-
摘要:
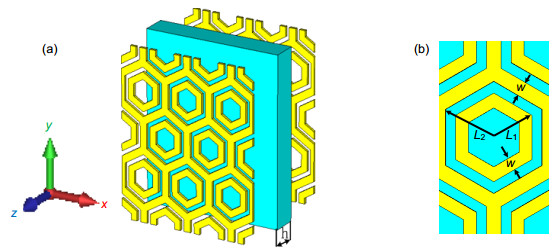
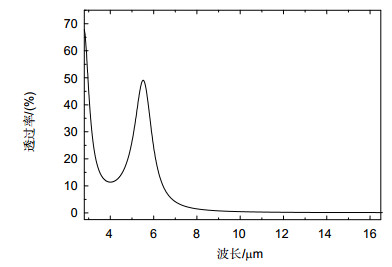
本文设计了工作在第二个大气窗口(3 μm~5 μm)和第三个大气窗口(8 μm~14 μm)的双频段FSS。该FSS为双屏结构,由六边形金属网格和六边形谐振环阵列组合而成。仿真结果表明,该FSS在两个大气窗口的平均透过率低于5%,且对不同角度入射的电磁波具有良好的角度稳定性。分析了结构主要尺寸参数对传输特性的影响,结果表明,调整六边形谐振环的单元尺寸能够有效调节3 μm~5 μm波段范围内-10 dB阻带的带宽,增大金属网格的单元尺寸会使得8 μm~14 μm波段范围内的阻带向长波方向移动。
 Abstract:
Abstract:A dual-band frequency selective surface (FSS) with double screen was designed to cover the mid-infrared atmospheric window (3 μm~5 μm) and the far-infrared atmospheric window (8 μm~14 μm). This structure is composed of hexagonal metallic mesh and hexagonal resonant ring array. Simulation results show that the average transmission of FSS in atmospheric window is lower than 5%, and this structure is insensitive to the incident angle. The effect of the parameters on transmission properties was analyzed. The results show that adjusting the size of hexagonal ring structure can effectively adjust the -10 dB stopband bandwidth in 3 μm~5 μm, and increasing the size of metallic mesh can move the stopband in 8 μm~14 μm to long wave direction.
-
Key words:
- atmospheric window /
- metallic mesh /
- frequency selective surface /
- angle stability
-

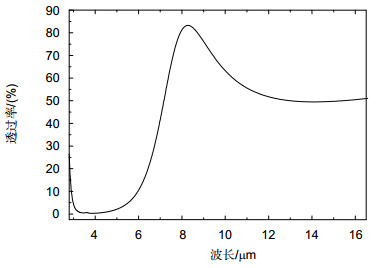
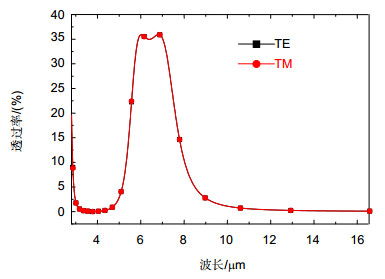
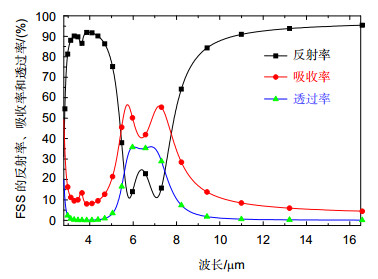
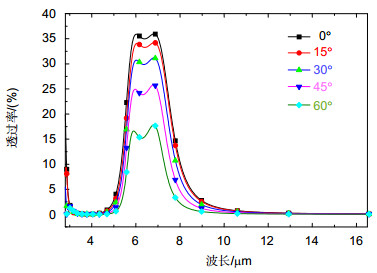
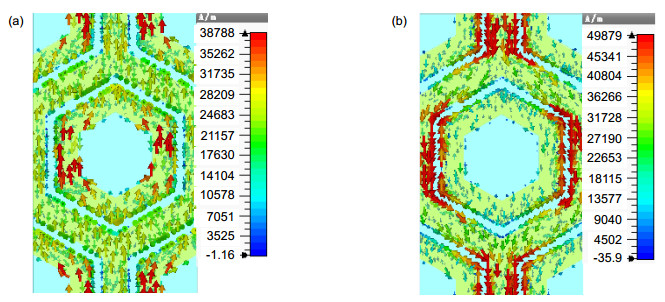
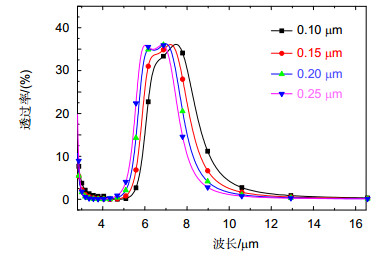
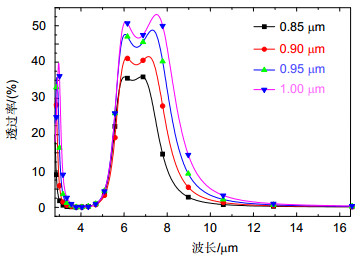
Military infrared detection technology mainly focuses on the infrared radiation of target in mid-infrared atmospheric window (3 μm~5 μm) and the far-infrared atmospheric window (8 μm~14 μm), therefore reducing the infrared transmittance of the target in these two atmospherics can effectively decrease the possibility of detection. Frequency selective surface (FSS) has good spatial filtering characteristics and can be used to suppress the infrared transmittance of the target in the band of interest. In order to extend the bandwidth of FSS and realize multi-band selection, we combine hexagonal ring structure with hexagonal metal mesh. Meanwhile, we adopt double layers to further expand the bandwidth. Simulation results show that the infrared transmission of the structure is lower than 5% in 3 μm~5 μm and 8 μm ~14 μm. The structure realizes the suppression of infrared transmission in mid-infrared atmospheric window and far-infrared atmospheric window. The absorption of the structure is nearly 10% in 3 μm~5 μm and 8 μm~14 μm, which indicates the low infrared radiation of the structure. Moreover, the reflection of the FSS is close to 90%, which suggests that the stopband characteristic of the structure is mainly due to the reflection enhancement caused by the scattering field produced by the surface current. The surface current distributions at 4 μm and 10 μm show that the stopband characteristics at 4 μm is mainly caused by the scattering field produced by the surface current of hexagonal ring structure, while the stopband characteristics at 10 μm is mainly caused by the scattering field produced by the surface current of hexagonal metal mesh. The structure is insensitive to polarization. At oblique incidence, the structure can still maintain low infrared transmittance in 3 μm~5 μm and 8 μm~14 μm. When the line width w decreases from 0.25 μm to 0.10 μm, the equivalent size of the hexagonal metal mesh increases and the spacing of the hexagonal ring structure units decreases, which causes the transmission curve moves towards the long wave and the -10 dB bandwidth in 3 μm~5 μm increases from 2.47 μm to 3.08 μm. When L1 reduces from 0.75 μm to 0.60 μm, the spacing of the hexagonal ring structure units increases, which weakens the coupling effect between the units, and the -10 dB bandwidth in 3 μm~5 μm reduces from 2.92 μm to 1.65 μm, meanwhile grating lobe appears in 3 μm~5 μm. When L2 changes from 0.85 μm to 1 μm, the transmission curve in 8 μm~14 μm moves towards long wave due to the increase of equivalent size of the hexagonal metal mesh.
-

-
-
[1] Munk B A. Frequency selective surface: theory and design[M]. New York: Wiley, 2000.
[2] 蒲明博, 王长涛, 王彦钦, 等.衍射极限尺度下的亚波长电磁学[J].物理学报, 2017, 66(14): 144101. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.144101
Pu Mingbo, Wang Changtao, Wang Yanqin, et al. Subwave-length electromagnetics below the diffraction limit[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(14): 144101. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.144101
[3] 郭迎辉, 蒲明博, 马晓亮, 等.电磁超构材料色散调控研究进展[J].光电工程, 2017, 44(1): 3-22. http://www.oejournal.org/J/OEE/Article/Details/A170317000570/CN
Guo Yinghui, Pu Mingbo, Ma Xiaoliang, et al. Advances of dispersion-engineered metamaterials[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017, 44(1): 3-22. http://www.oejournal.org/J/OEE/Article/Details/A170317000570/CN
[4] Liu Haitao, Cheng Haifeng, Chu Zengyong, et al. Absorbing properties of frequency selective surface absorbers with cross-shaped resistive patches[J]. Materials & Design, 2007, 28(7): 2166-2171. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0261306906001932
[5] Lin X Q, Cui T J, Fan Y, et al. Frequency selective surface designed using electric resonant structures in terahertz frequency bands[J]. Journal of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications, 2009, 23(1): 21-29. doi: 10.1163/156939309787604724
[6] Mittra R, Chan C H, Cwik T. Techniques for analyzing frequency selective surfaces-a review[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1988, 76(12): 1593-1615. doi: 10.1109/5.16352
[7] Romeu J, Rahmat-Samii Y. Fractal FSS: a novel dual-band frequency selective surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2000, 48(7): 1097-1105. doi: 10.1109/8.876329
[8] Gianvittorio J P, Rahmat-Samii Y, Romeu J. Fractal FSS: various self-similar geometries used for dual-band and dual-polarized FSS[C]// Proceedings of 2001 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, 2001, 3: 640-643.
[9] Gianvittorio J P, Romeu J, Blanch S, et al. Self-similar prefractal frequency selective surfaces for multiband and dual-polarized applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2003, 51(11): 3088-3096. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2003.818791
[10] Ranga Y, Matekovits L, Weily A R, et al. A low-profile dual-layer ultra-wideband frequency selective surface reflector[J]. Micro-wave and Optical Technology Letters, 2013, 55(6): 1223-1227. doi: 10.1002/mop.27583
[11] Ulrich R. Far-infrared properties of metallic mesh and its com-plementary structure[J]. Infrared Physics, 1967, 7(1): 37-55. doi: 10.1016/0020-0891(67)90028-0
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: