-
摘要:
在激光雷达系统设计中,光学系统的优化与设计是一个重要的研究方向,本文利用衍射光学元件(DOE)的设计自由度高和色散大等优势,将DOE用于激光雷达接收端,同时实现聚焦和滤光作用,降低了光学系统复杂度。本文基于DOE的原理,仿真分析了DOE的光学特性,并且以DOE作为激光雷达的光学接收端,完成了激光雷达测距实验,证明了DOE同时具有聚焦作用和窄带滤光作用,实验结果与仿真基本一致。本文利用DOE在激光雷达中的优势,实现激光雷达的轻量化、集成化和高效化。
Abstract:The optimization and design of optical systems is an important research direction in LiDAR. In this paper, the advantages of diffractive optical elements (DOE), such as high design degree of freedom and large dispersion, are used in the receiving end of LiDAR. The focusing and filtering effects are realized at the same time, which reduces the complexity of the optical system. Based on the principle of diffractive optical elements, the optical characteristics of diffractive optical elements are simulated and analyzed. The LiDAR ranging experiment is completed by using the diffractive optical element as the optical receiving end of the LiDAR. It proved that the diffractive optical elements have both a focusing effect and a narrow-band filtering effect. The experimental results are basically consistent with the simulation. Using the advantages of diffractive optical elements in LiDAR, the lightweight, integration, and high efficiency of LiDAR can be realized.
-
Key words:
- LiDAR /
- diffractive optical element /
- lightweight /
- filtration
-
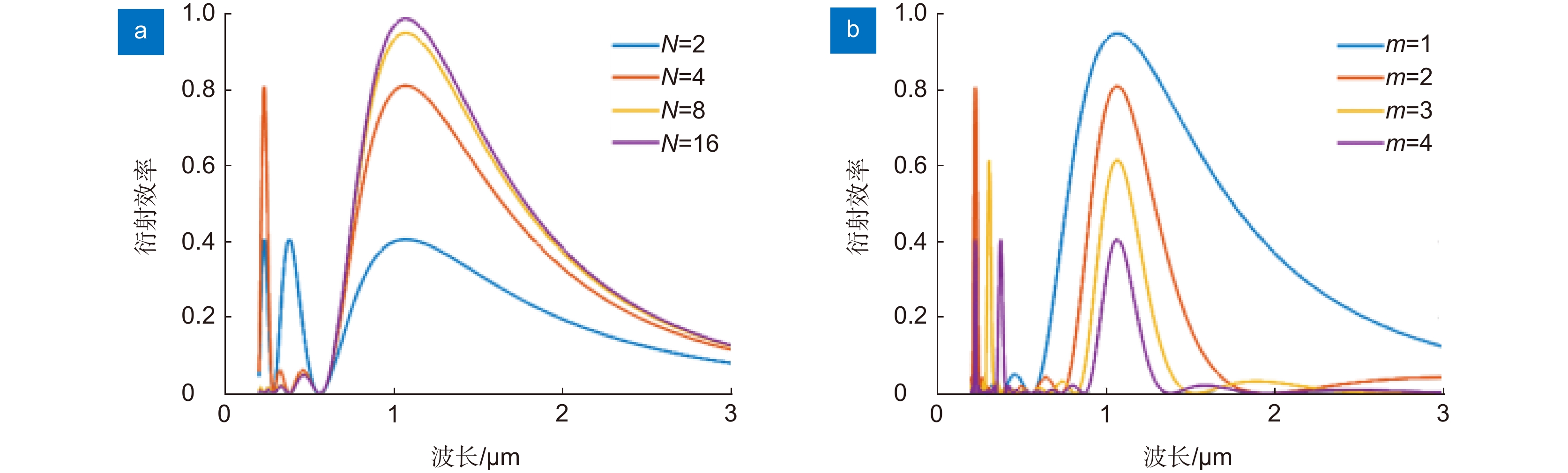
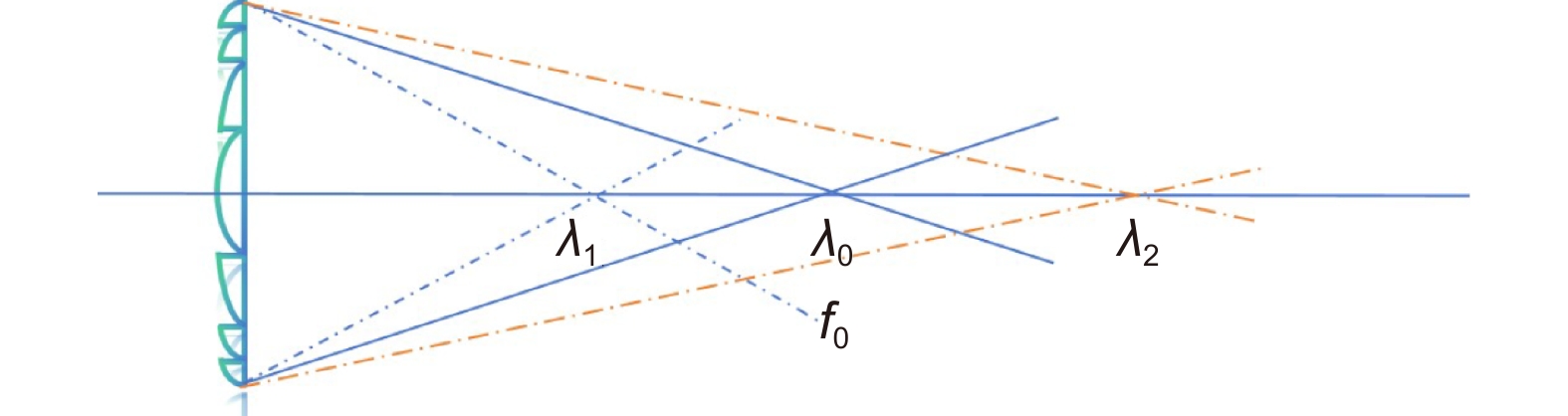
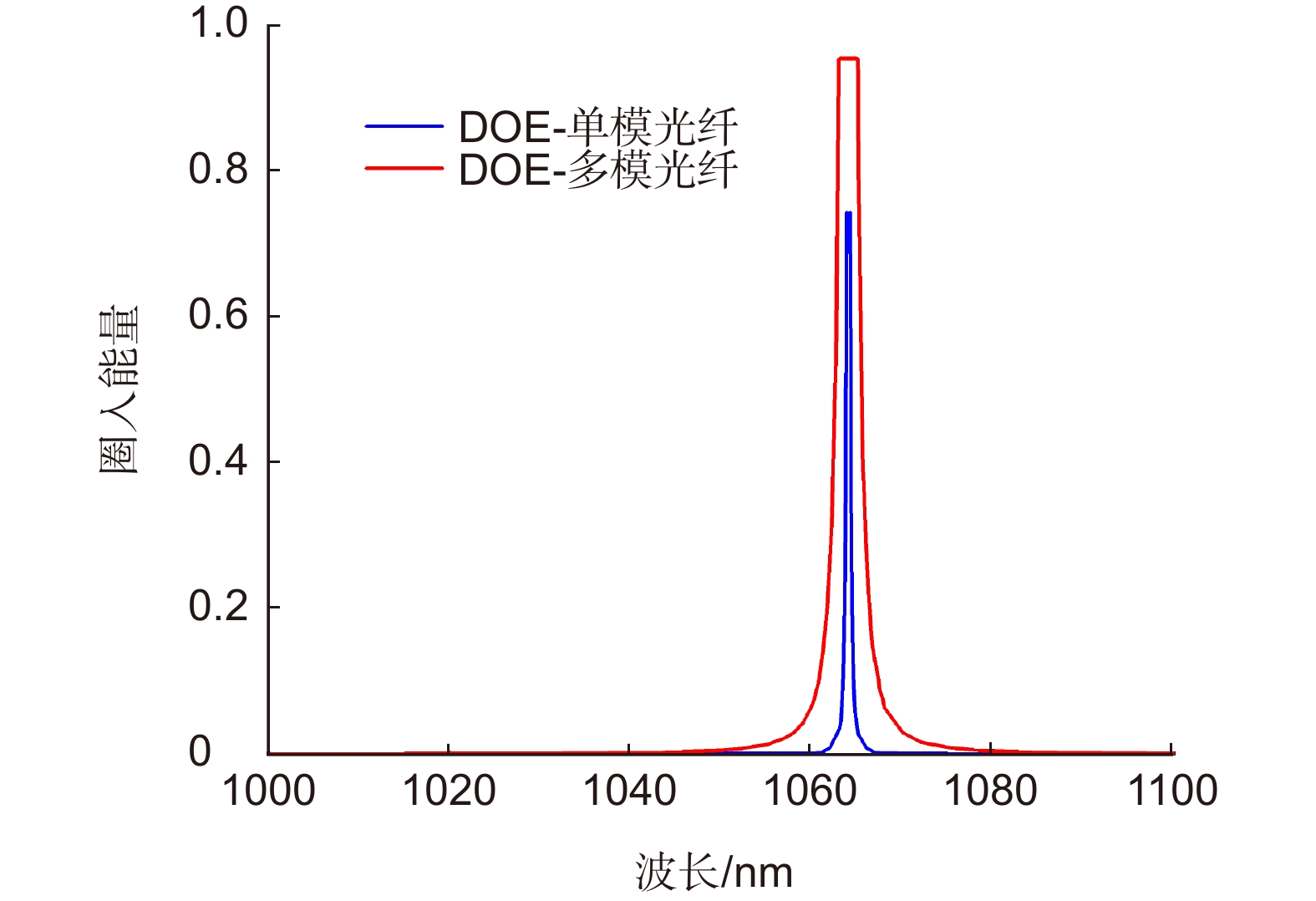
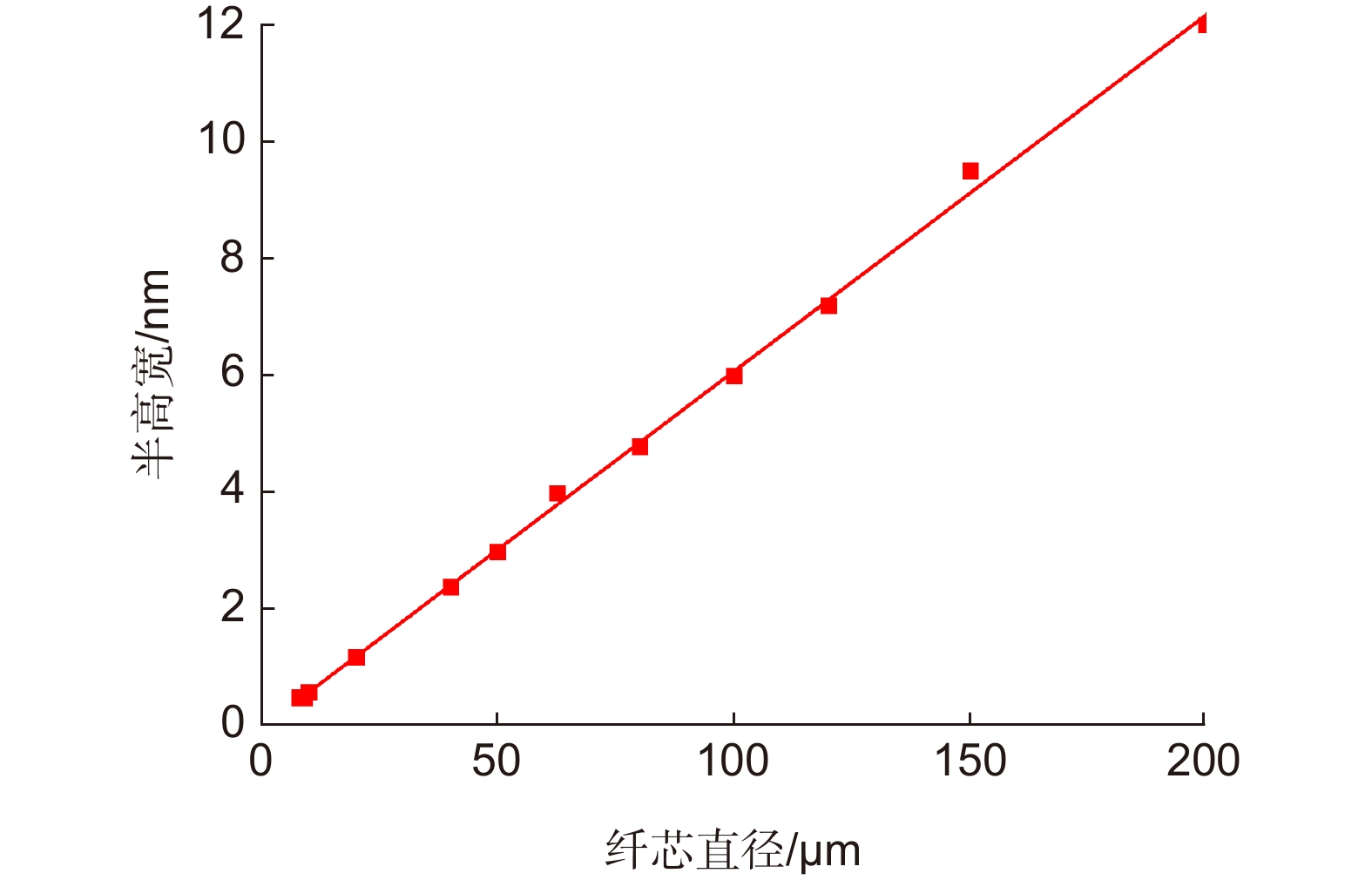
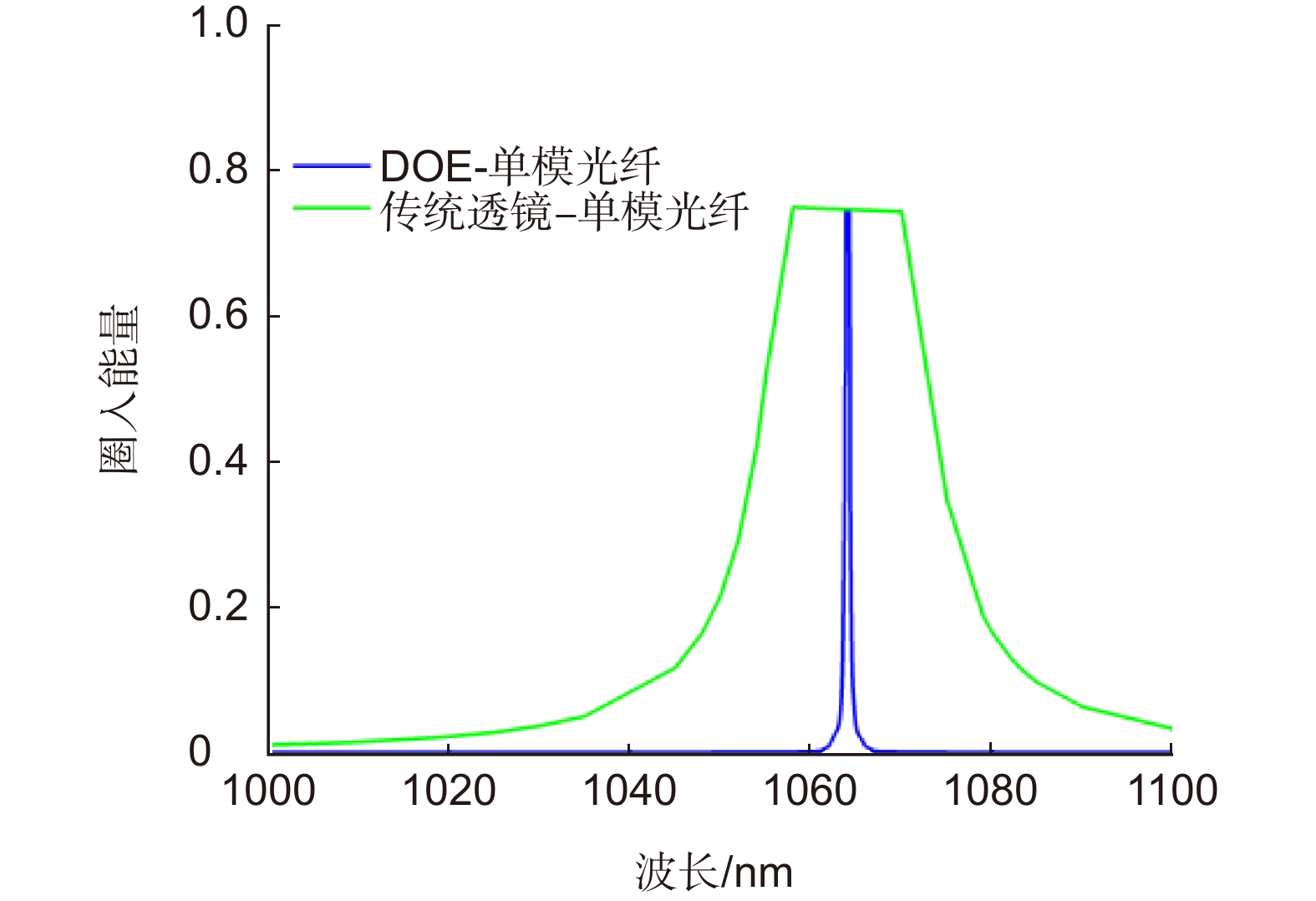
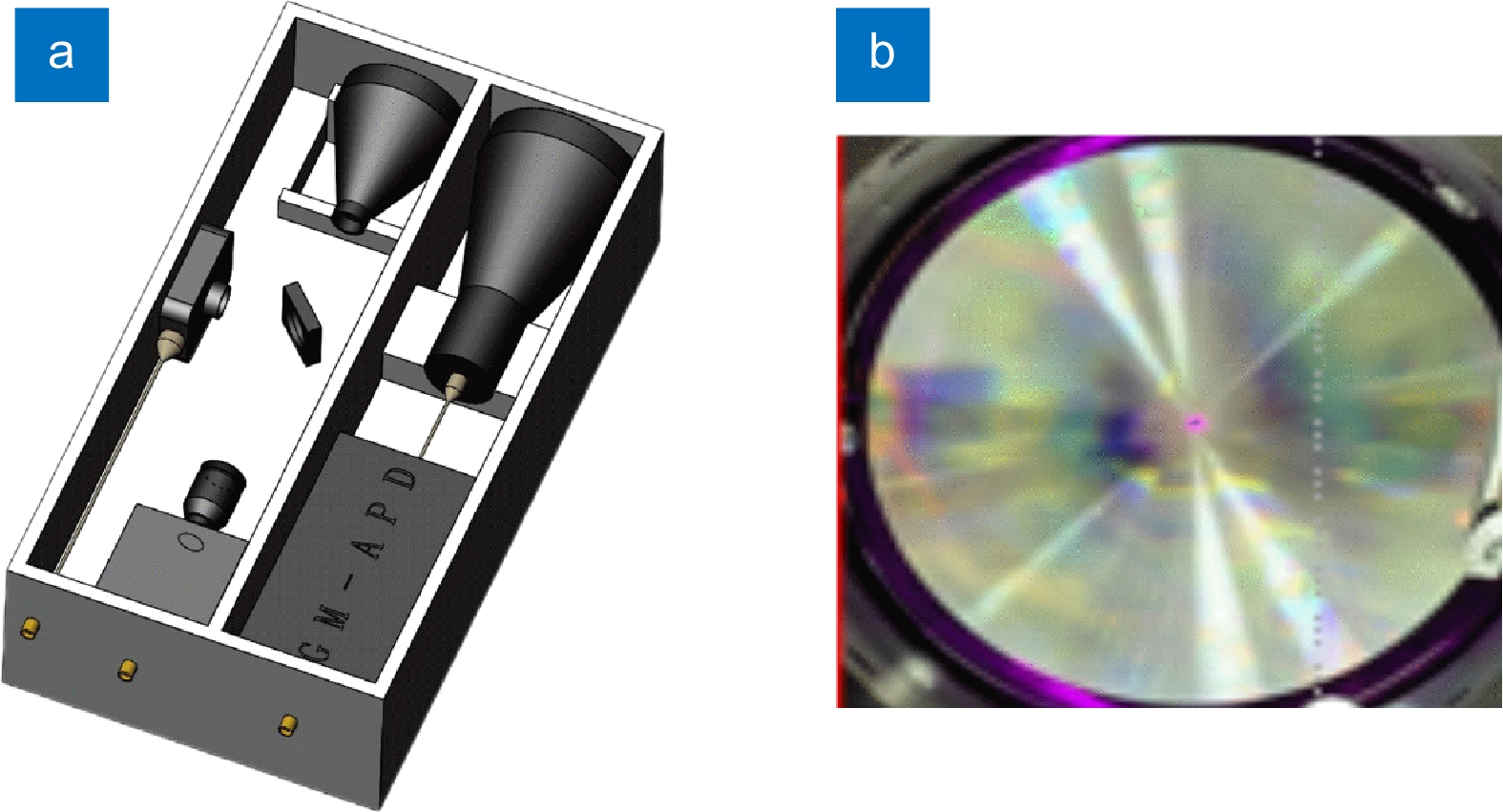
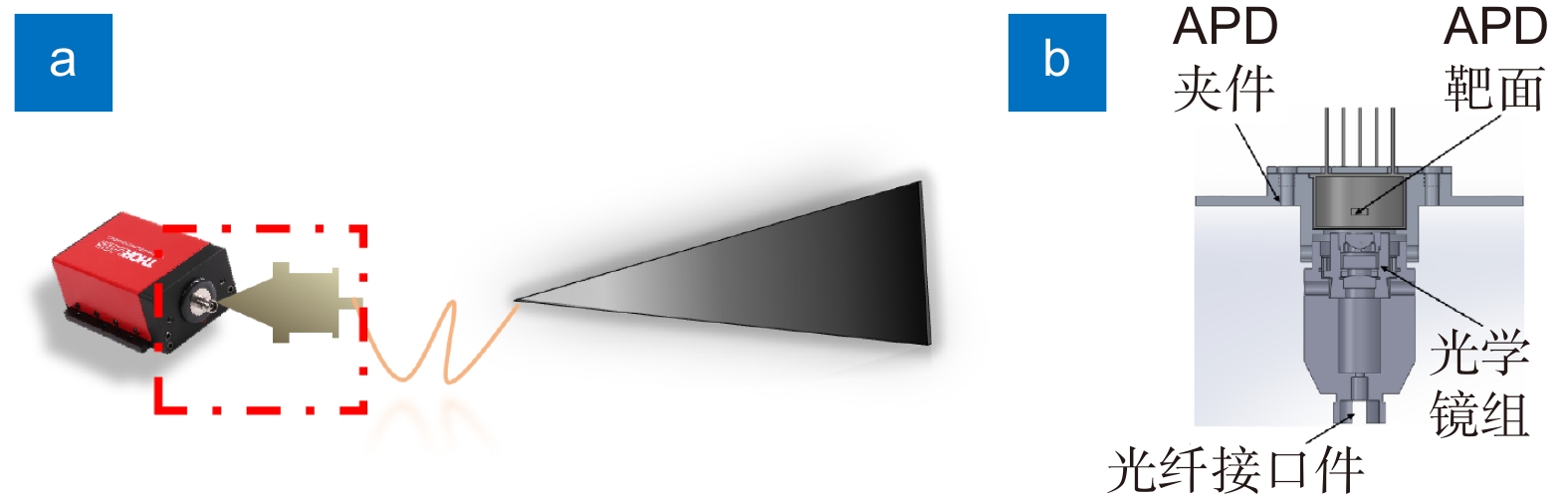
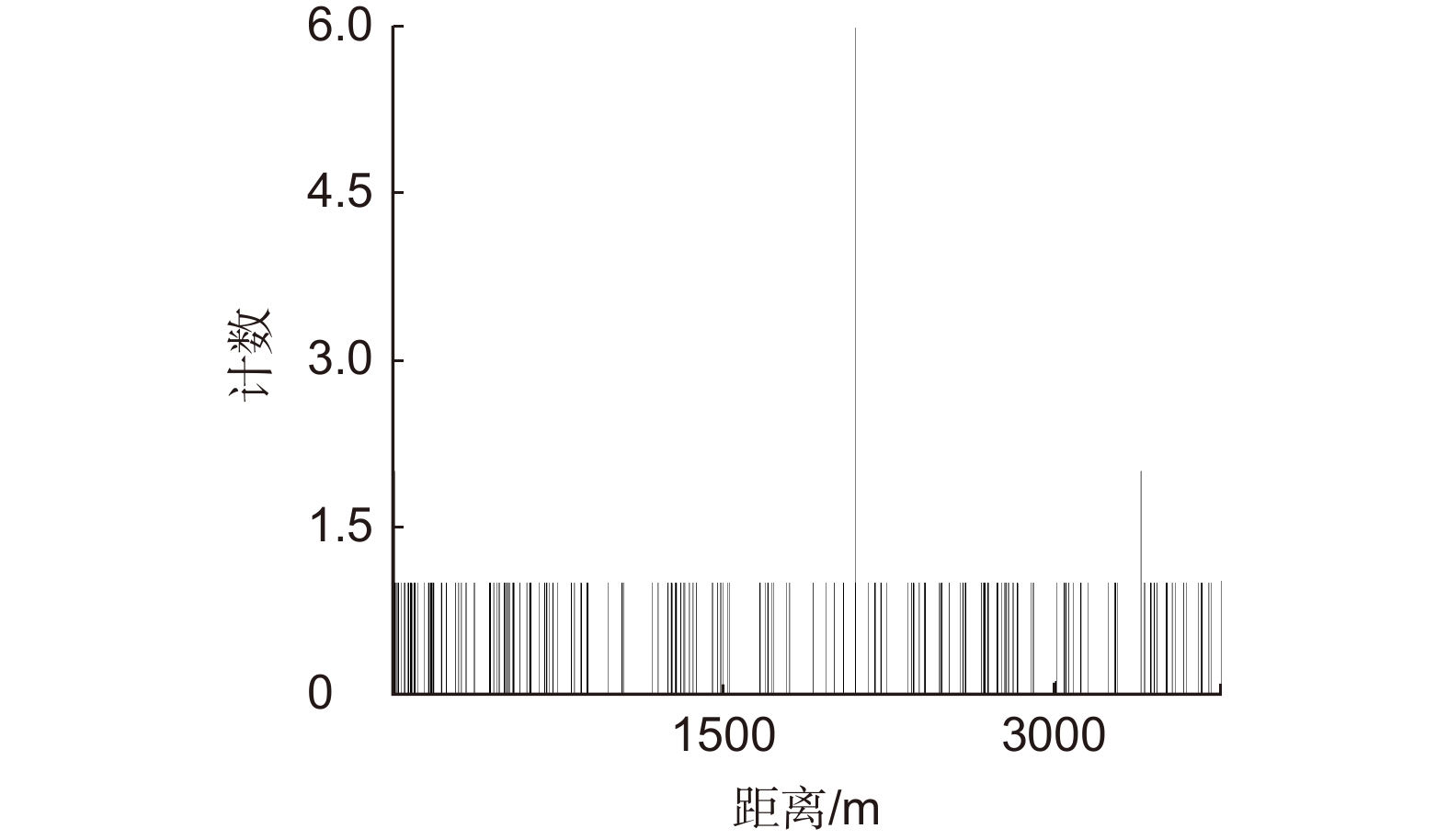
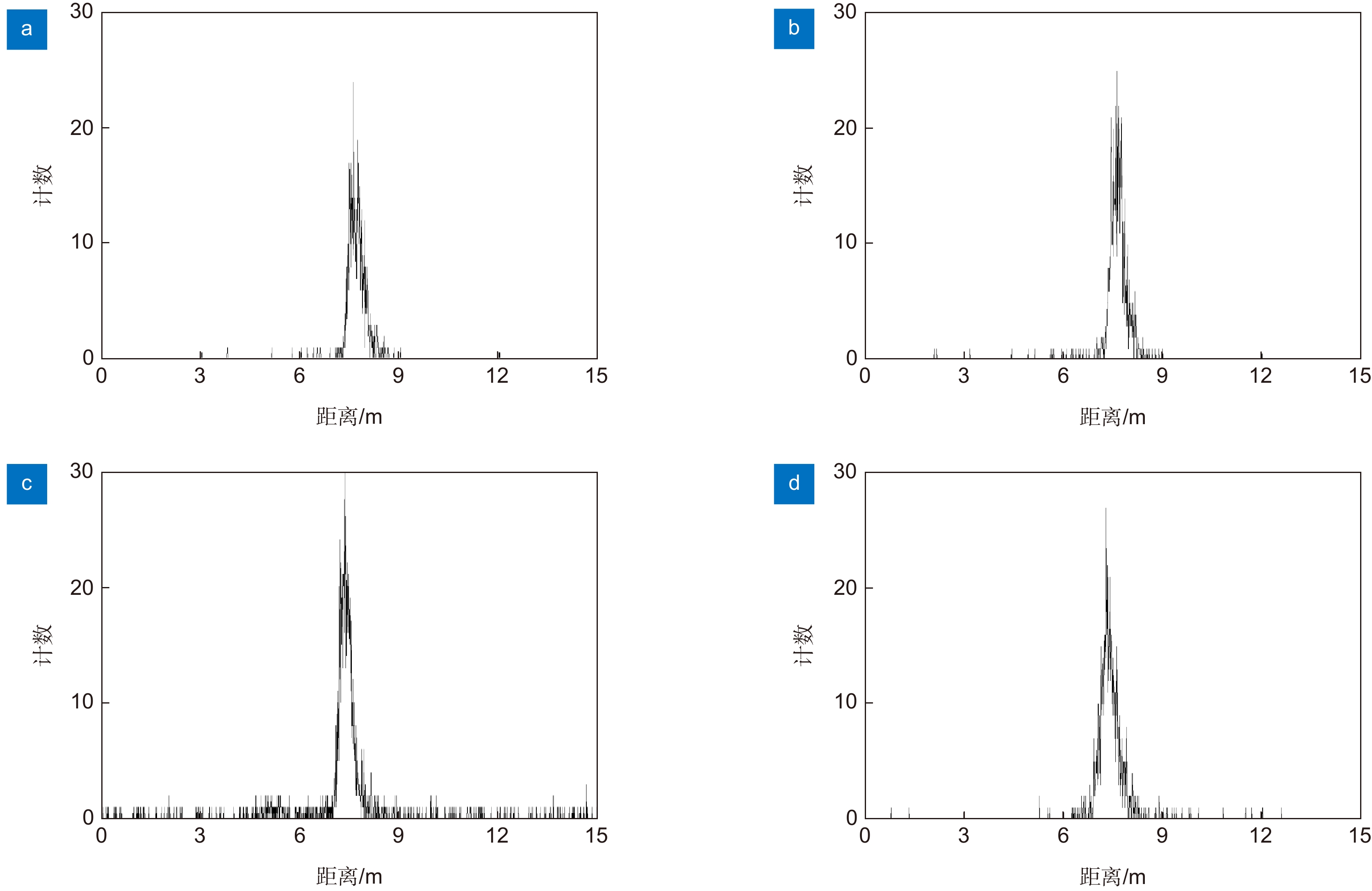
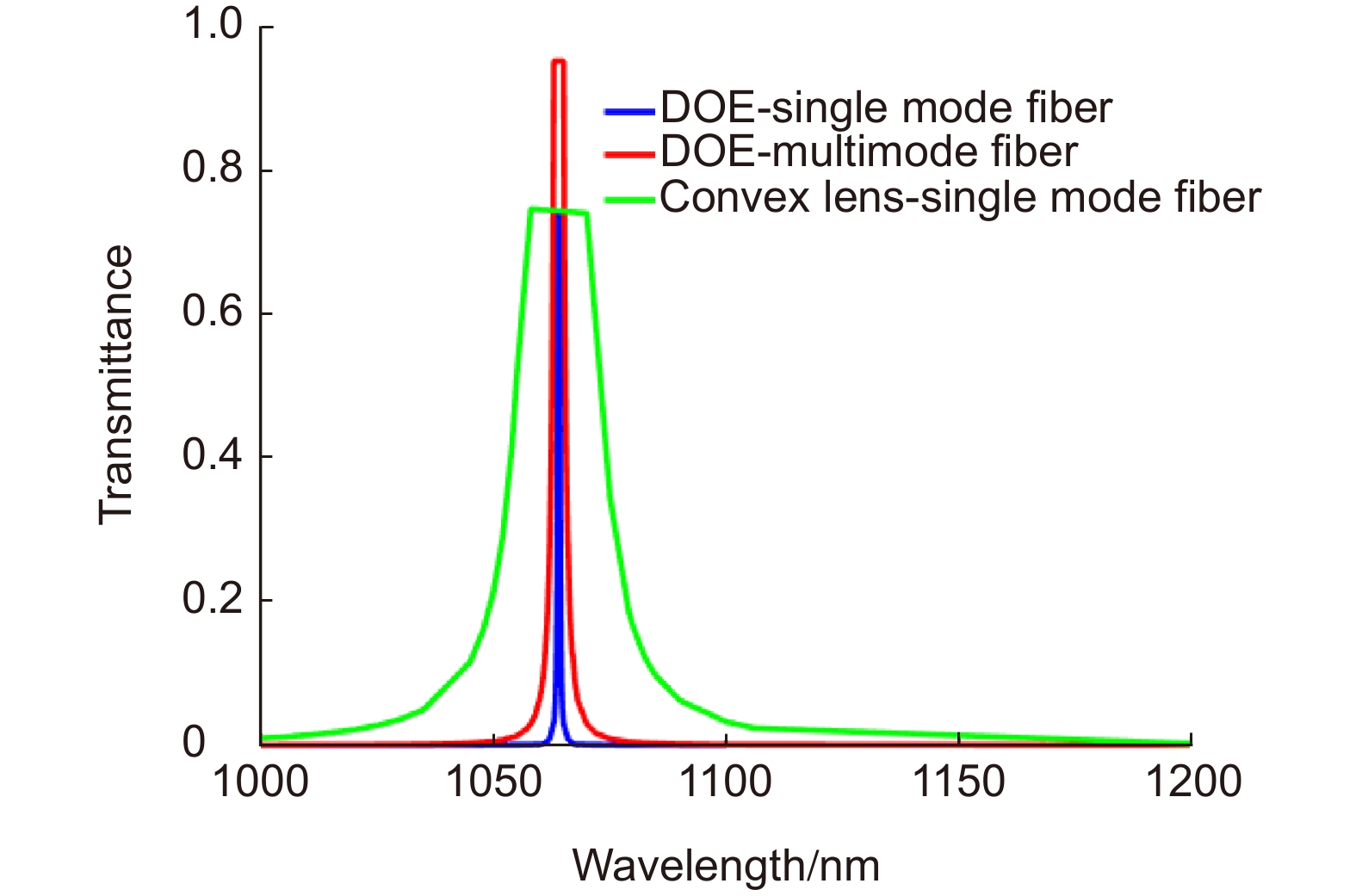
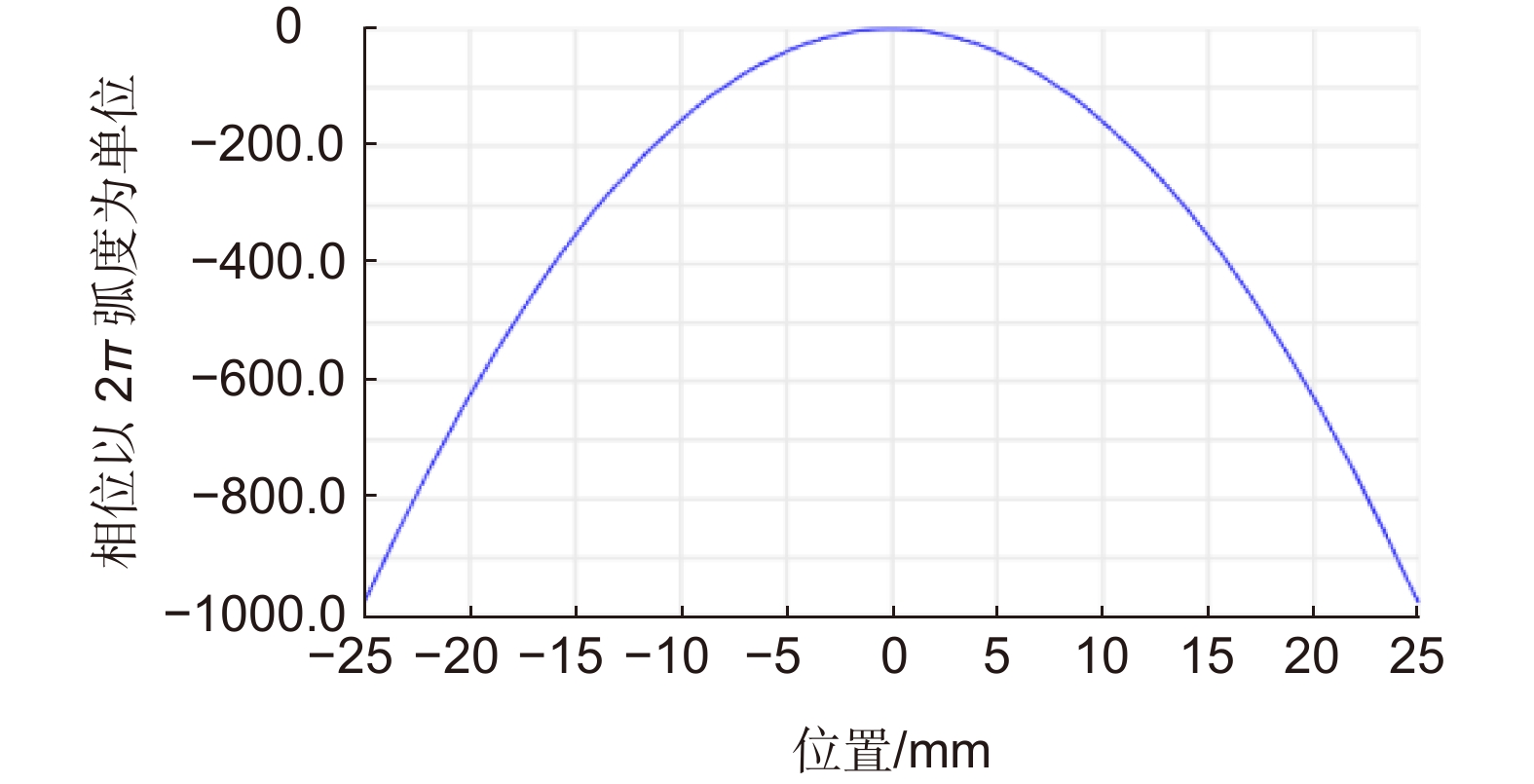
Overview: LiDAR is an advanced active detection system that combines laser technology and photoelectric detection technology, which can obtain the three-dimensional spatial information of the target quickly and accurately and is widely used in civil, aerospace, and military fields such as autonomous driving, space rendezvous, and docking, target recognition and so on. The design and optimization of optical systems is an important research direction for LiDAR systems. The traditional LiDAR receiver generally uses a set of lenses and filters (such as an interference filter, dispersion filter, etc) to achieve the focusing and filtering functions of the echo energy. The two are independent devices, which increases the complexity of the system. In contrast, the diffractive optical element (DOE) uses micro-nano processing technology to etch relief structure on the substrate to achieve phase control and has the advantages of lightweight and large dispersion, which can be introduced into the LiDAR receiver to achieve focusing and filtering functions at the same time. In this paper, the characteristics of DOE at the receiving end of LiDAR are analyzed and tested. Firstly, we simulate the filtering characteristics of the combination of DOE and fiber, and the formula between the fiber core diameter and the filter bandwidth is given, that the smaller the diameter of the fiber core, the better the filtering effect. For example, the equivalent bandwidth of the fiber with 10 μm core diameter combined with DOE is 0.6 nm and the 200 μm core diameter is 12 nm. Secondly, a LiDAR ranging system based on DOE receiving was set up, with 1064 nm designed wavelength, 50 mm aperture, and 300 mm focal length. The system successfully measures the range of the 2.1 km target outside the experimental platform. Finally, the filtering ability of DOE was tested by using single mode fiber with 10 μm core diameter and multimode fiber with 200 μm core diameter respectively. Through comparative experiments, it is verified that the DOE is applied to the LiDAR receiver to achieve focusing, and it also has a narrow-band filtering effect to suppress noise when combined with the fiber, which is consistent with the simulation. In summary, the advantages of DOE in LiDAR are used to realize the lightweight, integration, and high efficiency of LiDAR.
-

-
表 1 系统参数
Table 1. System parameter
系统参数 参数名称 值 系统发射端 激光波长($\lambda $) 1064 nm 激光脉冲宽度(${T_t}$) 10.00 ns 激光发散角(${\theta _{1/e}}$) 7.000 mrad 光学系统发射效率(${\eta _t}$) 50.00% 系统接收端 DOE口径(${D_{{\rm{DOE}}}}$) 50.00 mm 光学系统接收效率(${\eta _{\rm{r}}}$) 78.00% SPAD探测效率(${\eta _{{\rm{qe}}}}$) 2.800% SPAD死时间(${t_{\rm{d}}}$) 41.30 ns -
[1] Gargoum S, El-Basyouny K. Automated extraction of road features using LiDAR data: a review of LiDAR applications in transportation[C]//2017 4th International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety (ICTIS), Banff, AB, Canada, 2017: 563–574. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTIS.2017.8047822.
[2] Dassot M, Constant T, Fournier M. The use of terrestrial LiDAR technology in forest science: application fields, benefits and challenges[J]. Ann For Sci, 2011, 68(5): 959−974. doi: 10.1007/s13595-011-0102-2
[3] Rivera G, Porras R, Florencia R, et al. LiDAR applications in precision agriculture for cultivating crops: a review of recent advances[J]. Comput Electron Agric, 2023, 207: 107737. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2023.107737
[4] 刘博, 于洋, 姜朔. 激光雷达探测及三维成像研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(7): 15−27. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.190167
Liu B, Yu Y, Jiang S. Review of advances in LiDAR detection and 3D imaging[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2019, 46(7): 15−27. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.190167
[5] 马愈昭, 张岩峰, 冯帅. 基于神经网络的侧向激光雷达信号去噪算法[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(6): 220341. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220341
Ma Y Z, Zhang Y F, Feng S. A denoising algorithm based on neural network for side-scatter lidar signal[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2023, 50(6): 220341. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220341
[6] 陈海平, 李萌阳, 曹庭分, 等. 基于激光雷达数据的火星表面障碍物识别[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(2): 220240. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220240
Chen H P, Li M Y, Cao T F, et al. Obstacle recognition on Mars surface based on LiDAR data[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2023, 50(2): 220240. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220240
[7] 闫德立, 高尚, 李韶华, 等. 基于激光雷达的道路不平度及可行驶区域检测[J]. 激光技术, 2022, 46(5): 624−629. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2022.05.007
Yan D L, Gao S, Li S H, et al. Detection of road roughness and drivable area based on LiDAR[J]. Laser Technol, 2022, 46(5): 624−629. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2022.05.007
[8] Jaboyedoff M, Oppikofer T, Abellán A, et al. Use of LIDAR in landslide investigations: a review[J]. Nat Hazards, 2012, 61(1): 5−28. doi: 10.1007/s11069-010-9634-2
[9] 李孟麟, 朱精果, 孟柘, 等. 轻小型机载激光扫描仪设计[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2015, 44(5): 1426−1431. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2015.05.006
Li M L, Zhu J G, Meng Z, et al. Design of lightweight and small sized airborne laser scanner[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2015, 44(5): 1426−1431. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2015.05.006
[10] 刘博, 蒋贇, 王瑞, 等. 全天时单光子激光雷达技术进展与系统评价[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2023, 52(1): 20220748. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220748
Liu B, Jiang Y, Wang R, et al. Technical progress and system evaluation of all-time single photon Lidar[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2023, 52(1): 20220748. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220748
[11] 李瑞琛, 邹毅军, 陈天航, 等. 宽频消色散超表面全息成像[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(8): 230118. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230118
Li R C, Zou Y J, Chen T H, et al. Broadband achromatic metasurface holography[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2023, 50(8): 230118. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230118
[12] 柯岚, 章思梦, 李晨霞, 等. 超表面实现复杂矢量涡旋光束的研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(8): 230117. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230117
Ke L, Zhang S M, Li C X, et al. Research progress on hybrid vector beam implementation by metasurfaces[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2023, 50(8): 230117. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230117
[13] 俞建杰, 韩琦琦, 马晶, 等. 衍射光学元件在卫星激光通信终端中的潜在应用[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2013, 42(1): 130−137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.01.024
Yu J J, Han Q Q, Ma J, et al. Potential application of diffractive optical elements in satellite laser communication terminals[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2013, 42(1): 130−137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.01.024
[14] 李雄, 马晓亮, 罗先刚. 超表面相位调控原理及应用[J]. 光电工程, 2017, 44(3): 255−275. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.03.001
Li X, Ma X L, Luo X G. Principles and applications of metasurfaces with phase modulation[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2017, 44(3): 255−275. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.03.001
[15] 万源庆, 刘威骏, 林若雨, 等. 基于超构表面的光谱成像及应用研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(8): 230139. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230139
Wan Y Q, Liu W J, Lin R Y, et al. Research progress and applications of spectral imaging based on metasurfaces[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2023, 50(8): 230139. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230139
[16] Schwemmer G K, Wilkerson T D, Guerra D V. Compact scanning LiDAR systems using holographic optics[J]. Proc SPIE, 1998, 3504: 51−59. doi: 10.1117/12.319559
[17] Schwemmer G K. Holographic airborne rotating LiDAR instrument experiment (HARLIE)[C]//Nineteenth International Laser Radar Conference, 1998: 623–626.
[18] Schwemmer G K, Wilkerson T D. Development of a holographic telescope for optical remote sensing[J]. Proc SPIE, 1994, 2270: 40−47. doi: 10.1117/12.188834
[19] Marino R M, Davis W R, Jr. Jigsaw: a foliage-penetrating 3D imaging laser radar system[J]. Lincoln Lab J, 2005, 15(1): 23−36.
[20] Smith J G, Ramos-Izquierdo L, Stockham A, et al. Diffractive optics for moon topography mapping[J]. Proc SPIE, 2006, 6223: 622304. doi: 10.1117/12.665539
[21] 胡烜, 李道京. 10 m衍射口径天基合成孔径激光雷达系统[J]. 中国激光, 2018, 45(12): 1210002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201845.1210002
Hu X, Li D J. Space-based synthetic aperture LiDAR system with 10 m diffractive aperture[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2018, 45(12): 1210002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201845.1210002
[22] 李道京, 高敬涵, 崔岸婧, 等. 2m衍射口径星载双波长陆海激光雷达系统研究[J]. 中国激光, 2022, 49(3): 0310001. doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.0310001
Li D J, Gao J H, Cui A J, et al. Research on space-borne dual-wavelength land-sea LiDAR system with 2 m diffractive aperture[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2022, 49(3): 0310001. doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.0310001
[23] Shi H T, Shen G Y, Qi H Y, et al. Noise-tolerant Bessel-beam single-photon imaging in fog[J]. Opt Express, 2022, 30(7): 12061−12068. doi: 10.1364/OE.454669
[24] Shi H T, Qi H Y, Shen G Y, et al. High-resolution underwater single-photon imaging with Bessel beam illumination[J]. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron, 2022, 28(5): 8300106. doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2022.3144167
[25] Siemion A. The magic of optics—An overview of recent advanced terahertz diffractive optical elements[J]. Sensors, 2020, 21(1): 100. doi: 10.3390/s21010100
[26] 霍家琦, 胡源, 程彬鹏. 衍射光学技术发展历程及应用[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2023, 60(7): 0700002. doi: 10.3788/LOP213408
Huo J Q, Hu Y, Cheng B P. History and application of diffractive optics technology[J]. Laser OptoElectron Prog, 2023, 60(7): 0700002. doi: 10.3788/LOP213408
[27] Poleshchuk A G. Fabrication and application of diffractive optical elements[J]. Proc SPIE, 2010, 7544: 75443L. doi: 10.1117/12.887434
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: