-
摘要
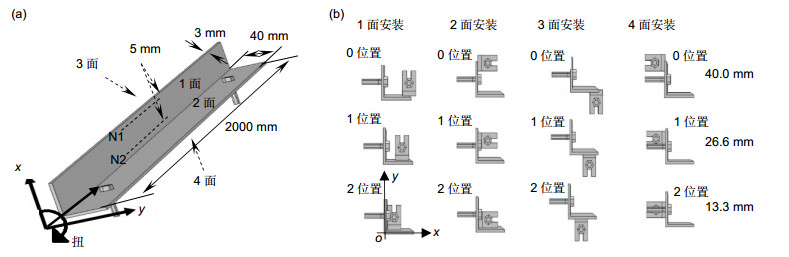
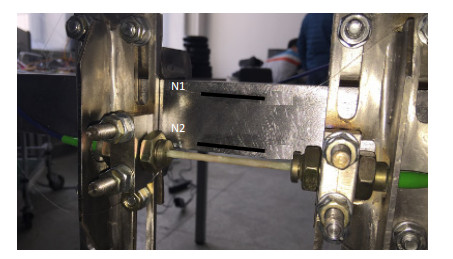
本文提出将两个纤维增强复合材料(FRP)封装的光纤光栅(FBG)安装于角钢梁的两个面上,用来实现对角钢梁位移大小和方向的测量,实现对角钢结构的健康检测。本文将传感器分别安装在角钢梁不同面上的各个位置,通过有限元分析模拟了角钢梁结构的位移和传感器应变传递的关系,对传感器的安装位置进行优化设计,并进行了实验验证。仿真模拟和实验结果表明,传感器安装在合理位置能够实现角钢梁一端位移的大小测量和方向判别。研究结果对于利用光纤传感器实现对角钢构成的结构如桥梁、电塔、吊车等的健康监测提供了基础研究。

Abstract
In this paper, two fiber reinforced polymer/plastic (FRP) encapsulated fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensors were installed on the two sides of the angle steel beam, which was used to measure the displacement and direction of the diagonal steel beam, so as to realize the health inspection of the angle steel structure. The sensors were respectively installed on the different positions of angle steel beam, and the relationship between displacement and strain transmission of angle steel beam was simulated by the finite element analysis. The optimum design of sensors installation were discussed and the experimental verification was carried out. The simulation and experimental results show that the sensor has the capacity to discriminate the direction and measure the size of one side of the angle steel beam displacement when installed in a reasonable position. To realize the health monitoring by using optical fiber sensors on the structures composed by angle steel, such as bridges, electric towers and cranes, and so on, a basic research was provided.
-
Overview

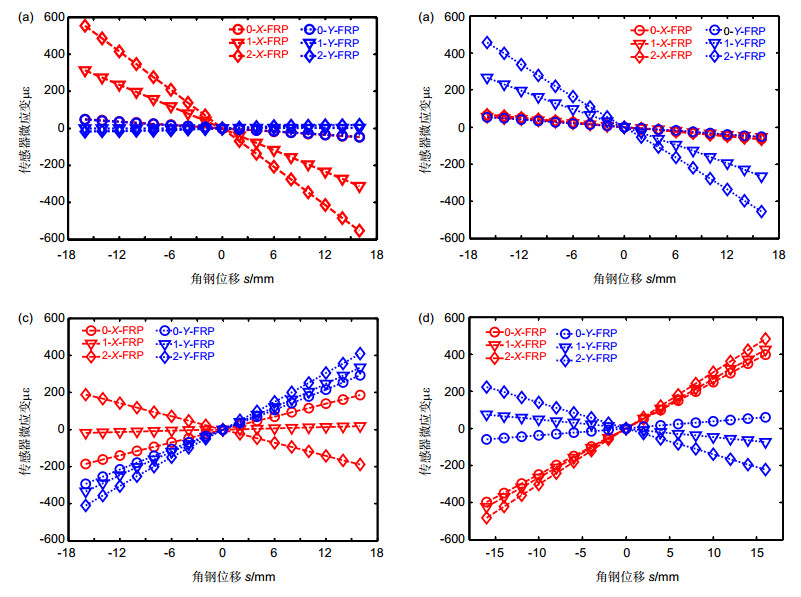
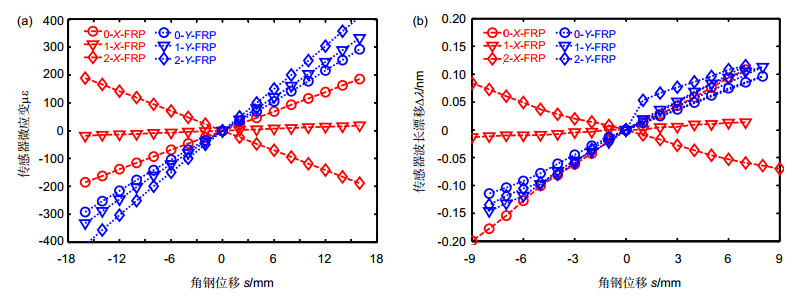
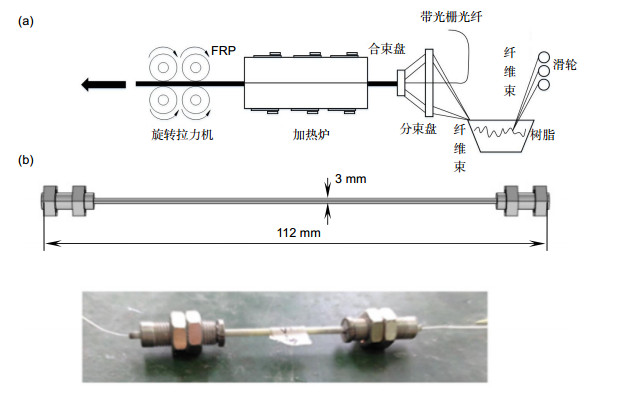
Overview: In this paper, two fiber reinforced polymer/plastic (FRP) encapsulated fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensors are installed on the two sides of the angle steel beam, which are used to measure the displacement and direction of the diagonal steel beam, so as to realize the health inspection of the angle steel structure. Compared with the traditional angle sensors, fiber Bragg grating is chosen as the sensor in this paper for its excellent characteristics of small volume, light weight, anti-electromagnetic interference, good electrical insulation and stable performance in harsh environment. The FBG is protected by FRP encapsulation to ensure that the sensor can work steadily in the severe working environment of the angle steel. Besides, according to the shape of the angle steel beam, the sensor installation fixture is designed to facilitate changing the installation position of the sensor on the angle steel beam. The influence of the installation of the sensor and the sensor fixture on the angle steel beam is analyzed by the finite element method. It is found that the fixture installation has no effect on the strain distribution on the surface of the angle steel beam, Based on these, the transfer relationship between sensor strain and displacement of angle beam are carefully analyzed on the different sensor installation positions of the angle beam. The sensitivity and errors of sensor are analyzed at each side of position 0, 1, 2 and gets the result that the sensor can achieve maximum sensitivity and minimum errors when being installed at position 2 on any surfaces or at any installation positions on surface 3 or 4. Finally, sensor mounted on surface 3 is chosen for experimental verification. The experimental results are in agreement with the simulation results. At the same time, it can be seen that the displacement and direction of the diagonal steel beams can be measured by the sensor installed at the position 2 on the surface 3. In this paper, optimization design of the installation positions of the FRP fiber Bragg grating sensor on the different surfaces of the angle steel beam are discussed and the experimental verification is carried out the experimental. To achieve the health monitoring by using optical fiber sensors on the structures composed by angle steel, such as bridges, electric towers and cranes, and so on, a basic research is provided.
-

-
表 1 传感器在各面及各位置处X, Y方向的灵敏度
Table 1. The sensor responds on all sides to the angular displacement
(με/mm) Position Surface 1 Surface 2 Surface 3 Surface 4 X Y X Y X Y X Y 0 -2.966 -2.865 -4.083 -3.275 11.584 18.012 24.835 3.687 1 -19.487 0.120 -3.464 -16.356 1.137 20.574 26.539 -4.704 2 -34.545 1.271 -4.239 -28.142 -11.831 25.402 30.166 -13.951 表 2 3面上传感器的灵敏度
Table 2. Sensitivity of the sensor on the surface 3
(με/mm) Position Simulation Experiment X Y X Y 0 11.584 18.012 15.741 11.191 1 1.137 20.574 1.425 14.149 2 -11.831 25.402 -7.341 15.229 -
参考文献
[1] 张利伟, 张慧.钢架用于桥梁加固的探索与研究[J].建筑技术, 2010, 41(09): 818-820. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4726.2010.09.011
Zhang L W, Zhang H. Exploration and research on application of steel frame for bridge strengthening[J]. Architecture Technology, 2010, 41(09): 818-820. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4726.2010.09.011
[2] 郭勇, 沈建国, 应建国.输电塔组合角钢构件稳定性分析[J].钢结构, 2012, 27(1): 11-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9963.2012.01.003
Guo Y, Shen J G, Ying J G. Stability analysis on the multiple angle members of transmission towers[J]. Steel Construction, 2012, 27(1): 11-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9963.2012.01.003
[3] Roveri N, Carcaterra A, Sestieri A. Real-time monitoring of railway infrastructures using fibre Bragg grating sensors[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2015, 60-61: 14-28. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.01.003
[4] 安雷, 胡勇.船舶肋骨冷弯中旁弯的有限元模拟分析研究[J].船海工程, 2011, 40(3): 40-43. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-7953.2011.03.012
An L, Hu Y. FE simulation and analysis of ship frames vertical-bending in cold-bending processing[J]. Ship & Ocean Engineering, 2011, 40(3): 40-43. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-7953.2011.03.012
[5] 王妮, 陈宗平, 燕柳斌, 等.角钢桁架型钢混凝土梁纯扭试验及损伤分析[J].建筑结构, 2014, 44(9): 15-21. doi: 10.19701/j.jzjg.2014.09.003
Wang N, Chen Z P, Yan L B, et al. Pure torsional experiment and damage analysis of angle steel truss reinforced concrete beams[J]. Building Structure, 2014, 44(9): 15-21. doi: 10.19701/j.jzjg.2014.09.003
[6] 范银平, 何晓波, 张全刚, 等.高强度热轧船用角钢的研制与开发[J].河南冶金, 2010, 18(6): 12-13, 17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3129.2010.06.004
Fan Y P, He X B, Zhang Q G, et al. Research and development of higt strength shipbuilding hot rolled angle steel[J]. Henan Metallurgy, 2010, 18(6): 12-13, 17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3129.2010.06.004
[7] 缪红燕, 徐鸿, 王楠, 等.大型组合管式反应塔的应力分析(一)——有限元应力分析模型[J].压力容器, 2003, 20(5): 26-28, 33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4837.2003.05.007
Miao H Y, Xu H, Wang N, et al. Stress analyse of the large combined tubular reactor (1)——finite element model for stress analysis[J]. Pressure Vessel Technology, 2003, 20(5): 26-28, 33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4837.2003.05.007
[8] 杨慧, 周国强. JJ225/43-K型井架模型试验研究[J].石油矿场机械, 2011, 40(02): 47-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3482.2011.02.012
Yang H, Zhou G Q. Experimental Research of JJ225/43-K Drilling Derrick Model[J]. Oil Field Equipment, 2011, 40(02): 47-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3482.2011.02.012
[9] 赵庆斌. 送电铁塔单角钢受压极限承载力研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2004: 9-19.
Zhao Q B. Power transmission tower angli iron bar critical load of compressive member[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2004: 9-19.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10613-2004106617.htm [10] 徐国权, 熊代余.光纤光栅传感技术在工程中的应用[J].中国光学, 2013, 6(3): 306-317. doi: 10.3788/CO.20130603.0306
Xu G Q, Xiong D Y. Applications of fiber Bragg grating sensing technology in engineering[J]. Chinese Optics, 2013, 6(3): 306-317. doi: 10.3788/CO.20130603.0306
[11] 杜志泉, 倪锋, 肖发新.光纤传感技术的发展与应用[J].光电技术应用, 2014, 29(06): 7-12, 17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1255.2014.06.002
Hou J F, Pei L, Li Z X, et al. Development and application of optical fiber sensing technology[J]. Electro-Optic Technology Application, 2014, 29(06): 7-12, 17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1255.2014.06.002
[12] 张桂花. 表面黏贴式光纤光栅传感原理及其实验研究[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2013: 15-39.
Zhang G H. Study on principle of surface adhesive for fiber Bragg grating sensor monitoring and its experiments[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2013: 15-39.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10704-1014072269.htm [13] 詹亚歌, 蔡海文, 耿建新, 等.铝槽封装光纤光栅传感器的增敏特性研究[J].光子学报, 2004, 33(8): 952-955. http://www.photon.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract11772.shtml
Zhan Y G, Cai H W, Geng J X, et al. Study on aluminum groove encapsulating technique and sensing characteristics of FBG sensor[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2004, 33(8): 952-955. http://www.photon.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract11772.shtml
[14] 甘望, 王华强, 谢忱, 等.光纤光栅管式封装工艺研究[J].光学仪器, 2016, 38(6): 544-548. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5630.2016.06.014
Gan W, Wang H Q, Xie C, et al. Steel capillary packaging technique for fiber Bragg grating sensor[J]. Optical Instruments, 2016, 38(6): 544-548. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5630.2016.06.014
[15] 叶列平, 冯鹏. FRP在工程结构中的应用与发展[J].土木工程学报, 2006, 39(3): 24-36. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2006.03.004
Ye L P, Feng P. Applications and development of fiber-reinforced polymer in engineering structures[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2006, 39(3): 24-36. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2006.03.004
[16] 王言磊, 周智, 郝庆多, 等. FRP-FBG智能复合板的制作及其传感器特性研究[J].光电子·激光, 2007, 18(8): 900-902. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-0086.2007.08.004
Wang Y L, Zhou Z, Hao Q D, et al. Research on fabrication technique and sensing properties of smart FRP-FBG composite laminates[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics·Laser, 2007, 18(8): 900-902. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-0086.2007.08.004
[17] 张志春, 王川, 周智, 等. FRP筋拉挤成型工艺过程的光纤光栅监测与结果分析[J].东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 35(S1): 23-26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0505.2005.z1.007
Zhang Z C, Wang C, Zhou Z, et al. FBG monitoring results analysis for fabrication processing of FRP bars[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2005, 35(S1): 23-26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0505.2005.z1.007
[18] Pramanik A, Basak A K, Dong Y, et al. Joining of carbon fibre reinforced polymer (CFRP) composites and aluminium alloys - a review[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2017, 101: 1-29. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.06.007
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: