detection of diabetic retinopathy exudates in color fundus images[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2016, 43(12): 183-192, 199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.12.028
[6] Wang X W, Li L H, Liu W, et al. An interactive system for computer-aided diagnosis of breast masses[J]. Journal of Digital Imaging, 2012, 25(5): 570-579. doi: 10.1007/s10278-012-9451-0
[7] Jen C C, Yu S S. Automatic detection of abnormal mammograms in mammographic images[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2015, 42(6): 3048-3055. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2014.11.061
[8] Sharma S, Khanna P. Computer-aided diagnosis of malignant mammograms using Zernike moments and SVM[J]. Journal of Digital Imaging, 2015, 28(1): 77-90. doi: 10.1007/s10278-014-9719-7
[9] 谭婉嫦, 王金花, 蔡洪明, 等.基于微钙化检测的计算机辅助诊断系统对于乳腺导管原位癌的诊断价值[J].临床放射学杂志, 2016, 35(9): 1352-1356. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lcfsxzz201609017
Tan W C, Wang J H, Cai H M, et al. The performance of computer-aided diagnosis for DCIS based on classification of clustered microcalcifications[J]. Journal of Clinical Radiology, 2016, 35(9): 1352-1356. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lcfsxzz201609017
[10] Moon W K, Lo C M, Huang C S, et al. Computer-aided diagnosis based on speckle patterns in ultrasound images[J]. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology, 2012, 38(7): 1251-1261. http://www.europepmc.org/abstract/MED/22579548
[11] Alam S K, Feleppa E J, Rondeau M, et al. Computer-Aided diagnosis of solid breast lesions using an ultrasonic multi-feature analysis procedure[J]. Bangladesh Journal of Medical Physics, 2013, 4(1): 1-10. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=475ee99e76be898ae05edd489103a319&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[12] Huang Q H, Yang F B, Liu L Z, et al. Automatic segmentation of breast lesions for interaction in ultrasonic computer-aided diagnosis[J]. Information Sciences, 2015, 314: 293-310. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2014.08.021
[13] Cheng J Z, Ni D, Chou Y H, et al. Computer-Aided diagnosis with deep learning architecture: Applications to breast lesions in us images and pulmonary nodules in CT scans[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 24454. doi: 10.1038/srep24454
[14] Masotti L, Biagi E, Granchi S, et al. Tissue differentiation based on radiofrequency echographic signal local spectral content[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Ultrasonics, 2003, 1: 1030-1033.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224748177_Tissue_differentiation_based_on_radiofrequency_echographic_signal_local_spectral_content_RULES_Radiofrequency_Ultrasonic_Local_Estimator [15] Moradi M, Mahdavi S S, Nir G, et al. Ultrasound RF time series for tissue typing: first in vivo clinical results[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2013, 8670: 86701I. doi: 10.1117/12.2007672
[16] Moradi M, Abolmaesumi P, Mousavi P. Tissue typing using ultrasound RF time series: experiments with animal tissue samples[J]. Medical Physics, 2010, 37(8): 4401-4413. doi: 10.1118/1.3457710
[17] 刘志东, 罗燕, 林江莉, 等.基于超声射频RF信号的脂肪肝分级量化方法[J].四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2011, 43(S1): 160-164. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK201101325132
Liu Z D, Luo Y, Lin J L, et al. Quantizing and grading of fatty liver based on ultrasonic RF signals[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 2011, 43(S1): 160-164. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK201101325132
[18] 庄淑莲, 周建华, 王建伟, 等.基于超声射频流的RF时间序列信号在乳腺病变良恶性鉴别中的价值[J].中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2016, 13(5): 393-397. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2016.05.014
Zhuang S L, Zhou J H, Wang J W, et al. Differential diagnosis of breast lesions with RF time-series signal based on ultrasonic radio-frequency flow[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Ultrasound (Electronic Edition), 2016, 13(5): 393-397. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2016.05.014
[19] 严郁, 方舸, 蔡润秋, 等.基于乳腺肿块的超声射频信号特征算法识别[J].中国医学装备, 2016, 13(9): 20-22. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1672-8270.2016.09.006
Yan Y, Fang G, Cai R Q, et al. Ultrasound radio-frequency characteristic signal processing for breast lump recognition[J]. China Medical Equipment, 2016, 13(9): 20-22. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1672-8270.2016.09.006
[20] Uniyal N, Eskandari H, Abolmaesumi P, et al. Ultrasound RF time series for classification of breast lesions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2015, 34(2): 652-661. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2014.2365030
[21] Guo K H, Labate D. Optimally sparse multidimensional representation using shearlets[J]. SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis, 2007, 39(1): 298-318. doi: 10.1137/060649781
[22] Gao G R, Xu L P, Feng D Z. Multi-focus image fusion based on non-subsampled shearlet transform[J]. IET Image Processing, 2013, 7(6): 633-639. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2012.0558
[23] 常莉红.基于剪切波变换和稀疏表示理论的图像融合方法[J].中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 56(4): 16-19. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zsdxxb201704003
Chang L H. Fusion method based on shearlet transform and sparse representation[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2017, 56(4): 16-19. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zsdxxb201704003
[24] 周飞, 贾振红, 杨杰, 等.基于剪切波域改进Gamma校正的医学图像增强算法[J].光电子·激光, 2017, 28(5): 566-572. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20172017062100055155
Zhou F, Jia Z H, Yang J, et al. Medical image enhancement method based on improved Gamma correction in shearlet domain[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics·Laser, 2017, 28(5): 566-572. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20172017062100055155
[25] 徐畅, 陈晓, 季仟亿.基于稀疏编码的Shearlet域图像去噪[J].激光杂志, 2017, 38(10): 96-100. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jgzz201710022
Xu C, Chen X, Ji Q Y. Shearlet domian image denoising via sparse coding[J]. Laser Journal, 2017, 38(10): 96-100. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jgzz201710022
[26] Easley G R, Labate D, Colonna F. Shearlet-based total variation diffusion for denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2009, 18(2): 260-268. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2008.2008070
[27] Vagharshakyan S, Bregovic R, Gotchev A. Light field reconstruction using Shearlet transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(1): 133-147. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2653101
[28] 许志良, 邓承志, 张运生.非局域自相似约束的Shearlet稀疏正则化图像恢复[J].电子科技大学学报, 2016, 45(1): 43-47, 101. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjdxxb201601006
Xu Z L, Deng C Z, Zhang Y S. Shearlet sparsity regularized image reconstruction based on nonlocal self-similarity[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2016, 45(1): 43-47, 101. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjdxxb201601006
[29] Zhou S C, Shi J, Zhu J, et al. Shearlet-based texture feature extraction for classification of breast tumor in ultrasound image[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2013, 8(6): 688-696. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2013.06.011
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: