Influence of thermal-vacuum environment on the recovered spectrum of spatial heterodyne spectrometer
-
摘要:
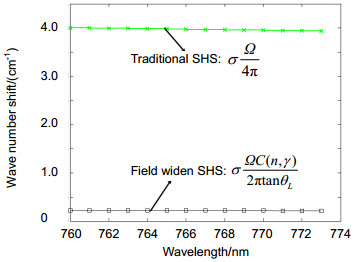
热真空环境适应性是空间光学遥感仪器的关键性能之一,对超光谱CO2监测仪的复原光谱精度尤为重要。基于空间外差干涉技术原理,采用理论分析和试验手段对仪器热真空环境适应性进行了讨论。理论分析了热真空环境对准直光束发散角、扩视场空间外差干涉仪组件基频波长、成像镜头离焦和缩放比等因素的改变对复原光谱的影响,并基于CS-800型热真空模拟设备开展了测量实验。实验结果表明,理论分析得到的系统基频波长与实验数据吻合,复原光谱廓线形状与理论分析一致。当干涉仪组件均采用融石英(SiLiCa),热控精度优于1.1 ℃时,仪器可具有0.01 nm的光谱稳定度,该分析为空间外差干涉光谱仪各功能组件的热控要求、地基常压条件下基频的选定等问题提供了理论依据。
 Abstract:
Abstract:Thermal-vacuum environment adaptability is one of the key performances of space optical instruments, especially for hyper-spectral instrument, and spatial heterodyne spectrometer (SHS) should provide high spectral stability for the detection of atmosphere CO2. Based on the research of the spatial heterodyne interference principle, simulation test in thermal-vacuum environment and quantitative analyses are carried out. The relationship among environment changes and the divergence half-angle of collimating lens, Littrow wavelength of field widened interferometer, different defocusing amount and pantograph ratio of imaging lens are analyzed. In order to verify the theoretical analysis, thermal-vacuum experiment is performed. The results show that the spectral deviation and profile are matched with theoretical analysis, and spectral stability is less than ±0.01 nm under the temperature from 19 ℃ to 21.2 ℃ by the substrates made of fused Silica (Corning 7980 0F). Quantitative analyses provide theoretical basis for the thermal control requirement and Littrow wavelength selection in normal atmospheric pressure.
-

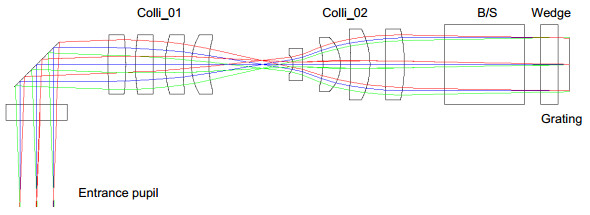
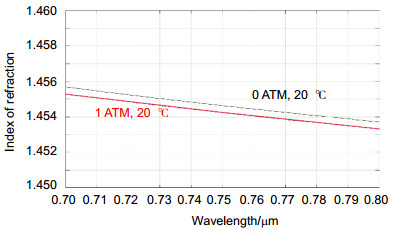
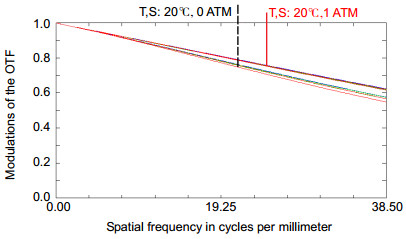
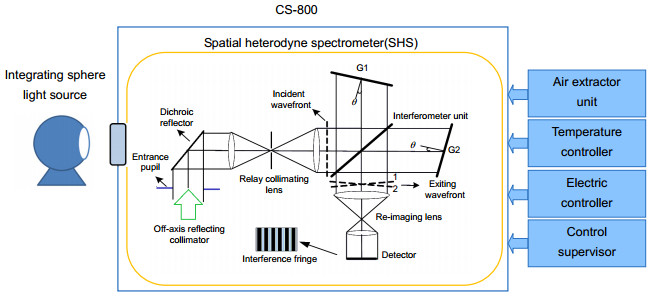
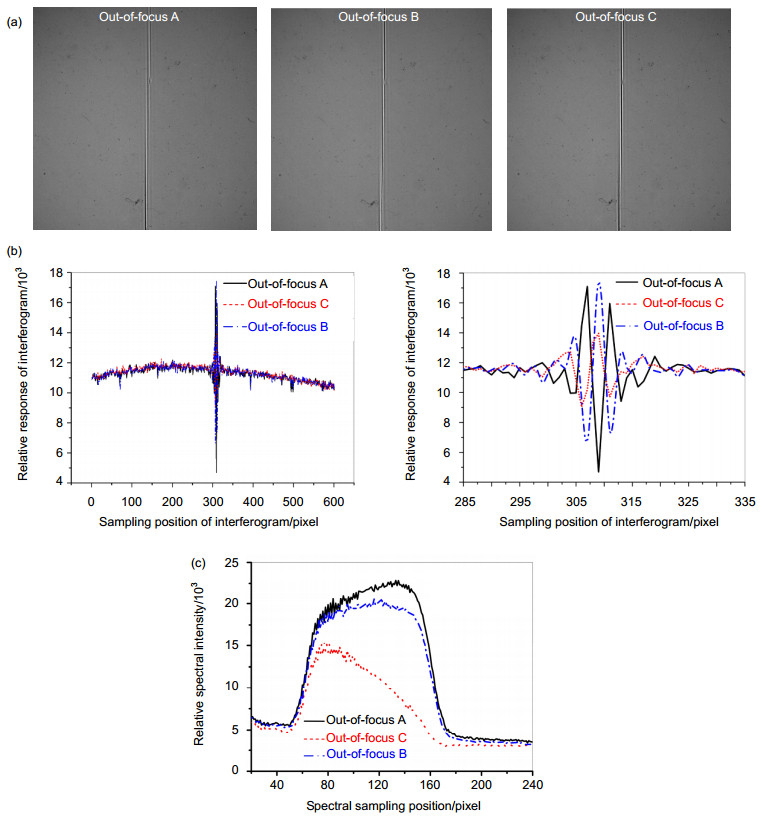
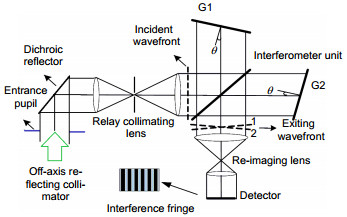
Abstract: Spatial heterodyne Spectroscopy is an interferometric technique to achieve many hyper-spectral detections that have been developed for several decades by J. M. Harlander, F. L. Roesler et al. In particular, passive hyper-spectral spatial heterodyne spectrometer (SHS) is significant instrument for space applications to measure colume densities of trace gases (CO2, CH4, CO), mesospheric OH density, global chlorophy Ⅱ fluorescence and so on from recent information and progress report. Hence, the recovered spectrum of SHS also depends on its thermal-vacuum environment. Thermal-vacuum environment adaptability is one of the key performances for hyper-spectral instrument, and SHS should provide high spectral stability especially for space detection of atmospheric trace gases. In this case, the spectral band spans 757 nm~771 nm with a spectral resolution of ~ 0.03 nm, even though an extended source (extent of ~73 mrad, entrance diameter of 21 mm) is used. This channel for Oxygen (O2) measurements is intended to investigate influence on Carbon Dioxide (CO2) column abundance including atmospheric parameters and surface height. Based on the research of the spatial heterodyne interference principle, simulation test in thermal-vacuum environment and quantitative analyses are carried out. The relationship between environmental changes and the divergence half-angle of collimating lens, Littrow wavelength of field widened interferometer, different defocusing amounts and pantograph ratio of imaging lens are analyzed. With low thermal expansion coefficient of 5.7×10-7/K and high thermal refraction index of 9.2×10-6/K, Fused Silica is well suited for grating substrates with high groove density, but it is not necessarily the best choice for beamsplliter and field widened wedge. In order to verify the theoretical analyses and determine if SHS performance would achieve its science goals, thermal-vacuum experiment by CS-800 and integrating sphere light source is performed at Key Laboratory of Optical Calibration and Characterization (KLOCC) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). The results, especially for relationship between recovered spectral profiles and different out-of-focus amounts due to optical degradation of interferogram modulation in the harsh space environment, show that the relative spectral intensity deviation and spectral profile are matched with theoretical analysis, and spectral stability is less than ±0.01 nm under the temperature from 19 ℃ to 21.2 ℃ by the substrates made of Fused Silica (Corning 7980 0F). Quantitative analysis provides theoretical basis for the thermal control requirement and Littrow wavelength selection in normal atmospheric pressure. SHS is well suited for low light and high spectral resolution detection, but active thermal controller, calibration and correction under on-orbit conditions are necessary for space applicaitions.
-

-
表 1 监测仪的O2-A波段光谱仪设计参数.
Table 1. Design specifications of SHS for O2-A waveband.
No. Aspect Attribute Design (Temperature: 20 ℃, 1ATM) 1 Functional unit Narrow band filter 759 nm~769 nm full width at half maximum Collimating lens Entrance diameter 21 mm; IFOV 73 mrad Imaging lens 6-element relay system Detector 1024×1024, 13 µm×13 µm CCD 2 Interferometer Gratings Clear aperture 22.12 mm×22.12 mm; 600 gr/mm;
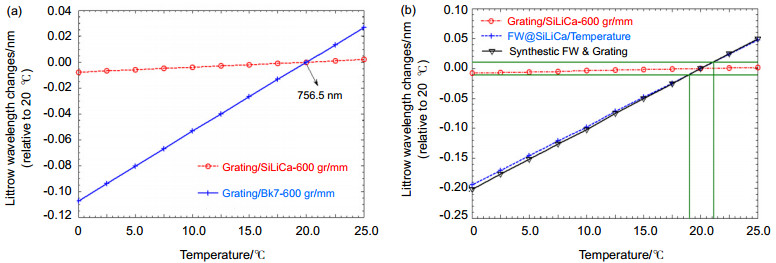
Littrow wavelength 756.5 nm; Substrates material SiLiCaField-widening prisms Wedge angle 17.0736°; Incident angle 12.4657°; Material SiLiCa Beam splitter Clear aperture 35 mm×35 mm 3 Performance Spectral resolution 0.6 cm-1@756.5 nm Achieved spectral range Filter limited 表 2 中继准直镜头出射发散半角.
Table 2. Divergence half-angles of the relay collimating lens.
No. Pressure, Temperature Divegence half-angle 1 1 ATM, 30 ℃ 1.9829° 2 1 ATM, 25 ℃ 1.9859° 3 1 ATM, 20 ℃ 1.9890° 4 1 ATM, 15 ℃ 1.9918° 5 1 ATM, 10 ℃ 1.9947° 6 0 ATM, 30 ℃ 1.9600° 7 0 ATM, 25 ℃ 1.9626° 8 0 ATM, 20 ℃ 1.9651° 9 0 ATM, 15 ℃ 1.9677° 10 0 ATM, 10 ℃ 1.9702° 表 3 不同光源类型对空间外差光谱仪性能的影响.
Table 3. The parameters of SHS used in different types of sources.
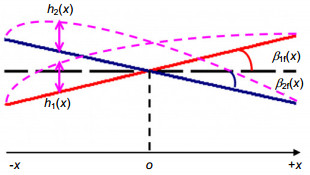
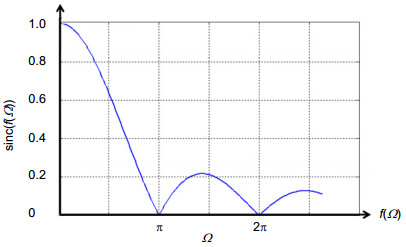
Source type Solid angle Modulation Fringe frequencey Littrow wavelength shift Point 0 1 $4(\sigma -{{\sigma }_{0}})\tan {{\theta }_{L}}$ 0 Extend $$\frac{2\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}{R}$$ ≥0.63 $4[\sigma (1-\frac{{{\Omega }_{m1}}}{4\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }})-{{\sigma }_{0}}]\tan {{\theta }_{L}}$ $$(1-\frac{{{\Omega }_{m1}}}{4\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }})\sigma $$ Field widened $$\frac{2\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}{R}\frac{\tan {{\theta }_{L}}}{C(n,\gamma )}$$ ≥0.63 $4[\sigma (1-\frac{{{\Omega }_{m1}}C(n,\gamma )}{2\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }\tan {{\theta }_{L}}})-{{\sigma }_{0}}]\tan {{\theta }_{L}}$ $$(1-\frac{{{\Omega }_{m1}}C(n,\gamma )}{2\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }\tan {{\theta }_{L}}})\sigma $$ -
[1] Harlander J M. Spatial heterodyne spectroscopy: interferometric performance at any wavelength without scanning[D]. USA: University of Wisconsin-Madison, 1991.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/259014093_Spatial_Heterodyne_Spectroscopy_Interferometric_Performance_at_any_Wavelength_Without_Scanning [2] Smith B W, Harlander J M. Imaging spatial heterodyne spec-troscopy: theory and practice[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1999, 3698: 925–931. doi: 10.1117/12.354497
[3] Harlander J M, Roesler F L, Cardon J G, et al. SHIMMER: a spatial heterodyne spectrometer for remote sensing of Earth's middle atmosphere[J]. Applied Optics, 2002, 41(7): 1343–1352. doi: 10.1364/AO.41.001343
[4] Englert C R, Stevens M H, Siskind D E, et al. Spatial hetero-dyne imager for mesospheric radicals on STPSat-1[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2010, 115(D20): D20306. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/253039376_Validation_of_Aura_MLS_HOx_measurements_with_remote-sensing_balloon_instruments
[5] Lin Yunlong, Shepherd G, Solheim B, et al. Introduction to spatial heterodyne observations of water (SHOW) project and its instrument development[C]. ITSC-ⅩⅣ Proceedings, Beijing, China, 2005.
https://cimss.ssec.wisc.edu/itwg/itsc/itsc14/proceedings/B48_Lin.pdf [6] Doe R A, Watchorn S. Climate-monitoring CubeSat mission (CM2): a project for global mesopause temperature sensing[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2011, 8153: 81530Q. doi: 10.1117/12.894460
[7] 施海亮, 熊伟, 邹铭敏, 等.空间外差光谱仪定标方法研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2010, 30(6): 1683–1687. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gpxygpfx201006052
Shi Hailiang, Xiong Wei, Zou Mingmin, et al. Study on calibra-tion method of spatial heterodyne spectrometer[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2010, 30(6): 1683–1687. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gpxygpfx201006052
[8] 罗海燕, 施海亮, 李双, 等.空间外差光谱仪干涉仪组件的容差分析[J].光学学报, 2014, 34(3): 0330002. http://www.opticsjournal.net/abstract.htm?id=OJ140226000141dKgNjP
Luo Haiyan, Shi Hailiang, Li Shuang, et al. Study on the performance indexes of spatial heterodyne spectrometer influenced by elements tolerances[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2014, 34(3): 0330002. http://www.opticsjournal.net/abstract.htm?id=OJ140226000141dKgNjP
[9] 施海亮, 李志伟, 罗海燕, 等.超光谱大气CO2监测仪光谱定标误差修正[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2016, 36(7): 2296–2299. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gpxygpfx201607056
Shi Hailiang, Li Zhiwei, Luo Haiyan, et al. Error correction of spectral calibration for hyper-spectral atmosphere CO2 monitoring instrument[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2016, 36(7): 2296–2299. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gpxygpfx201607056
[10] 叶擎昊, 施海亮, 熊伟.空间外差光谱仪数据盲元误差修正[J].光电工程, 2015, 42(12): 25–29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2015.12.005
Ye Qinghao, Shi Hailiang, Xiong Wei. Blind-data error correction of spatial heterodyne spectrometer[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2015, 42(12): 25–29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2015.12.005
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: