Saturation-to-hue mapping algorithm for improving the visibility of bleeding points under endoscopy
-
摘要
针对内窥镜手术中淹没性出血点可见性差影响止血操作时间的问题,提出了一种4LED照明结合饱和度-色调映射算法的出血点增强显示方法。该方法使用对粘膜组织和不同浓度血液成像具有特异性的4个窄带LED进行同步照明,以代替传统的氙灯光源实现彩色成像;然后在
xyY 颜色空间中,对彩色图像的饱和度信息进行拉伸后再向色调映射,进而有效提升淹没性出血点与出血点周围区域的色差。针对动物材料的硬镜体外实验结果表明,饱和度-色调映射成像(saturation-to-hue mapping imaging, SHMI)在出血点与出血点周围区域的色差明显大于常规白光图像(41.31>11.78),有效提高了淹没性出血点的可见性,可进一步降低内窥镜手术风险。Abstract
To address the poor visibility of submerged bleeding points during endoscopic surgery, which can extend hemostasis procedures, a method combining 4-LED illumination with a saturation-to-hue mapping algorithm is proposed for enhancing bleeding points visibility. With imaging specificity for tissue and blood of varying concentrations, four narrow-band LEDs synchronous lighting are used for imaging, replacing the conventional xenon light source. In the
xyY color space, the saturation information of the image is stretched and then mapped to the hue, effectively increasing the color differences between submerged bleeding points and the surrounding areas. Vitro experimental results using rigid endoscopes on animal materials demonstrate that the enhanced images achieved significantly higher color difference between bleeding points and their surroundings than conventional white-light images (41.31>11.78). Saturation-to-hue mapping imaging (SHMI) effectively improves the visibility of submerged bleeding points and reduces the risk associated with endoscopic surgeries.-
Key words:
- image enhancement /
- endoscopy /
- multispectral imaging /
- bleeding point detection
-
Overview
Overview: Bleeding frequently occurs during endoscopic procedures for diagnosis and surgery. The presence of blood can obstruct the endoscopic field of view, causing difficulty in detecting bleeding points. Excessive or frequent coagulation may lead to carbonation in the submucosal layer, which increases surgical difficulty and risk. Therefore, enhancing the visibility of the surgical field, and increasing the color difference between bleeding points and surroundings are clinically significant. To address the issue of poor visibility of submerged bleeding points during endoscopic surgery, a method combining 4-LED illumination with a saturation-to-hue mapping algorithm is proposed for enhancing bleeding points' visibility.
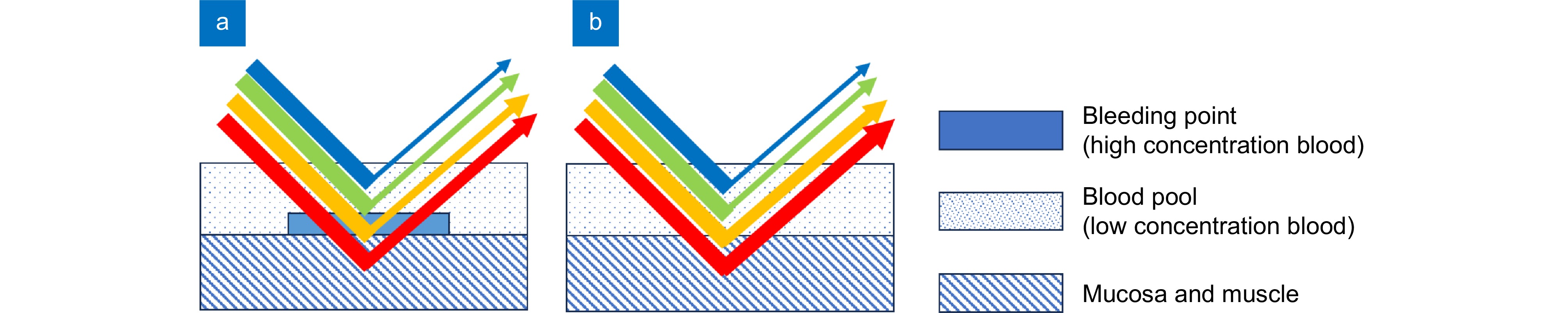
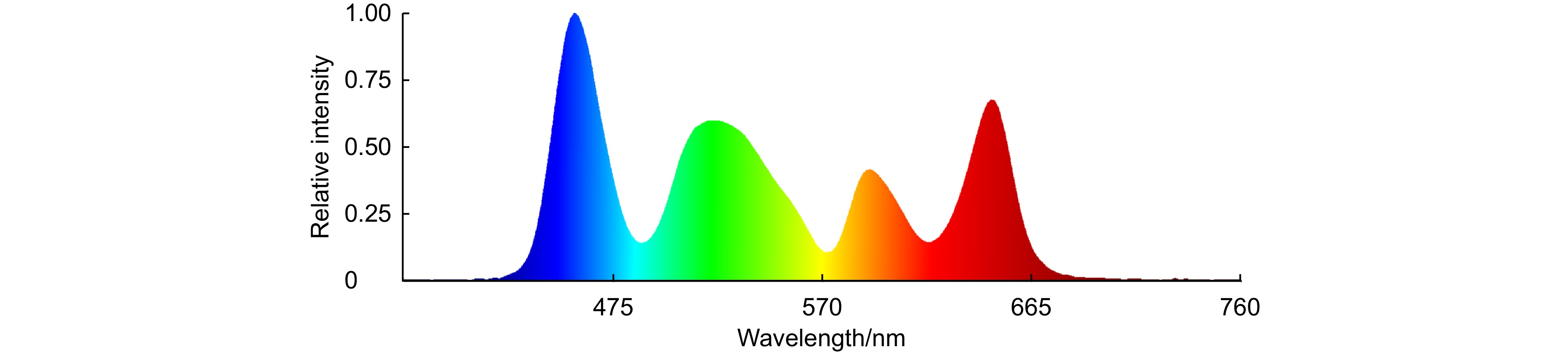
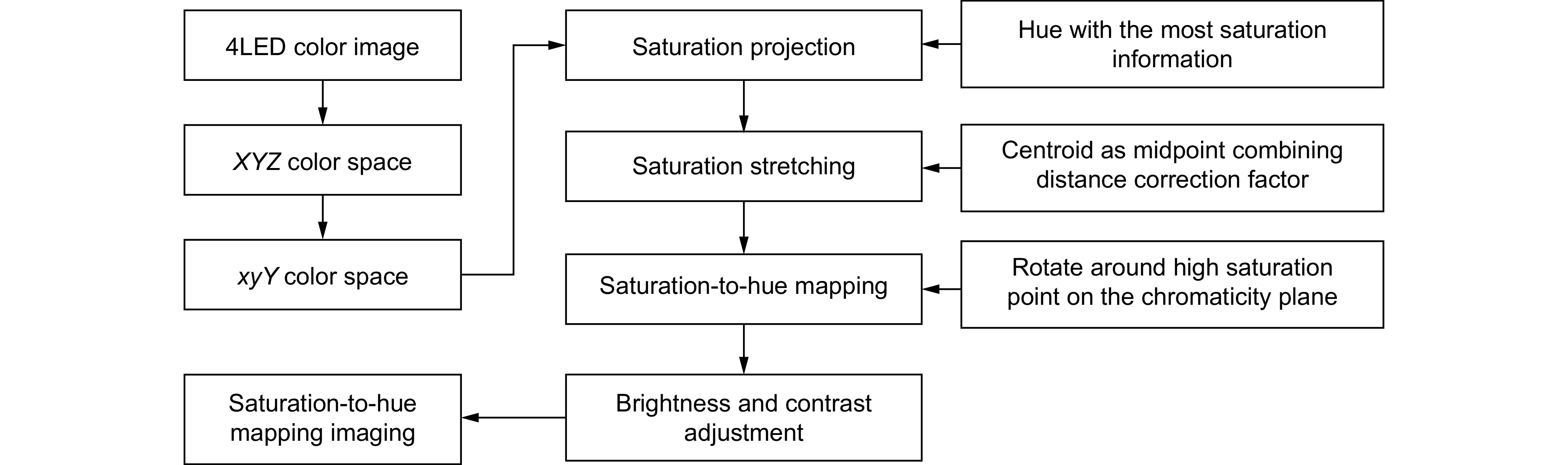
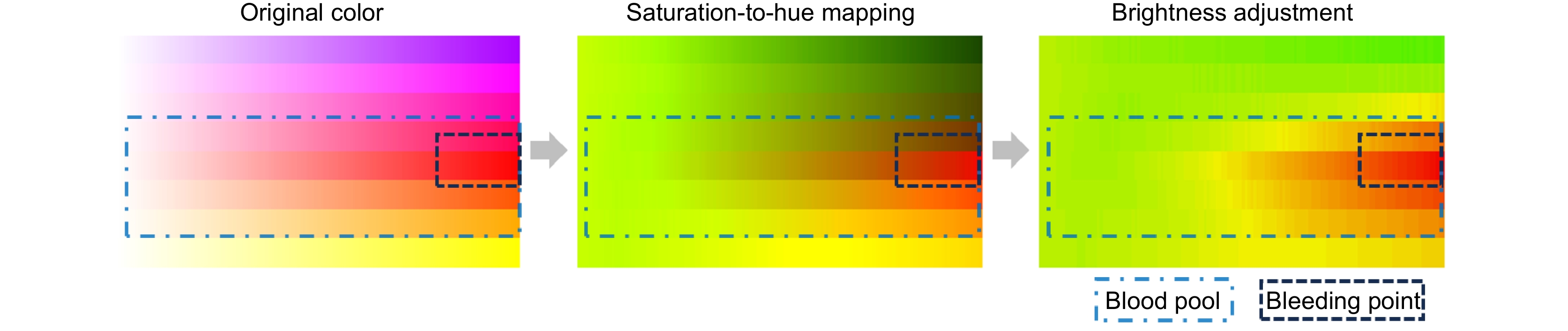
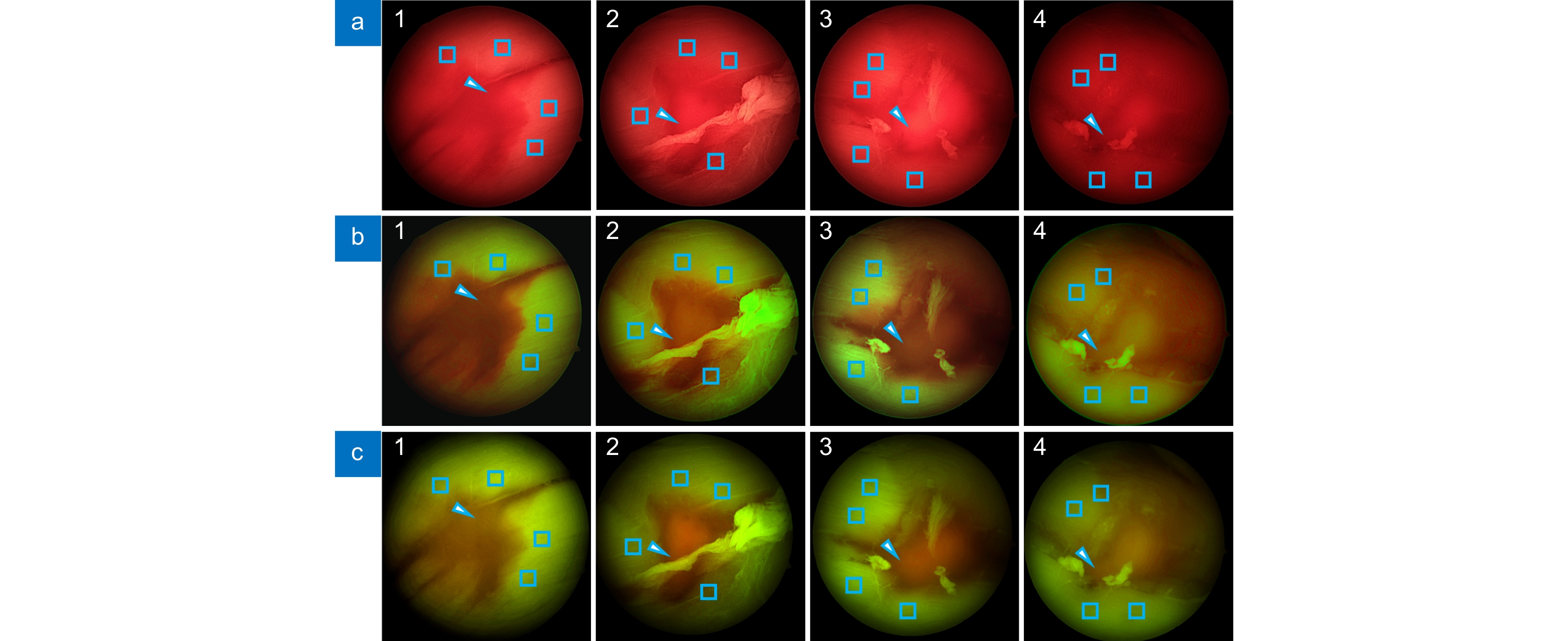
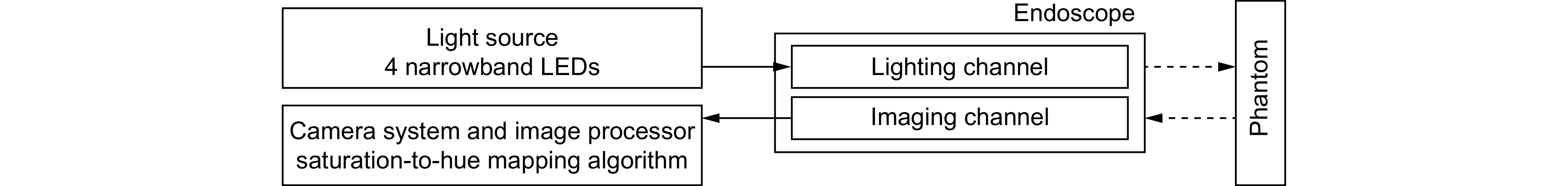
Based on imaging theory through multilayer tissue, four narrowband LEDs (450 nm, 520 nm, 590 nm, 650 nm) with specificity for imaging tissues and different concentrations of blood are used for synchronous illumination, replacing traditional xenon lamp light sources for imaging. This can capture more information about bleeding points through low-concentration blood. Then, in the xyY color space, the saturation information of the color image is stretched and mapped to hue. Combined with image brightness and contrast adjustment, the low-concentration blood areas are mapped to cyan-yellow, and the high-concentration bleeding points as orange-red, effectively improving the color difference between the submerged bleeding point and the surroundings. The need for specialized video camera systems or RDIver circuits for the light source is eliminated, and the issues of color fringing and image misalignment associated with separate narrowband illumination are avoided.
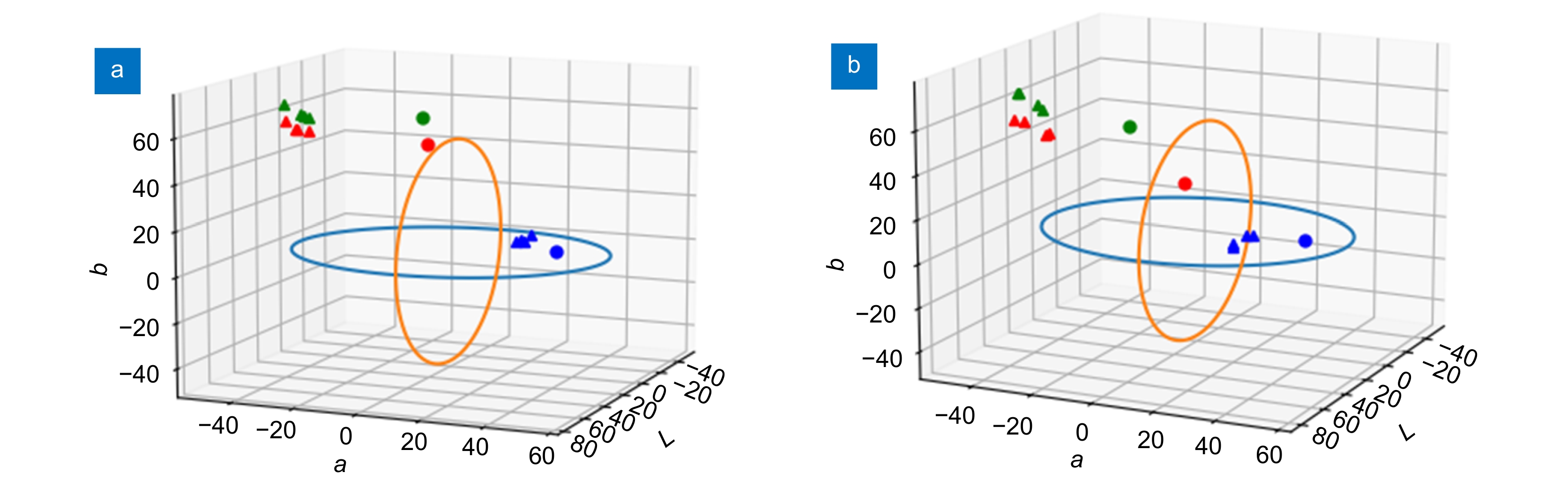
The sample set is derived from in vitro experiments conducted with phantoms crafted from animal materials. Regarding the experimental equipment, rigid endoscopes are used for in vitro experimentation, and the complementary apparatus includes a 4K endoscope camera system and a 5-LED medical endoscope cold light source. After enhancing the phantom images, the color difference between the bleeding points and their surrounding areas is significantly higher than that in conventional white light images (41.31 > 11.78). Paired Student's t-test was conducted to compare the enhanced images with the white light images, and the statistical significance score is less than 0.01. This effectively improves the visibility of submerged bleeding points, further reducing the risks associated with endoscopic surgeries.
-

-
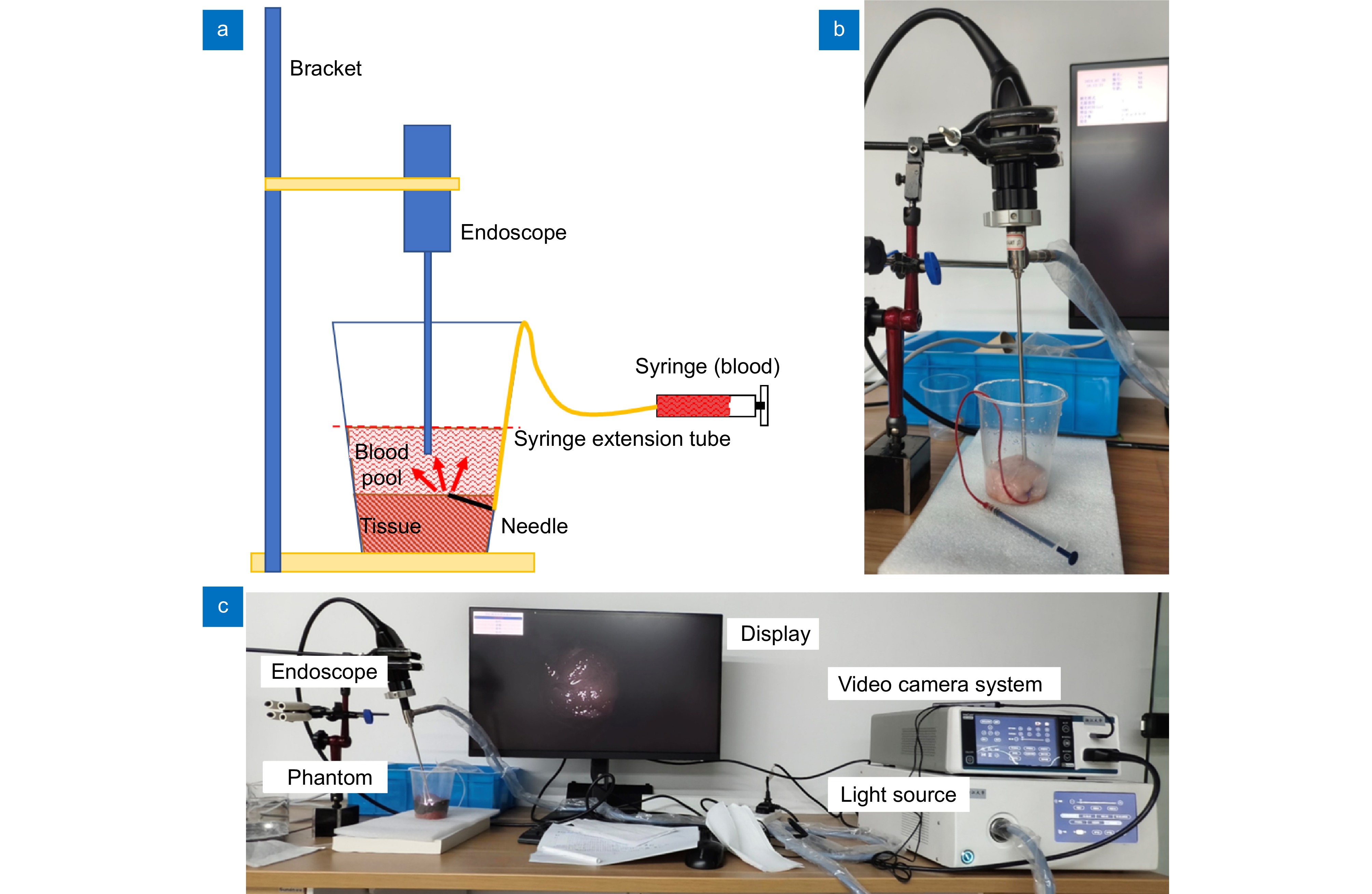
图 6 实验装置示意图与实物图。(a)实验装置示意图;(b)内窥镜与仿体实际结构;(c)实验系统图,包括视频摄像系统、光源、显示屏、内窥镜、仿体
Figure 6. Schematic and actual views of the experimental setup. (a) Schematic of experimental setup; (b) Actual structure of the endoscope and phantom; (c) Experimental system diagram including the video camera system, light source, display, endoscope, and phantom
表 1 不同情况下的色差统计数据(数据为平均值)
Table 1. Color difference statistics in different situations (data is average)
Lighting type
Image groupa b c $ \Delta E $ $ p $ $ \Delta E $ $ p $ $ \Delta E $ $ p$ 1 (0.68%) 17.50 — 53.00 <0.01 30.75 <0.01 2 (0.72%) 10.75 — 35.75 0.011 34.00 <0.01 3 (1.16%) 6.00 — 49.50 <0.01 43.50 <0.01 4 (2.04%) 4.75 — 21.16 <0.01 23.16 <0.01 表 2 不同图像的颜色差异
Table 2. Color differences between different images
lmage $ \Delta E $ $ p$ WLI 11.78±7.57 — SHMI 41.31±25.54 <0.01 RDI 42.11±15.11 <0.01 表 3 不同血池浓度的图像增强效果比较
Table 3. Comparison of image enhancement effects with different blood pool concentrations
Blood pool concentration Number of groups SHMI > RDI SHMI ≈ RDI (<5%) SHMI < RDI Total Low (c<0.9%) 12 4 1 17 Medium (0.9%<c<1.8%) 7 5 4 16 High (c>1.8%) 2 1 11 14 Total 21 10 16 47 表 4 中低血池浓度的31组增强图像和白光图像的颜色差异
Table 4. Color differences between 31 sets of enhanced images and white light images with low to medium blood pool concentrations
lmage $ \Delta E $ $ p$ WLI 14.29±4.44 — SHMI 51.64±13.60 <0.01 RDI 47.66±10.69 <0.01 -
参考文献
[1] Fakhr Abdollahi A, Shaheed M H, Thaha M A, et al. A review of modeling and control of remote-controlled capsule endoscopes[J]. Expert Rev Med Devices, 2024, 21(4): 293−306. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2024.2336135
[2] Wu G X, Zhu R Z, Lu Y Q, et al. Optical scanning endoscope via a single multimode optical fiber[J]. Opto-Electron Sci, 2024, 3(3): 230041. doi: 10.29026/oes.2024.230041
[3] Uchima H, Yao K S. Endoscopic microanatomy of the normal gastrointestinal mucosa with narrow band technology and magnification[J]. Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 42(2): 117−126. doi: 10.1016/j.gastre.2019.02.006
[4] Abraham E, Zhou J X, Liu Z W. Speckle structured illumination endoscopy with enhanced resolution at wide field of view and depth of field[J]. Opto-Electron Adv, 2023, 6(7): 220163. doi: 10.29026/oea.2023.220163
[5] 王双园, 姚志远, 张玉荣, 等. 一种多层线性融合的内窥镜图像增强算法[J]. 光电工程, 2024, 51(6): 240063. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.240063
Wang S Y, Yao Z Y, Zhang Y R, et al. A multilayer linear fusion algorithm for endoscopic image enhancement[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2024, 51(6): 240063. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.240063
[6] Utsunomiya H, Akazawa Y, Ueyama H, et al. Gastric juvenile polyposis with intramucosal cancer diagnosed by magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging[J]. Intern Med, 2023, 62(22): 3333−3339. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1612-23
[7] 姜鸿鹏, 章科建, 袁波, 等. 一种血管内窥镜图像增强算法[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(1): 180167. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180167
Jiang H P, Zhang K J, Yuan B, et al. A vascular enhancement algorithm for endoscope image[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2019, 46(1): 180167. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180167
[8] 王强, 陶沛, 袁波, 等. 多颜色空间的内窥镜图像血管增强方法[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(1): 190268. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190268
Wang Q, Tao P, Yuan B, et al. Vessel enhancement of endoscopic image based on multi-color space[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(1): 190268. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190268
[9] Moskalev A, Kalyagina N, Kozlikina E, et al. Validation of a white light and fluorescence augmented panoramic endoscopic imaging system on a bimodal bladder wall experimental model[J]. Photonics, 2024, 11(6): 514. doi: 10.3390/photonics11060514
[10] Yang C H, Qiu Y, Li X, et al. Bleeding after endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric lesions[J]. J Dig Dis, 2020, 21(3): 139−146. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12850
[11] Funasaka K, Miyahara R, Horiguchi N, et al. Novel image enhancement technology that helps find bleeding points during endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric neoplasms[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 37(10): 1955−1962. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15975
[12] Oka K, Iwai N, Okuda T, et al. Red dichromatic imaging improves visibility of bleeding during gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 8560. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35564-z
[13] Furuichi Y, Abe M, Takeuchi H, et al. Red dichromatic imaging reduces endoscopic treatment time of esophageal varices by increasing bleeding point visibility (with video)[J]. Dig Endosc, 2022, 34(1): 87−95. doi: 10.1111/den.14011
[14] Takahashi J, Hirota M, Morita Y. Endoscope apparatus, operating method of endoscope apparatus, and information storage medium: 20210401268[P]. 2021-12-30.
[15] Smucker M D, Allan J, Carterette B. Agreement among statistical significance tests for information retrieval evaluation at varying sample sizes[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd international ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Boston, 2009: 630–631. https://doi.org/10.1145/1571941.1572050.
[16] Mokrzycki W S, Tatol M. Colour difference ΔE - a survey[J]. Mach Graph Vis Int J, 2011, 20(4): 383−411.
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: