-
摘要
合成孔径激光雷达成像技术是一种能够突破光学系统衍射极限的主动光学成像技术,其概念来自工作在微波波段的合成孔径雷达,相比于合成孔径雷达,合成孔径激光雷达具有成像速度快、成像分辨率高以及能获取符合人眼感知的图像的优势,在远距离目标感知与识别中具有很高的潜在价值。本文从合成孔径激光雷达的工作原理出发,回顾和梳理了合成孔径激光雷达的主要关键技术的主要进展,包括合成孔径激光雷达的系统模型和基础理论、系统设计与架构、激光相位噪声抑制、运动补偿技术以及成像算法;同时对国内外重要的外场实验进展进行了总结。最后探讨了后续实现工程化所需面对的困难和挑战。
Abstract
Synthetic aperture ladar is an advanced active optical imaging technology that overcomes the diffraction limit of the traditional optical system. This technology is inspired by the working principles of synthetic aperture radar in the microwave band. Compared with synthetic aperture radar, synthetic aperture ladar has several advantages such as fast imaging speed, high resolution, and its images being similar to what the eye is used to seeing, thanks to its operation wavelength, which makes synthetic aperture ladar potentially valuable. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive review of the progress made in key technologies related to synthetic aperture ladar, including its system model and basic theory, system design and structures, laser phase noise suppression technology, motion compensation technologies, and imaging algorithms. Furthermore, some important outdoor experiments at home and abroad were summarized. At last, the difficulties and challenges for the subsequent implementation of engineering were discussed.
-
Overview
Overview: Ladar is an active sensing technology employing laser for detecting, measuring and imaging. According to the detection modes, ladars are usually divided into two types: non-coherent ladar and coherent ladar. Coherent ladar employing heterodyne detection can provide more information, such as frequency shift and phase. This combination of features enables multi-functional, high-precision, and operationally important detection and sensing applications.
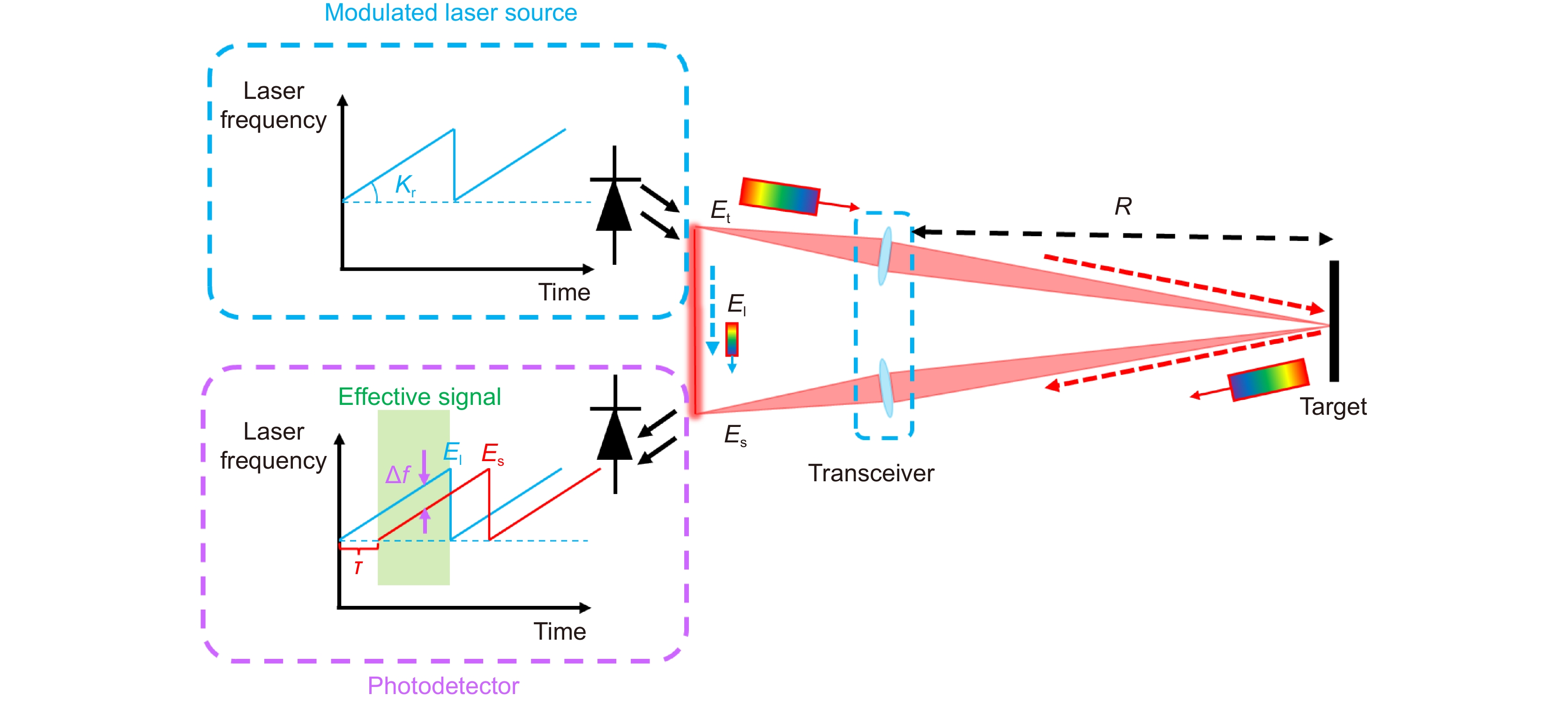
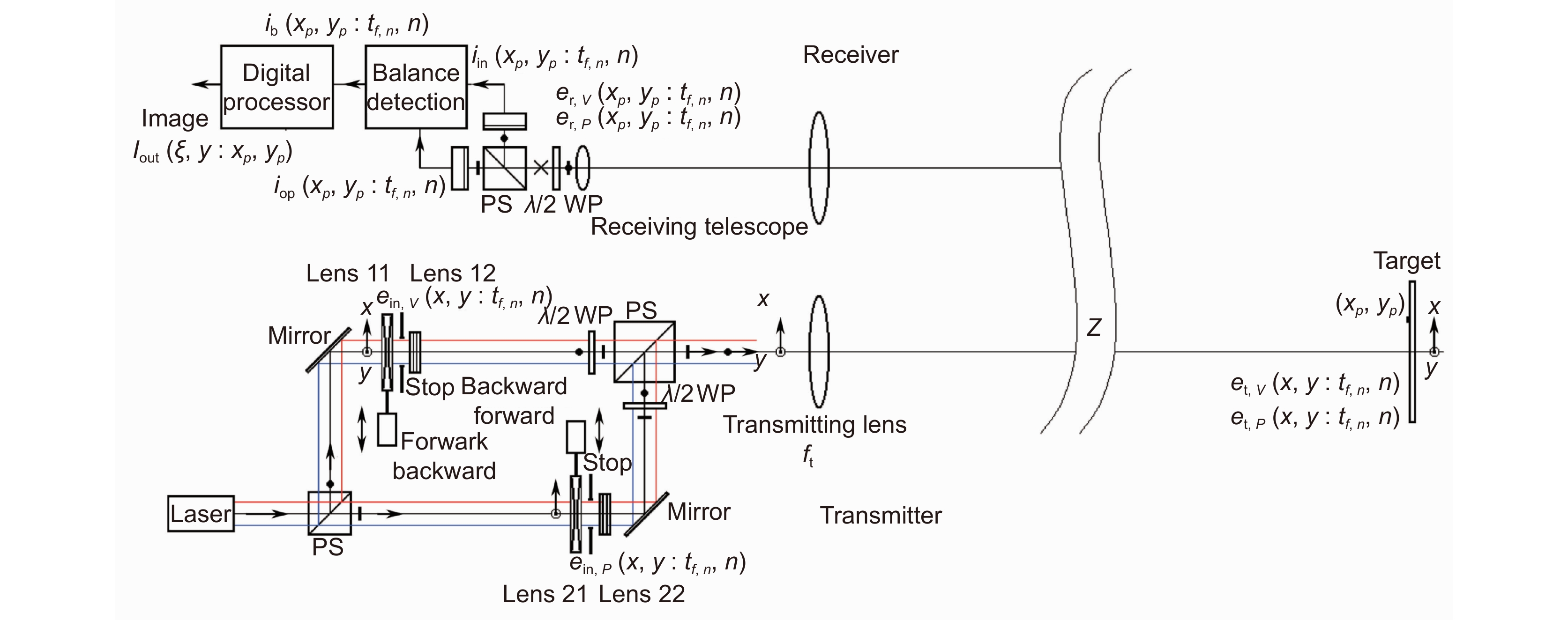
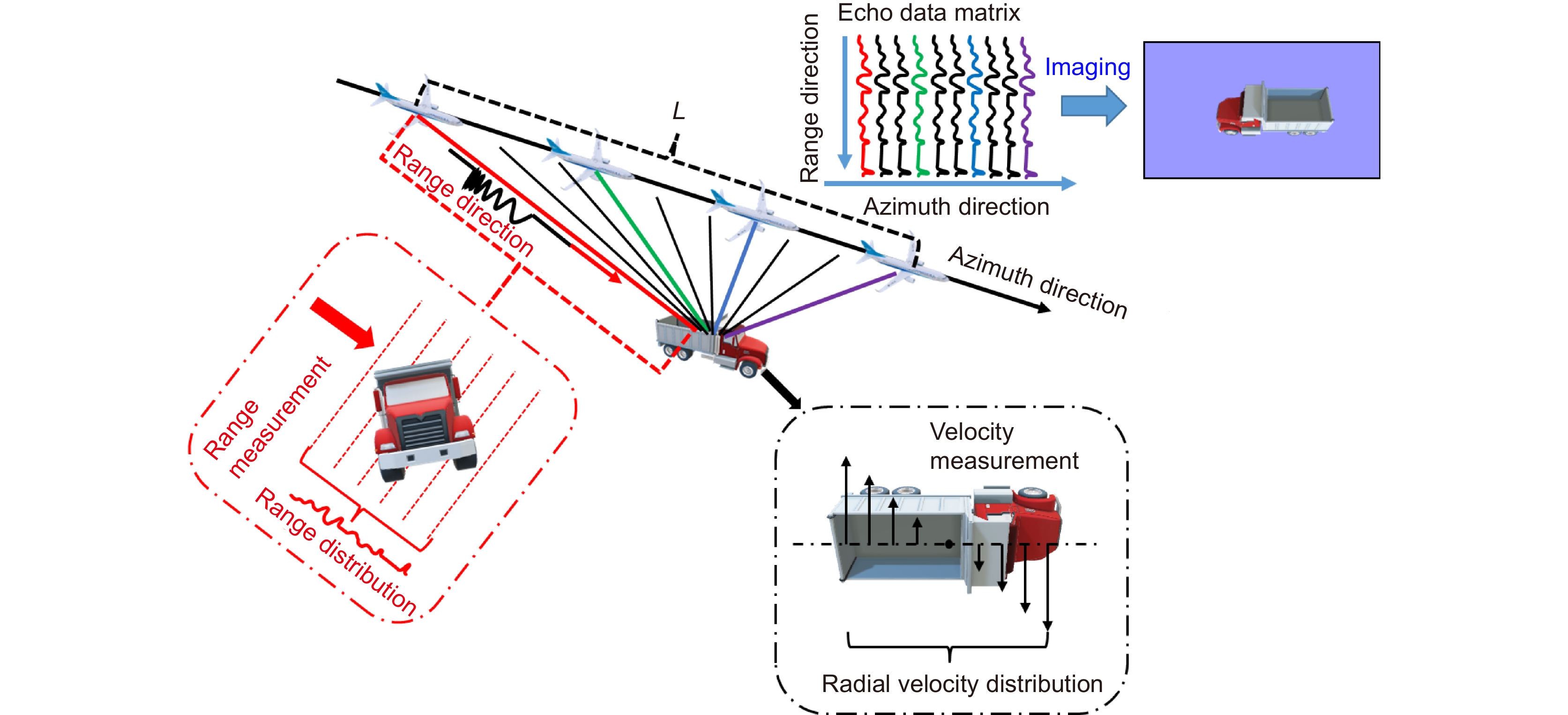
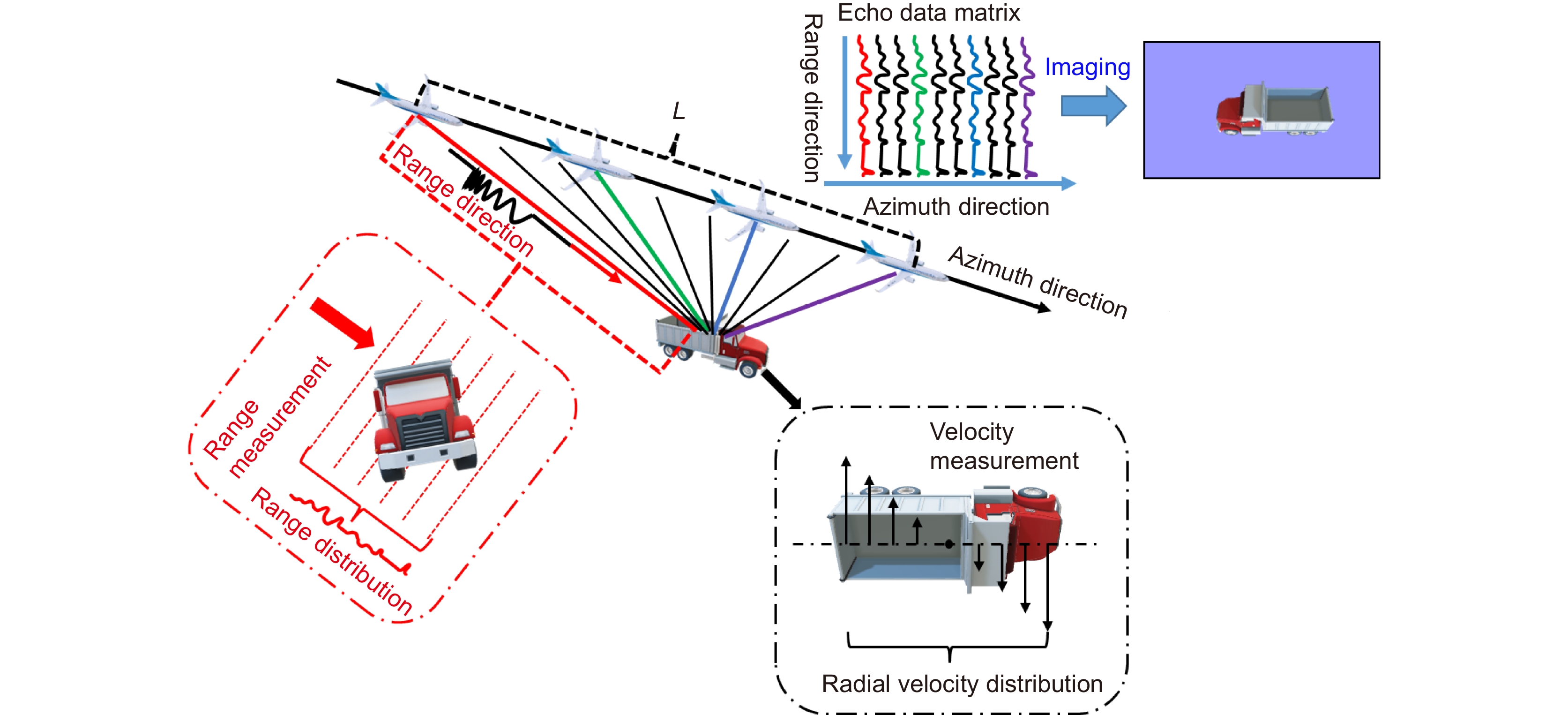
Synthetic aperture ladar (SAL) is a special type of coherent ladar whose principle is similar to synthetic aperture radar (SAR) operating in the microwave band. It utilizes a wideband modulated signal to obtain a high axial resolution, which is called range resolution. In another dimension called cross-range direction or azimuth direction, the moving ladar platform transmits and receives a series of coherent pulses, and then these pulses are coherently accumulated to achieve an equivalent large aperture. Thus, its resolution is independent of the optical aperture. Compared with SAR, it has higher imaging speed and higher imaging resolution. It can obtain images similar to what the human is used to seeing, thanks to the operation wavelength of SAL. These characteristics make SAL become a potentially valuable technology in the field of remote sensing and object identification.
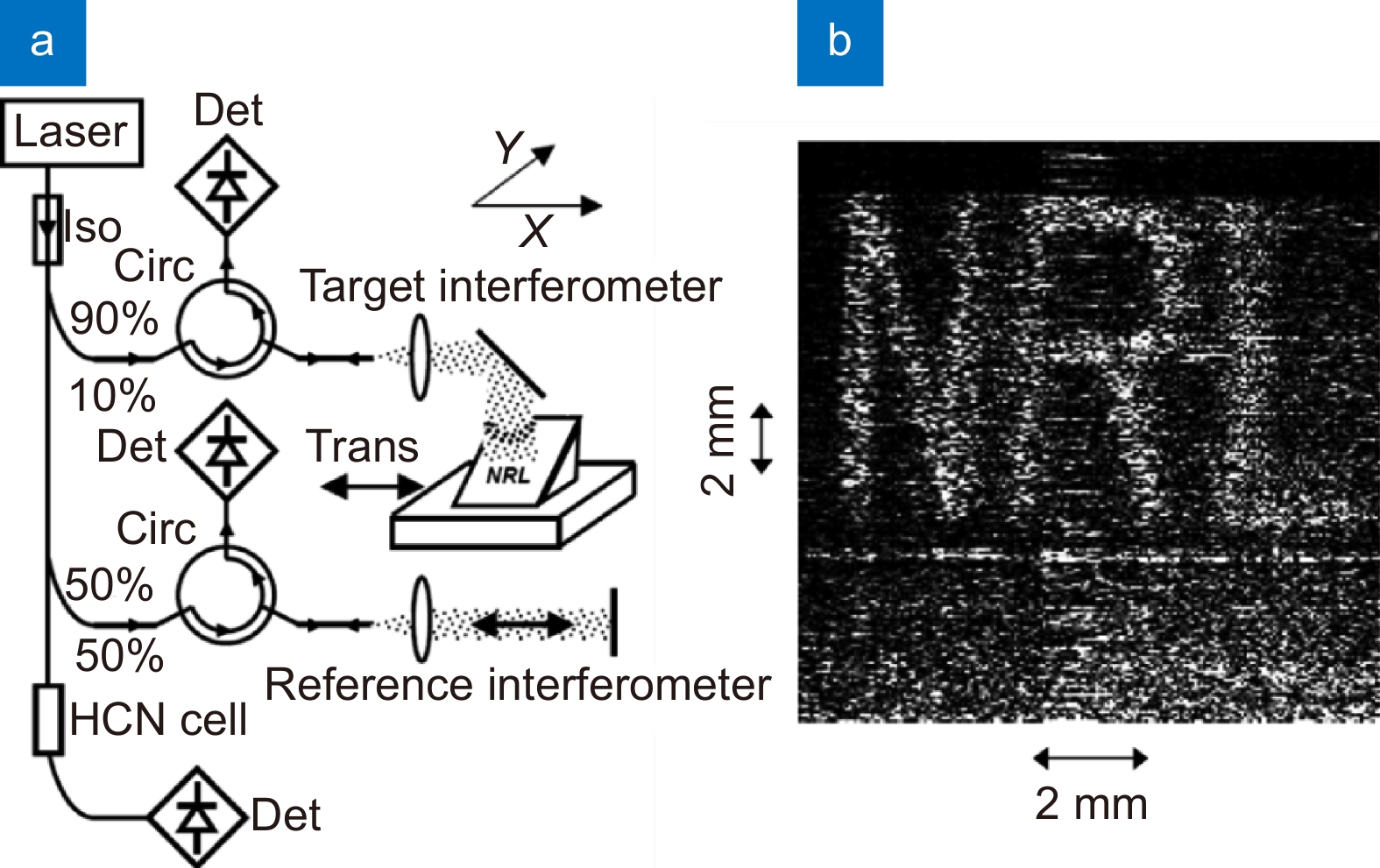
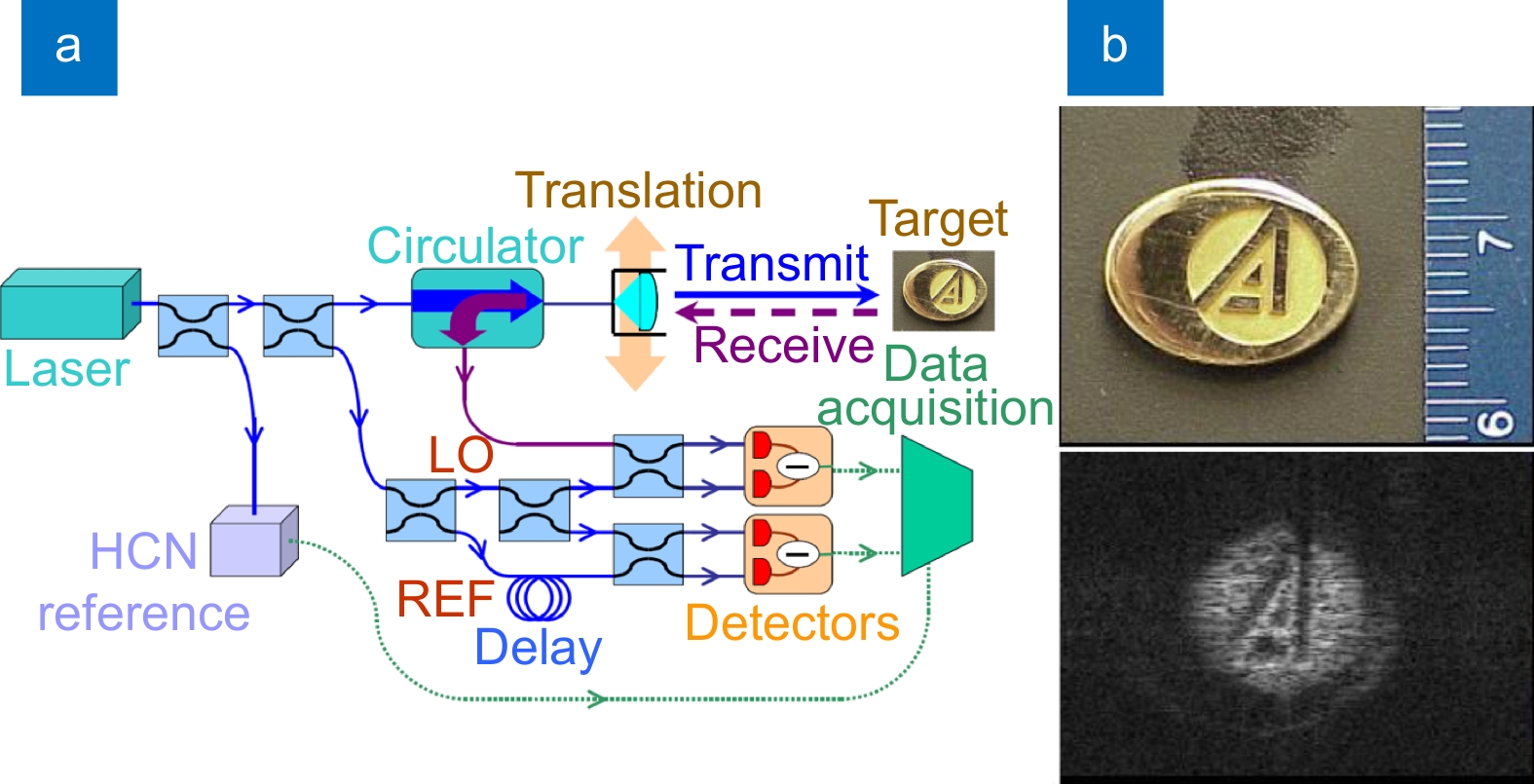
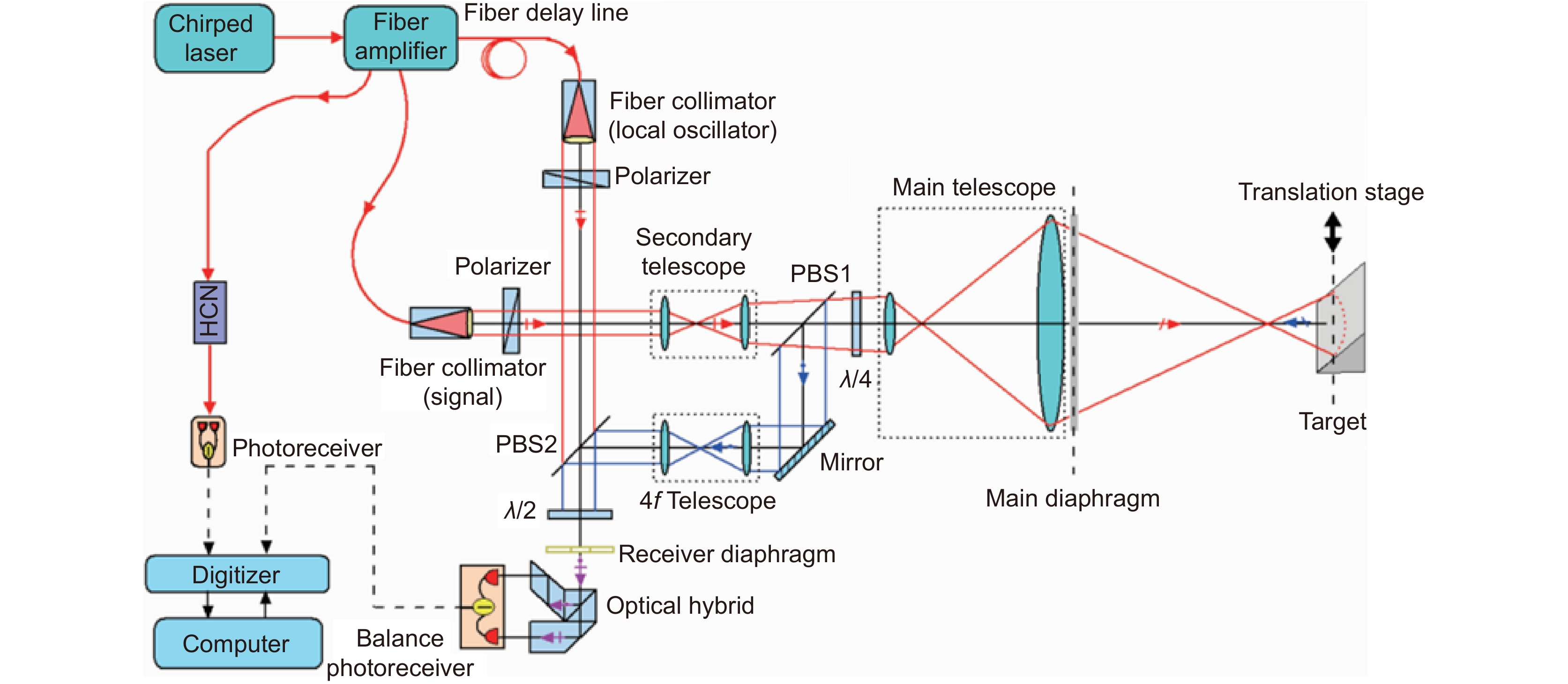
Although SAL is a kind of coherent ladar, it has higher coherence requirements than other systems, which makes SAL face many technical problems like atmosphere disturbance, laser phase noise, motion errors, etc. To address these issues, considerable efforts have been undertaken by a wide array of research professionals and collaborative teams across the field. The main goal of this paper is to provide a review of the progress of these efforts and point out the challenges faced in future development. First, this paper will briefly introduce the working principle of SAL. The second part introduces the research progress of the key technologies in the field of SAL. These key technologies include the system model and basic theoretical problems, system design and architecture, laser phase noise suppression technology, motion error compensation method, and imaging algorithms. The third part reviews the progress of the outdoor experiments at home and abroad. Outdoor experiment is an important step before practical application, which is able to reveal the defects and deficiencies of the system in the real environment. Finally, we summarized the challenges that prevent SAL systems from becoming practical and provided some future directions.
-

-
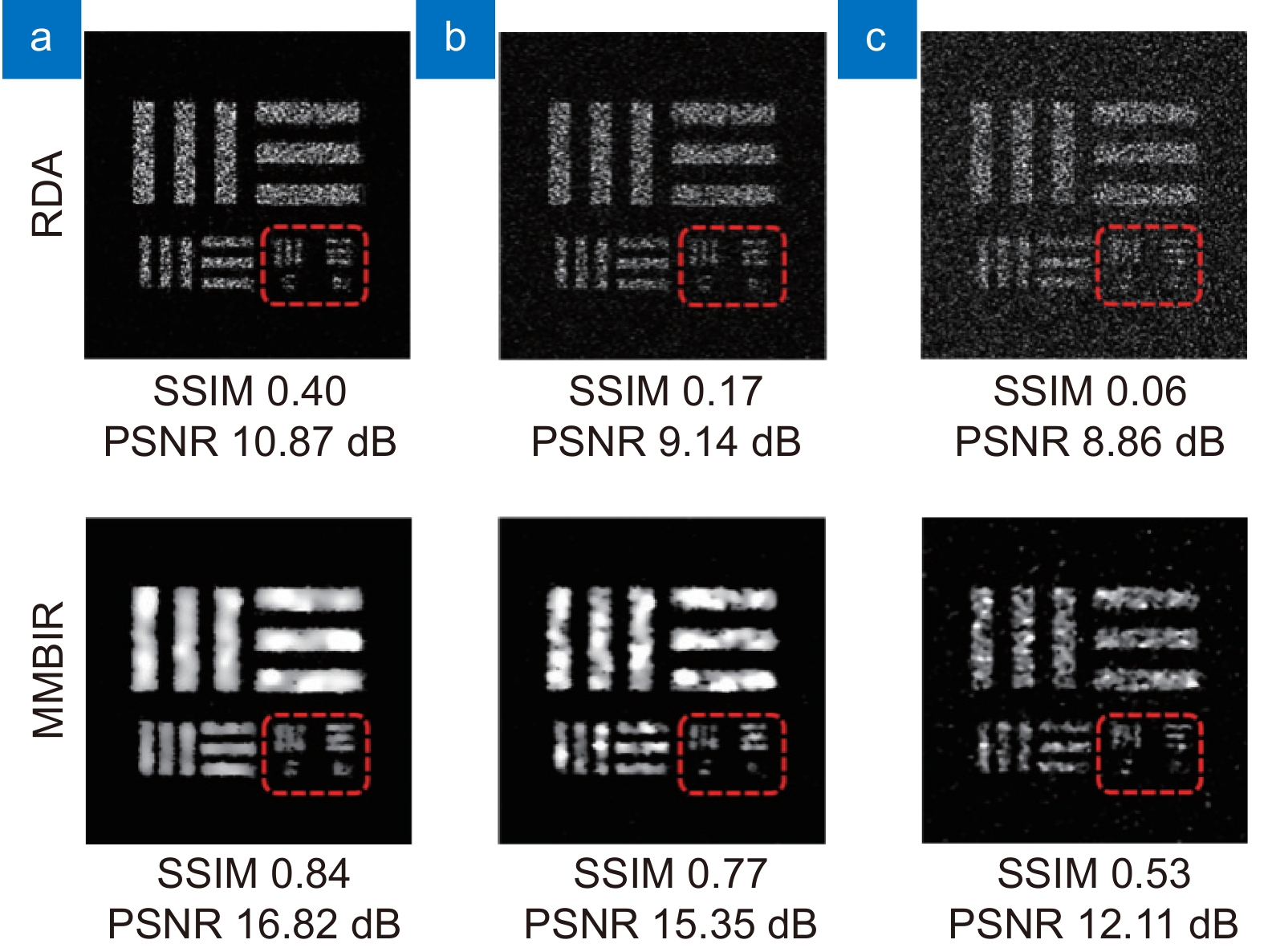
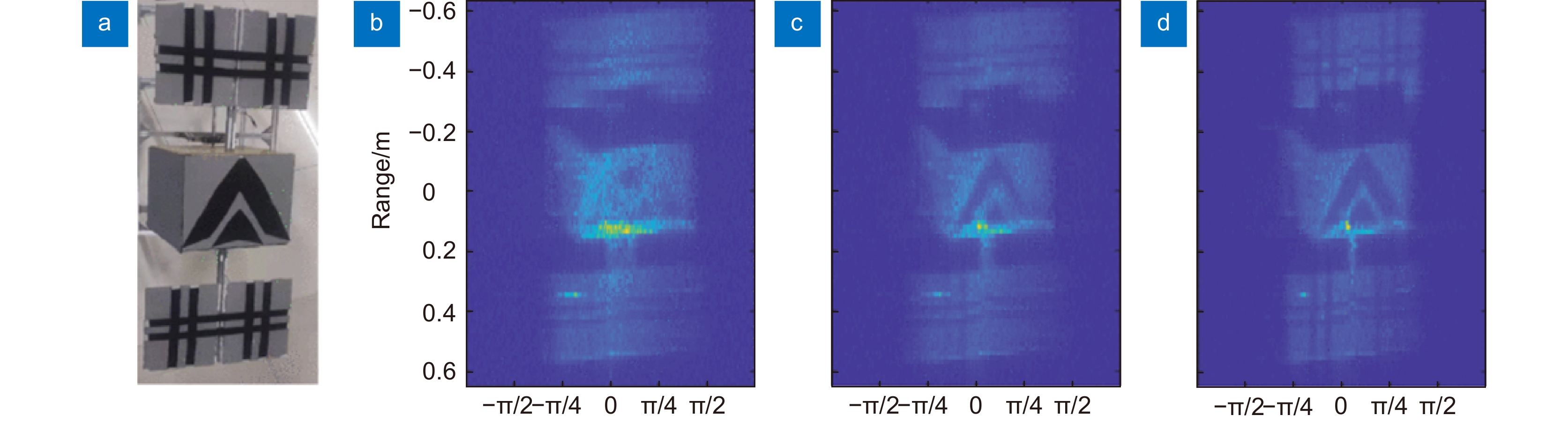
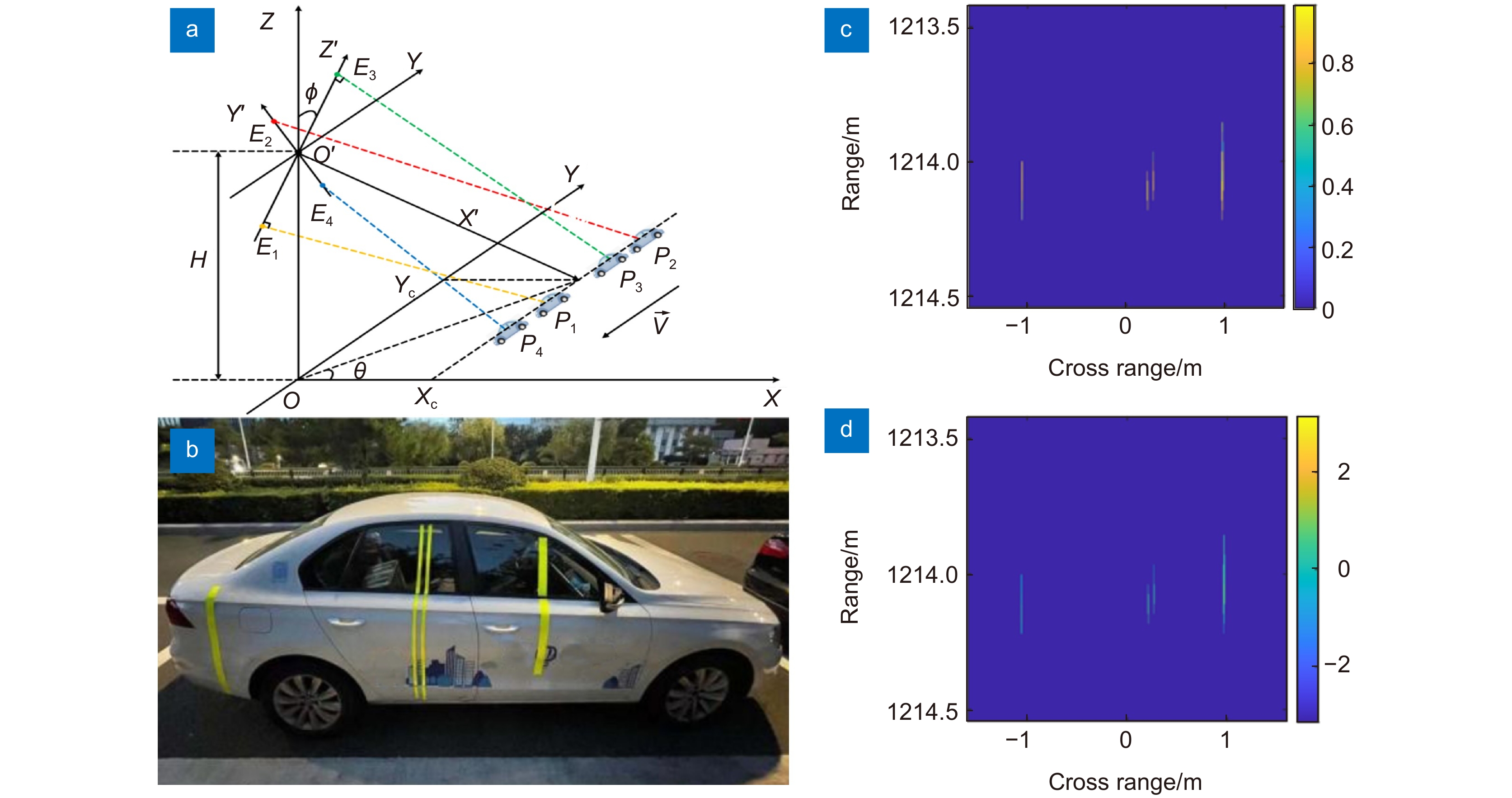
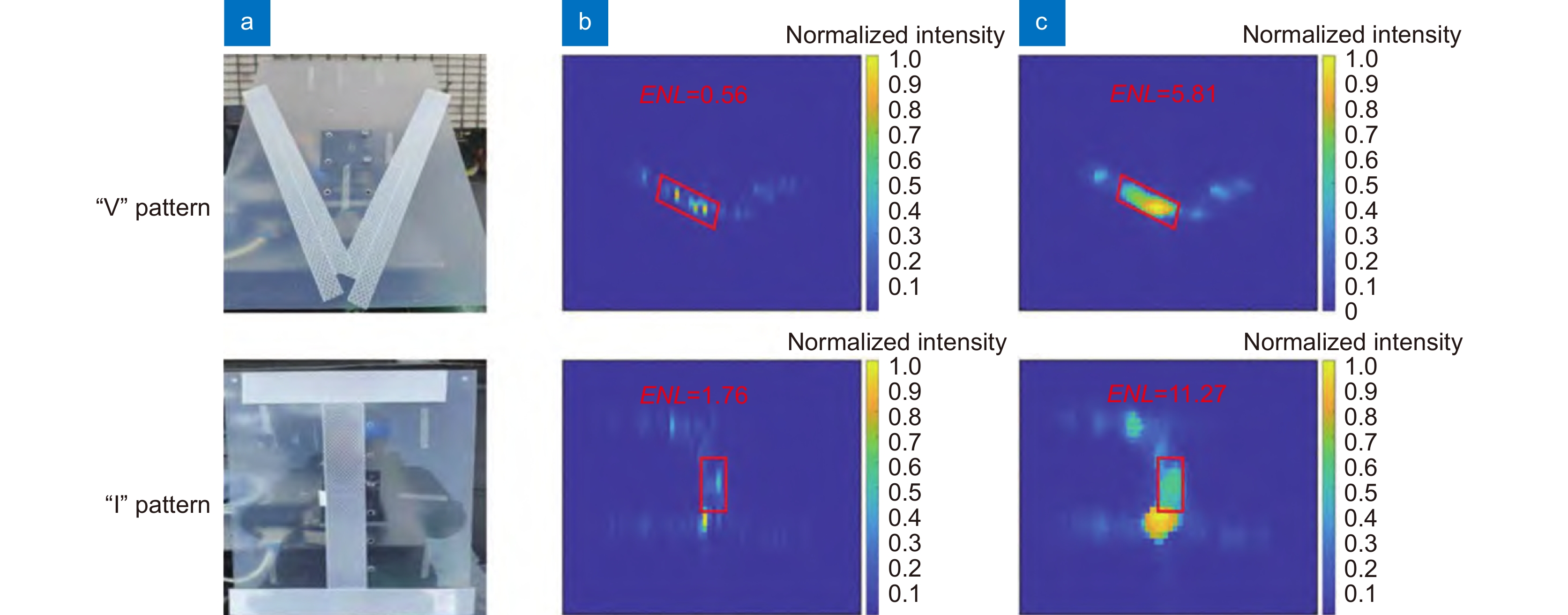
图 11 卫星微小振动补偿实验结果[45]。(a)实验目标;(b)未补偿结果;(c) PGA补偿结果;(d)所提方法的补偿结果
Figure 11. The experimental results of micro-vibration error compensation[45]. (a) Photography of the satellite model; Image formatted (b) Without phase error compensation; (c) By method using PGA algorithm; (d) By using the proposed algorithm
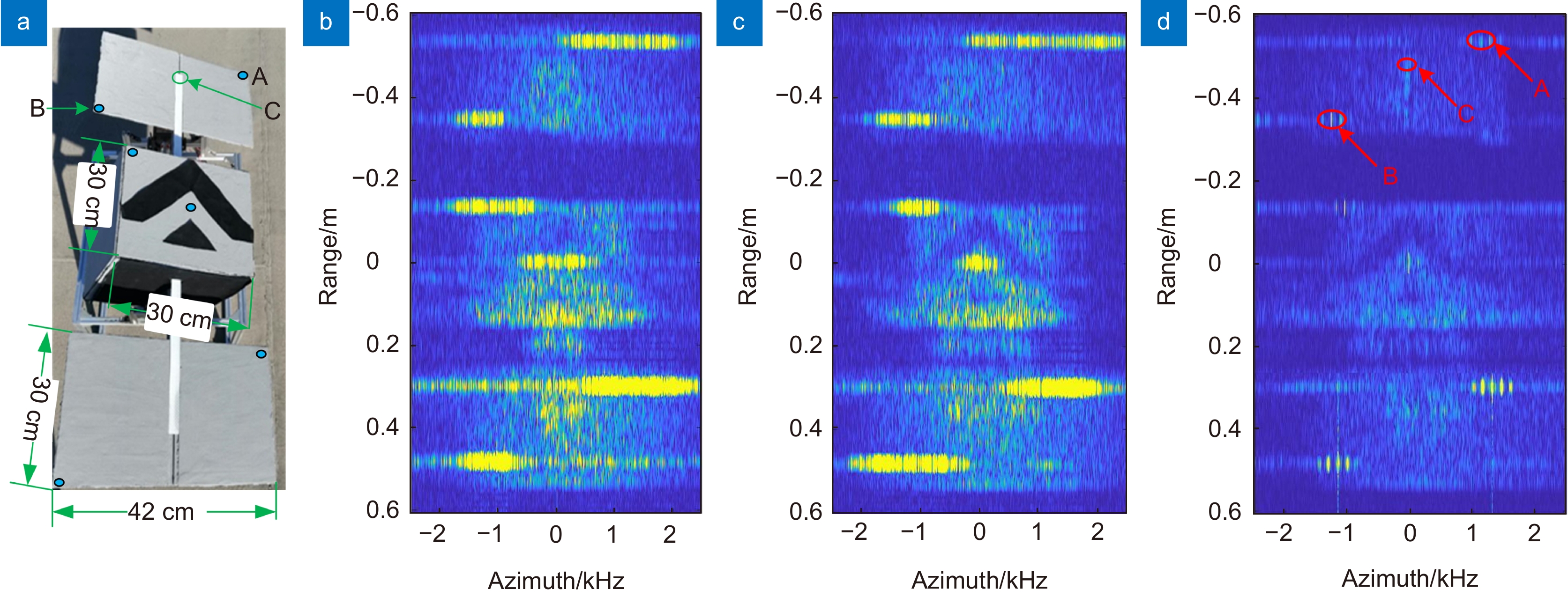
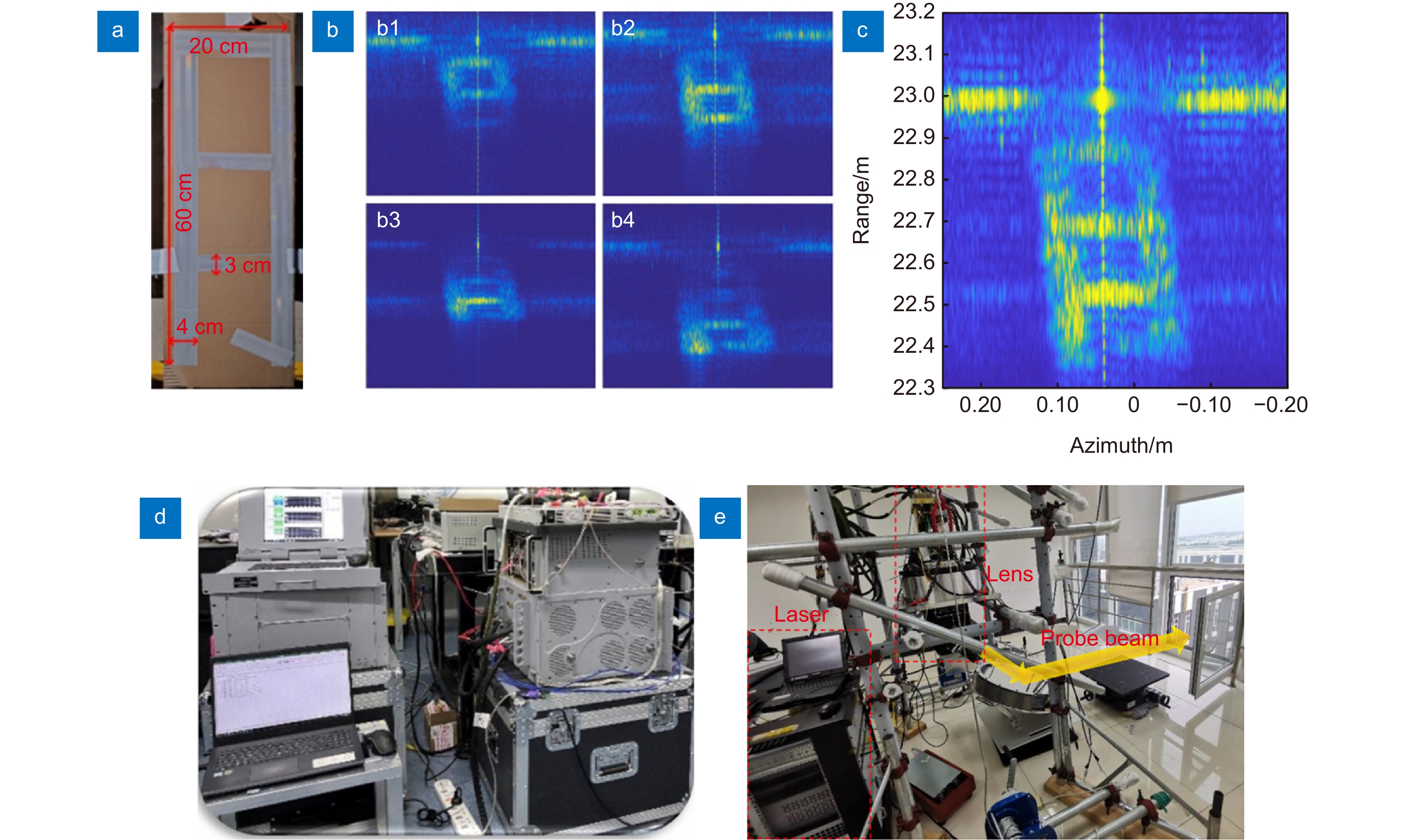
图 15 发射参考通道和本振参考通道补偿实验结果[85]。(a)目标实物图;(b)补偿前的距离-多普勒域成像结果;(c)发射参考通道补偿结果;(d)发射参考通道与本振参考通道联合补偿结果
Figure 15. Correction and compensation effect of TRC and LORC[85]. (a) Photo of the target; (b) Range-doppler domain imaging results before correction; (c) Range-doppler domain imaging results after TRC correction; (d) Range-doppler domain imaging results after TRC correction and LORC compensation
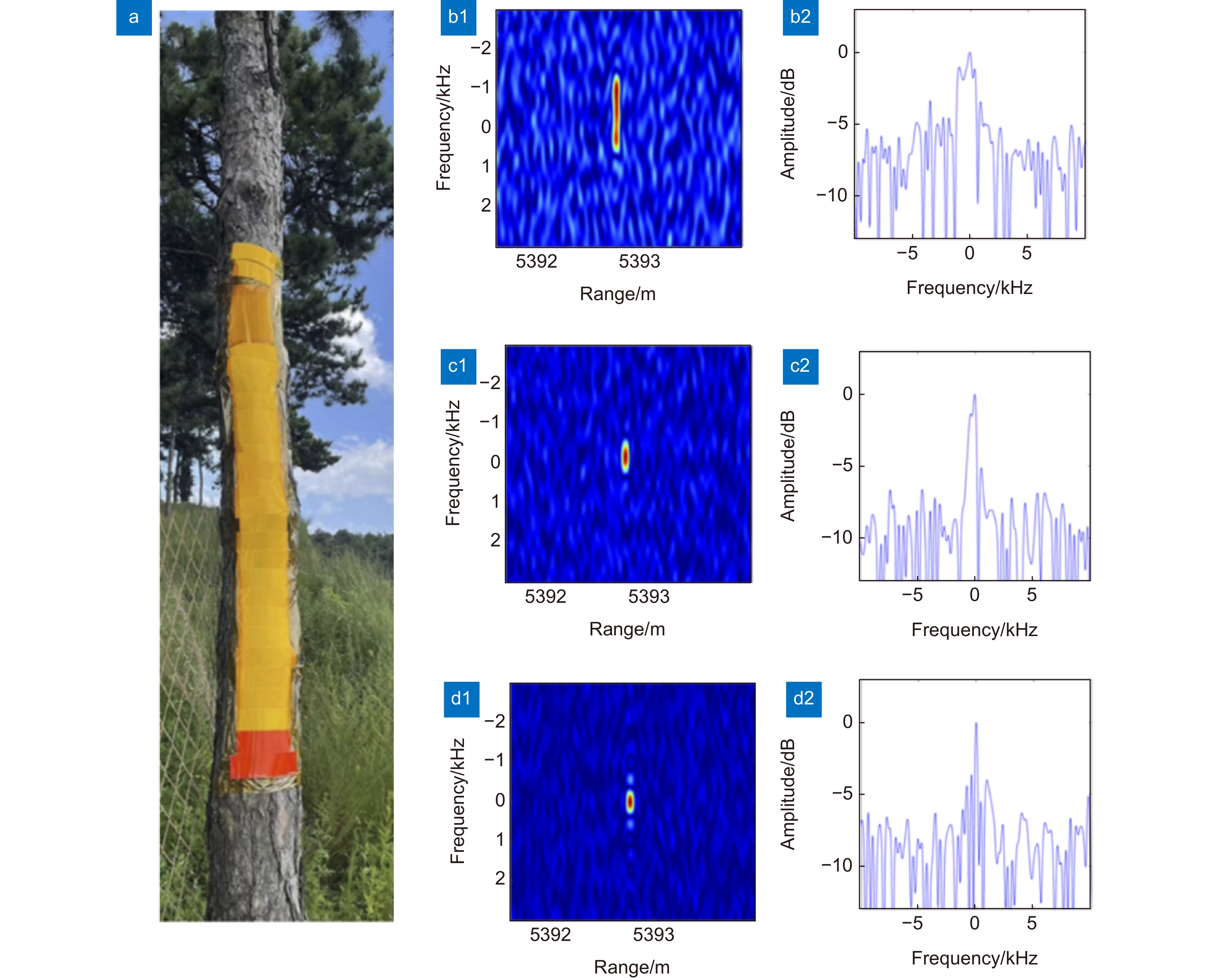
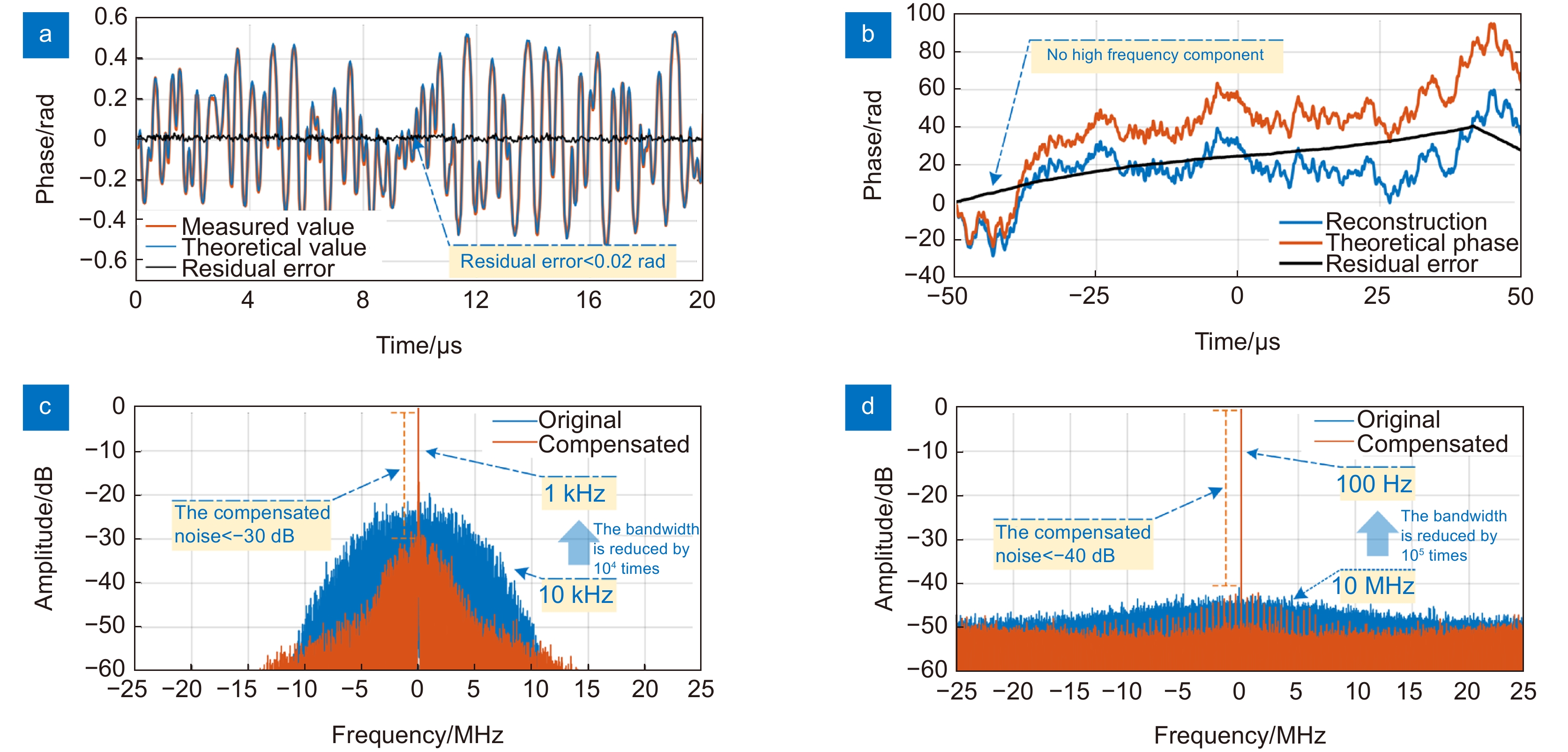
图 16 激光相位噪声测量与补偿结果[90]。(a)相干探测信号相位的测量值和理论值;(b)激光相位噪声的估计结果;(c)高斯线宽激光相位噪声补偿结果;(d)洛伦兹线宽激光相位噪声补偿结果
Figure 16. Measured and compensated results for laser phase noise[90]. (a) Comparison of the measured and theoretical values for the phase of the heterodyne signal; (b) The estimation results of the laser phase noise; (c) The compensation results with Gaussian linewidth; (d) The compensation results with Lorentz linewidth
-
参考文献
[1] 李晟, 王博文, 管海涛, 等. 远场合成孔径计算光学成像技术: 文献综述与最新进展[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(10): 230090. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230090
Li S, Wang B W, Guan H T, et al. Far-field computational optical imaging techniques based on synthetic aperture: a review[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2023, 50(10): 230090. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230090
[2] Cumming I G, Wong F H. Digital Signal Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2004.
[3] Brown W M. Synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst, 1967, AES-3(2): 217−229. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1967.5408745
[4] Wiley C A. Pulsed Doppler radar methods and apparatus: 3196436[P]. 1965-07-20.
[5] 丁俊华, 袁明辉. 基于双分支多尺度融合网络的毫米波SAR图像多目标语义分割方法[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(12): 230242. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230242
Ding J H, Yuan M H. A multi-target semantic segmentation method for millimetre wave SAR images based on a dual-branch multi-scale fusion network[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2023, 50(12): 230242. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230242
[6] 赵洪强, 张星祥, 王夺, 等. SAR实时成像光学处理器光机系统设计[J]. 光电工程, 2022, 49(9): 210421. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.210421
Zhao H Q, Zhang X X, Wang D, et al. Optical-mechanical system design of SAR real-time imaging optical processor[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2022, 49(9): 210421. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.210421
[7] 刘立人. 高分辨率遥感新途径−合成孔径激光成像雷达[J]. 科学, 2014, 66(6): 25−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0368-6396.2014.06.006
Liu L R. A new way to high-resolution remote sensing: synthetic aperture imaging ladar[J]. Science, 2014, 66(6): 25−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0368-6396.2014.06.006
[8] 吴谨. 关于合成孔径激光雷达成像研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(4): 353−360. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20076
Wu J. On the development of synthetic aperture ladar imaging[J]. J Radars, 2012, 1(4): 353−360. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20076
[9] Lucke R L, Rickard L, Bashkansky M, et al. Synthetic aperture ladar (SAL): fundamental theory, design equations for a satellite system, and laboratory demonstration[R]. Washington: Naval Research Laboratory, 2002.
[10] 李道京, 高敬涵, 崔岸婧, 等. 成像探测相干激光雷达技术研究进展[J]. 现代雷达, 2023, 45(11): 1−6. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2023.11.001
Li D J, Gao J H, Cui A J, et al. Research progress of coherent ladar technology for imaging and detection[J]. Mod Radar, 2023, 45(11): 1−6. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2023.11.001
[11] Aleksoff C C, Accetta J S, Peterson L M, et al. Synthetic aperture imaging with a pulsed Co2 tea laser[J]. Proc SPIE, 1987, 783: 29−41. doi: 10.1117/12.940575
[12] Aleksoff C C. Interferometric two-dimensional imaging of rotating objects[J]. Opt Lett, 1977, 1(2): 54−55. doi: 10.1364/OL.1.000054
[13] Aleksoff C C. Synthetic interferometric imaging technique for moving objects[J]. Appl Opt, 1976, 15(8): 1923−1929. doi: 10.1364/AO.15.001923
[14] Aleksoff C C, Christensen C R. Holographic Doppler imaging of rotating objects[J]. Appl Opt, 1975, 14(1): 134−141. doi: 10.1364/AO.14.000134
[15] Lewis T S, Hutchins H S. A synthetic aperture at 10.6 microns[J]. Proc IEEE, 1970, 58(10): 1781−1782. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1970.8012
[16] Marcus S, Colella B D, Green T J. Solid-state laser synthetic aperture radar[J]. Appl Opt, 1994, 33(6): 960−964. doi: 10.1364/AO.33.000960
[17] Green T J, Marcus S, Colella B D. Synthetic-aperture-radar imaging with a solid-state laser[J]. Appl Opt, 1995, 34(30): 6941−6949. doi: 10.1364/AO.34.006941
[18] Yoshikado S, Aruga T. Short-range verification experiment of a trial one-dimensional synthetic aperture infrared laser radar operated in the 10-µm band[J]. Appl Opt, 2000, 39(9): 1421−1425. doi: 10.1364/AO.39.001421
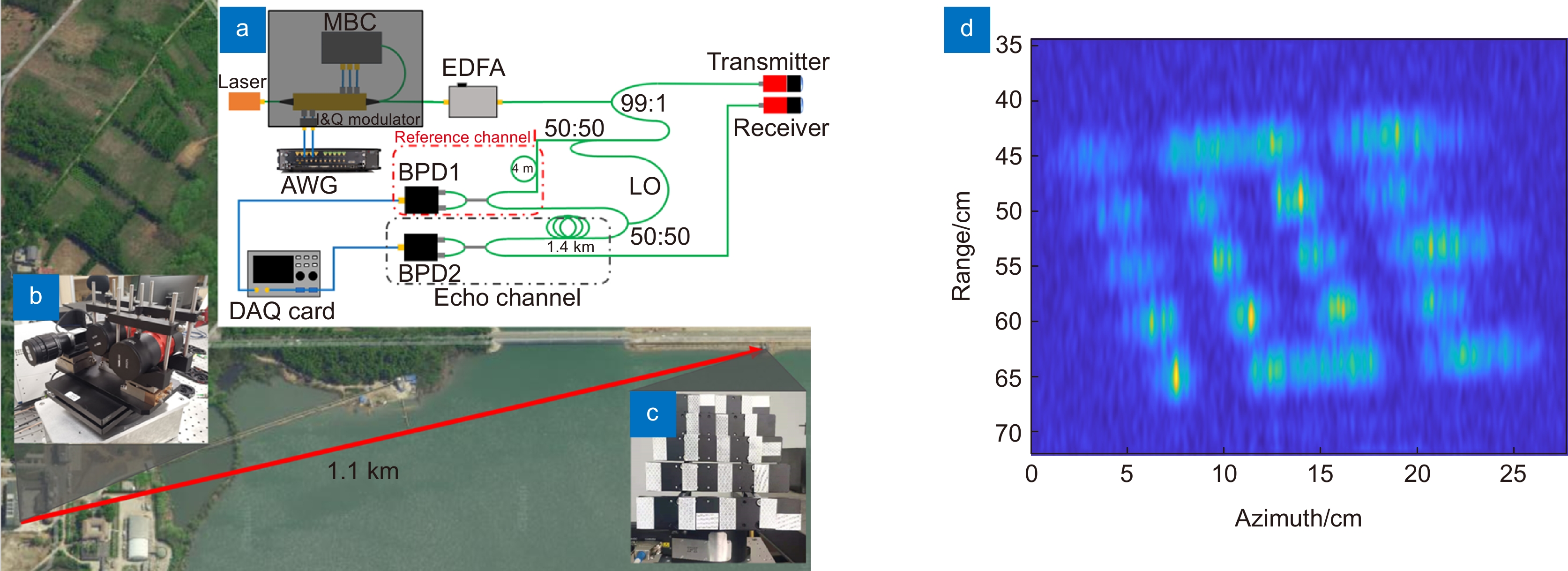
[19] Yoshikado S, Aruga T. Feasibility study of synthetic aperture infrared laser radar techniques for imaging of static and moving objects[J]. Appl Opt, 1998, 37(24): 5631−5639. doi: 10.1364/AO.37.005631
[20] Bashkansky M, Lucke R L, Funk E E, et al. Synthetic aperture imaging at 1.5μ: laboratory demonstration and potential application to planet surface studies[J]. Proc SPIE, 2002, 4849: 48−56. doi: 10.1117/12.460767
[21] Bashkansky M, Lucke R L, Funk E, et al. Two-dimensional synthetic aperture imaging in the optical domain[J]. Opt Lett, 2002, 27(22): 1983−1985. doi: 10.1364/OL.27.001983
[22] Karr T J. Synthetic aperture ladar resolution through turbulence[J]. Proc SPIE, 2003, 4976: 22−33. doi: 10.1117/12.479209
[23] Lucke R L. Synthetic aperture ladar simulations with phase screens and Fourier propagation[C]//Proceedings of 2004 IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1109/AERO.2004.1367959.
[24] Schumm B E, Dierking M P. Wave optics simulations of synthetic aperture ladar performance through turbulence[J]. J Opt Soc Am A, 2017, 34(10): 1888−1895. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.34.001888
[25] Rustowicz R M, Ross J W, Barnes L J, et al. Atmospheric effects and impact on target classification for Synthetic Aperture Ladar (SAL) imagery[J]. Proc SPIE, 2018, 10636: 1063609. doi: 10.1117/12.2303925
[26] 艾则孜姑丽·阿不都克热木, 陶志炜, 刘世韦, 等. 大气湍流对接收光场时间相干特性的影响[J]. 物理学报, 2022, 71(23): 234201. doi: 10.7498/aps.71.20221202
Azizigul A, Tao Z W, Liu S W, et al. Influence of atmospheric turbulence on temporal coherence characteristics of received optical field[J]. Acta Phys Sin, 2022, 71(23): 234201. doi: 10.7498/aps.71.20221202
[27] Barber Z W, Dahl J R. Sensitivity in synthetic aperture ladar imaging[C]//Proceedings of 2014 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO) - Laser Science to Photonic Applications, 2014.
[28] Barber Z W, Dahl J R. Synthetic aperture ladar imaging demonstrations and information at very low return levels[J]. Appl Opt, 2014, 53(24): 5531−5537. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.005531
[29] Cai G Y, Hou P P, Ma X P, et al. The laser linewidth effect on the image quality of phase coded synthetic aperture ladar[J]. Opt Commun, 2015, 356: 495−499. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2015.08.033
[30] 许倩, 周煜, 孙建锋, 等. 合成孔径激光成像雷达时空散斑效应模拟与分析[J]. 光学学报, 2013, 33(10): 1028002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201333.1028002
Xu Qian, Zhou Yu, Sun Jianfeng, et al. Analysis and Simulation of Space-Time Speckle Effect Based on Synthetic Aperture Imaging Ladar[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2013, 33(10): 1028002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201333.1028002
[31] 刘立人. 合成孔径激光成像雷达(VI): 时空散斑效应和外差探测信噪比[J]. 光学学报, 2009, 29(8): 2326−2332. doi: 10.3788/AOS20092908.2326
Liu L R. Synthetic aperture imaging ladar (VI): space-time speckle effect and heterodyne signal-to-noise ratio[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2009, 29(8): 2326−2332. doi: 10.3788/AOS20092908.2326
[32] 许倩, 周煜, 孙建锋, 等. 合成孔径激光成像雷达散斑天线接收特性分析[J]. 光学学报, 2014, 34(3): 0328002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201434.0328002
Xu Q, Zhou Y, Sun J F, et al. Analysis of integrated speckle receiving characteristics based on synthetic aperture imaging ladar[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2014, 34(3): 0328002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201434.0328002
[33] Xu Q, Zhou Y, Sun J F, et al. Influence of space–time speckle effect on the image quality in a synthetic aperture imaging ladar[J]. Opt Commun, 2014, 333: 265−273. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2014.07.034
[34] Xu Q, Sun Z W, Sun J F, et al. Speckle reduction of synthetic aperture imaging ladar based on wavelength characteristics[J]. Chin Opt Lett, 2014, 12(8): 080301. doi: 10.3788/COL201412.080301
[35] 党文佳, 曾晓东, 冯喆珺. 目标粗糙对合成孔径激光雷达回波的退相干效应[J]. 物理学报, 2013, 62(2): 024204. doi: 10.7498/aps.62.024204
Dang W J, Zeng X D, Feng Z J. Decoherence effect of target roughness in synthetic aperture ladar[J]. Acta Phys Sin, 2013, 62(2): 024204. doi: 10.7498/aps.62.024204
[36] 卢炤宇, 葛春风, 王肇颖, 等. 频率调制连续波激光雷达技术基础与研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(7): 190038. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.190038
Lu Z Y, Ge C F, Wang Z Y, et al. Basics and developments of frequency modulation continuous wave LiDAR[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2019, 46(7): 190038. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.190038
[37] Buell W, Marechal N, Buck J, et al. Demonstration of synthetic aperture imaging ladar[J]. Proc SPIE, 2005, 5791: 152−166. doi: 10.1117/12.609682
[38] Beck S M, Buck J R, Buell W F, et al. Synthetic-aperture imaging laser radar: laboratory demonstration and signal processing[J]. Appl Opt, 2005, 44(35): 7621−7629. doi: 10.1364/AO.44.007621
[39] 邢孟道, 郭亮, 唐禹, 等. 合成孔径成像激光雷达实验系统设计[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2009, 38(2): 290−294. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2009.02.022
Xing M D, Guo L, Tang Y, et al. Design on the experiment optical system of synthetic aperture imaging lidar[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2009, 38(2): 290−294. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2009.02.022
[40] 郭亮, 马瑜杰, 邢孟道, 等. 合成孔径成像激光雷达旋转目标成像[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2009, 38(4): 637−641. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2009.04.014
Guo L, Ma Y J, Xing M D, et al. Rotating objects imaging of synthetic aperture imaging lidar[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2009, 38(4): 637−641. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2009.04.014
[41] Guo L, Xing M D, Zhang L, et al. Research on indoor experimentation of range SAL imaging system[J]. Sci China Ser E:Technol Sci, 2009, 52(10): 3098−3104. doi: 10.1007/s11431-009-0157-6
[42] 刘立人, 周煜, 职亚楠, 等. 大口径合成孔径激光成像雷达演示样机及其实验室验证[J]. 光学学报, 2011, 31(9): 0900112. doi: 10.3788/AOS201131.0900112
Liu L R, Zhou Y, Zhi Y N, et al. A large-aperture synthetic aperture imaging ladar demonstrator and its verification in laboratory space[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2011, 31(9): 0900112. doi: 10.3788/AOS201131.0900112
[43] Adany P, Allen C, Hui R Q. Chirped lidar using simplified homodyne detection[J]. J Lightwave Technol, 2009, 27(16): 3351−3357. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2009.2016220
[44] Wang N, Wang R, Li G Z, et al. Experiment of inverse synthetic aperture ladar at 1.1 km[J]. Proc SPIE, 2016, 10155: 101551G. doi: 10.1117/12.2246531
[45] Song Z Q, Mo D, Wang N, et al. Inverse synthetic aperture ladar autofocus imaging algorithm for micro-vibrating satellites based on two prominent points[J]. Appl Opt, 2019, 58(25): 6775−6783. doi: 10.1364/AO.58.006775
[46] Wang N, Wang R, Mo D, et al. Inverse synthetic aperture LADAR demonstration: system structure, imaging processing, and experiment result[J]. Appl Opt, 2018, 57(2): 230−236. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.000230
[47] Mo D, Wang R, Wang N, et al. Three-dimensional inverse synthetic aperture lidar imaging for long-range spinning targets[J]. Opt Lett, 2018, 43(4): 839−842. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.000839
[48] 张珂殊, 李光祚, 王然, 等. 机载激光合成孔径雷达研究[C]//第四届高分辨率对地观测学术年会论文集, 2017: 12.
Zhang K S, Li G Z, Wang R, et al. The study on airborne laser synthetic aperture radar[C]//Proceedings of the 4th China High Resolution Earth Observation Conference, 2017: 12.
[49] Mo D, Wang R, Wang N, et al. Experiment of inverse synthetic aperture LADAR on real target[C]//Proceedings of 2017 7th IEEE International Conference on Electronics Information and Emergency Communication, 2017: 319–321. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEIEC.2017.8076572.
[50] Li G Z, Wang N, Wang R, et al. Imaging method for airborne SAL data[J]. Electron Lett, 2017, 53(5): 351−353. doi: 10.1049/el.2016.4205
[51] Li G Z, Wang R, Song Z Q, et al. Linear frequency-modulated continuous-wave ladar system for synthetic aperture imaging[J]. Appl Opt, 2017, 56(12): 3257−3262. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.003257
[52] Krause B W, Buck J, Ryan C, et al. Synthetic aperture ladar flight demonstration[C]//Proceedings of 2011 - Laser Science to Photonic Applications, 2011.
[53] 黄宇翔, 张鸿翼, 李飞, 等. 相位调制激光雷达成像设计及仿真[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2017, 46(5): 0506003. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.0506003
Huang Y X, Zhang H Y, Li F, et al. Phase modulated lidar imaging design and simulation[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2017, 46(5): 0506003. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.0506003
[54] 黄宇翔, 宋盛, 徐卫明, 等. 连续m序列相位调制的实时逆合成孔径激光雷达系统[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2017, 54(7): 072801. doi: 10.3788/LOP54.072801
Huang Y X, Song S, Xu W M, et al. Real-time inverse synthetic aperture ladar system based on continuous m-sequence phase modulation[J]. Laser Optoelectron Prog, 2017, 54(7): 072801. doi: 10.3788/LOP54.072801
[55] Gao S, Zhang Z H, Yu W X, et al. Inverse synthetic aperture ladar imaging based on modified cubic phase function[J]. Appl Opt, 2021, 60(7): 2014−2021. doi: 10.1364/AO.413512
[56] Xu X W, Gao S, Zhang Z H. Inverse synthetic aperture ladar demonstration and outdoor experiments[C]//Proceedings of 2018 China International SAR Symposium, 2018: 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/SARS.2018.8551972.
[57] Gao S, Zhang Z H, Xu X W, et al. The laboratory demonstration and signal processing of the inverse synthetic aperture imaging ladar[J]. Proc SPIE, 2017, 10427: 104271I. doi: 10.1117/12.2278055
[58] Cui A J, Li D J, Wu J, et al. Moving target imaging of a dual-channel ISAL with binary phase shift keying signals and large squint angles[J]. Appl Opt, 2022, 61(18): 5466−5473. doi: 10.1364/AO.458595
[59] Song A P, Jin K, Xu C, et al. Subcarrier modulation based phase-coded coherent lidar[J]. Opt Express, 2024, 32(1): 52−61. doi: 10.1364/OE.504166
[60] Wahl D E, Eichel P H, Ghiglia D C, et al. Phase gradient autofocus-a robust tool for high resolution SAR phase correction[J]. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst, 1994, 30(3): 827−835. doi: 10.1109/7.303752
[61] Eichel P H, Jakowatz C V. Phase-gradient algorithm as an optimal estimator of the phase derivative[J]. Opt Lett, 1989, 14(20): 1101−1103. doi: 10.1364/OL.14.001101
[62] Chen V C. Adaptive time-frequency ISAR processing[J]. Proc SPIE, 1996, 2845: 133−140. doi: 10.1117/12.257216
[63] Högbom J A. Aperture synthesis with a non-regular distribution of interferometer baselines[J]. Astron Astrophys Suppl, 1974, 15: 417−426.
[64] Pellizzari C J, Bos J, Spencer M F, et al. Performance characterization of Phase Gradient Autofocus for inverse synthetic aperture LADAR[C]//Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Aerospace Conference, 2014: 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1109/AERO.2014.6836491.
[65] 李明磊, 吴谨, 白涛, 等. 大随机相位误差下条带模式合成孔径激光雷达成像实验[J]. 中国光学, 2019, 12(1): 130−137. doi: 10.3788/co.20191201.0130
Li M L, Wu J, Bai T, et al. Stripmap mode synthetic aperture ladar imaging under large random phase errors condition[J]. Chin Opt, 2019, 12(1): 130−137. doi: 10.3788/co.20191201.0130
[66] 张洁, 王然, 张珂殊. 相位梯度自聚焦算法在合成孔径激光雷达中的应用与改进[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2016, 53(6): 062801. doi: 10.3788/LOP53.062801
Zhang J, Wang R, Zhang K S. Application and improvement of phase gradient autofocus algorithm in synthetic aperture lidar[J]. Laser Optoelectron Prog, 2016, 53(6): 062801. doi: 10.3788/LOP53.062801
[67] Song Z, Mo D, Li B, et al. Phase gradient matrix autofocus for ISAL Space-time-varied phase error correction[J]. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2020, 32(6): 353−356. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2020.2974505
[68] Xu G, Xing M D, Yang L, et al. Joint approach of translational and rotational phase error corrections for high-resolution inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging using minimum-entropy[J]. IET Radar Sonar Navig, 2016, 10(3): 586−594. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0356
[69] 刘盛捷, 付翰初, 魏凯, 等. 基于Nelder-Mead单纯形法的逆合成孔径激光雷达联合补偿成像算法[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(7): 0711002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0711002
Liu S J, Fu H C, Wei K, et al. Jointly compensated imaging algorithm of inverse synthetic aperture lidar based on nelder-mead simplex method[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2018, 38(7): 0711002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0711002
[70] 李建, 王鲲鹏, 晋凯, 等. 逆合成孔径激光雷达机动目标运动补偿成像算法[J]. 光学学报, 2021, 41(19): 1928001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1928001
Li J, Wang K P, Jin K, et al. Inverse synthetic aperture lidar motion compensation imaging algorithm for maneuvering targets[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2021, 41(19): 1928001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1928001
[71] Li J, Jin K, Xu C, et al. Adaptive motion error compensation method based on bat algorithm for maneuvering targets in inverse synthetic aperture LiDAR imaging[J]. Opt Eng, 2023, 62(9): 093103. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.62.9.093103
[72] 阮航, 张强, 杨雨昂, 等. 非均匀转动空间目标天基逆合成孔径激光雷达成像[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2023, 52(2): 20220406. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220406
Ruan H, Zhang Q, Yang Y A, et al. Spaceborne inverse synthetic aperture lidar imaging of nonuniformly rotating orbit object[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2023, 52(2): 20220406. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220406
[73] Yin H F, Li Y C, Guo L, et al. Spaceborne ISAL imaging algorithm for high-speed moving targets[J]. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens, 2023, 16: 7486−7496. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3302570
[74] 阮航, 吴彦鸿, 叶伟, 等. 逆合成孔径激光雷达相位误差补偿算法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2013, 50(10): 102801. doi: 10.3788/LOP50.102801
Ruan H, Wu Y H, Ye W, et al. Algorithm of phase error compensation for inverse synthetic aperture ladar[J]. Laser Optoelectron Prog, 2013, 50(10): 102801. doi: 10.3788/LOP50.102801
[75] 张鸿翼, 李飞, 徐卫明, 等. 利用优化算法对合成孔径激光雷达相位误差补偿的研究[J]. 电子学报, 2016, 44(9): 2100−2105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.09.012
Zhang H Y, Li F, Xu W M, et al. Research on the phase error compensation in synthetic aperture ladar by using optimization algorithm[J]. Acta Electron Sin, 2016, 44(9): 2100−2105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.09.012
[76] Graham L C. Synthetic interferometer radar for topographic mapping[J]. Proc IEEE, 1974, 62(6): 763−768. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1974.9516
[77] 刘立人. 自干涉合成孔径激光三维成像雷达原理[J]. 光学学报, 2014, 34(5): 0528001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201434.0528001
Liu L R. Principle of self-interferometric synthetic aperture ladar for 3D imaging[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2014, 34(5): 0528001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201434.0528001
[78] 马萌, 李道京, 杜剑波. 振动条件下机载合成孔径激光雷达成像处理[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(5): 591−602. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13132
Ma M, Li D J, Du J B. Imaging of airborne synthetic aperture ladar under platform vibration condition[J]. J Radars, 2014, 3(5): 591−602. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13132
[79] 杜剑波, 李道京, 马萌, 等. 基于干涉处理的机载合成孔径激光雷达振动估计和成像[J]. 中国激光, 2016, 43(9): 0910003. doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0910003
Du J B, Li D J, Ma M, et al. Vibration estimation and imaging of airborne synthetic aperture ladar based on interferometry processing[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2016, 43(9): 0910003. doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0910003
[80] Hu X, Li D J. Vibration phases estimation based on multi-channel interferometry for ISAL[J]. Appl Opt, 2018, 57(22): 6481−6490. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.006481
[81] Zhou K, Li D J, Gao J H, et al. Vibration phases estimation based on orthogonal interferometry of inner view field for ISAL imaging and detection[J]. Appl Opt, 2023, 62(11): 2845−2854. doi: 10.1364/AO.481186
[82] Gallion P, Debarge G. Quantum phase noise and field correlation in single frequency semiconductor laser systems[J]. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 1984, 20(4): 343−349. doi: 10.1109/JQE.1984.1072399
[83] 胡烜, 李道京, 赵绪锋. 基于本振数字延时的合成孔径激光雷达信号相干性保持方法[J]. 中国激光, 2018, 45(5): 0510003. doi: 10.3788/CJL201845.0510003
Hu X, Li D J, Zhao X F. Maintaining method of signal coherence in synthetic aperture ladar based on local oscillator digital delay[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2018, 45(5): 0510003. doi: 10.3788/CJL201845.0510003
[84] 胡烜, 李道京, 田鹤, 等. 激光雷达信号相位误差对合成孔径成像的影响和校正[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2018, 47(3): 0306001. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201847.0306001
Hu X, Li D J, Tian H, et al. Impact and correction of phase error in ladar signal on synthetic aperture imaging[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2018, 47(3): 0306001. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201847.0306001
[85] Gao J H, Li D J, Zhou K, et al. Maintenance method of signal coherence in lidar and experimental validation[J]. Opt Lett, 2022, 47(20): 5356−5359. doi: 10.1364/OL.470127
[86] Ke J Y, Song Z Q, Wang P S, et al. Long distance high resolution FMCW laser ranging with phase noise compensation and 2D signal processing[J]. Appl Opt, 2022, 61(12): 3443−3454. doi: 10.1364/AO.454001
[87] Ke J Y, Song Z Q, Cui Z M, et al. Phase noise compensation experiment with frequency modulated continuous wave laser in atmospheric propagation[J]. Opt Eng, 2022, 61(7): 073101. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.61.7.073101
[88] Ito F, Fan X Y, Koshikiya Y. Long-range coherent OFDR with light source phase noise compensation[J]. J Lightwave Technol, 2012, 30(8): 1015−1024. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2011.2167598
[89] Fan X Y, Koshikiya Y, Ito F. Phase-noise-compensated optical frequency domain reflectometry with measurement range beyond laser coherence length realized using concatenative reference method[J]. Opt Lett, 2007, 32(22): 3227−3229. doi: 10.1364/OL.32.003227
[90] Wu S B, Mo D, Wang R, et al. Surpassing the limitation of a coherence length in lidar by digital coherence[J]. Opt Lett, 2023, 48(21): 5455−5458. doi: 10.1364/OL.498990
[91] 保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005.
Bao Z, Xing M D, Wang T. Radar Imaging Technology[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005.
[92] Yegulalp A F. Fast backprojection algorithm for synthetic aperture radar[C]//Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Radar Conference. Radar into the Next Millennium, 1999: 60–65. https://doi.org/10.1109/NRC.1999.767270.
[93] Pellizzari C J, Trahan R, Zhou H Y, et al. Synthetic aperature LADAR: a model-based approach[J]. IEEE Trans Comput Imaging, 2017, 3(4): 901−916. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2017.2663320
[94] Pellizzari C J, Bouman C A. Inverse synthetic aperture LADAR image construction: an inverse model-based approach[J]. Proc SPIE, 2016, 9982: 99820F. doi: 10.1117/12.2236133
[95] 徐晨, 宋岸鹏, 晋凯, 等. 改进的基于光学成像模型的逆合成孔径激光雷达成像算法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2023, 60(12): 1228001. doi: 10.3788/LOP221548
Xu C, Song A P, Jin K, et al. Modified imaging algorithm for inverse synthetic aperture LiDAR based on optical imaging model[J]. Laser Optoelectron Prog, 2023, 60(12): 1228001. doi: 10.3788/LOP221548
[96] Buck J R, Krause B W, Malm A I R, et al. Synthetic aperture imaging at optical wavelengths[C]//Proceedings of the International Quantum Electronics Conference 2009, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1364/IQEC.2009.PThB3.
[97] Luan Z, Sun J F, Zhou Y, et al. Down-looking synthetic aperture imaging ladar demonstrator and its experiments over 1.2 km outdoor[J]. Chin Opt Lett, 2014, 12(11): 111101. doi: 10.3788/COL201412.111101
[98] 卢智勇, 周煜, 孙建峰, 等. 机载直视合成孔径激光成像雷达外场及飞行实验[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(1): 0110001. doi: 10.3788/CJL201744.0110001
Lu Z Y, Zhou Y, Sun J F, et al. Airborne down-looking synthetic aperture imaging ladar field experiment and its flight testing[J]. Chine J Lasers, 2017, 44(1): 0110001. doi: 10.3788/CJL201744.0110001
[99] Li G Y, Sun J F, Zhou Y, et al. Attitude-error compensation for airborne down-looking synthetic-aperture imaging lidar[J]. Opt Commun, 2017, 402: 355−361. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2017.05.010
[100] 李光远, 卢智勇, 周煜, 等. 直视逆合成孔径激光成像雷达外场实验[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(4): 0401001. doi: 10.3788/LOP202158.1811017
Li G Y, Lu Z Y, Zhou Y, et al. Outdoor experiment of down-looking inverse synthetic aperture imaging lidar[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2018, 38(4): 0401001. doi: 10.3788/LOP202158.1811017
[101] Wang S, Xiang M S, Wang B N, et al. A channel phase error compensation method for multi-channel synthetic aperture ladar[J]. Optik, 2019, 178: 830−840. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.10.074
[102] Wang S, Wang B N, Xiang M S, et al. Analysis and compensation of telescopes' gaps effect on aperture synthesis in a multi-channel synthetic aperture ladar system[J]. Appl Opt, 2019, 58(18): 4884−4891. doi: 10.1364/AO.58.004884
[103] Wang R R, Xiang M S, Li C. Denoising FMCW ladar signals via EEMD with singular spectrum constraint[J]. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett, 2020, 17(6): 983−987. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2936603
[104] Wang S, Wang B N, Xiang M S, et al. Synthetic aperture ladar motion compensation method based on symmetrical triangular linear frequency modulation continuous wave[J]. Opt Commun, 2020, 471: 125901. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2020.125901
[105] Wang R R, Xiang M S, Wang B N, et al. Time-frequency domain nonlinear phase compensation for FMCW ladar signals[C]//Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS39084.2020.9323798.
[106] Wang R R, Xiang M S, Wang B N, et al. Nonlinear phase estimation and compensation for FMCW ladar based on synchrosqueezing wavelet transform[J]. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett, 2021, 18(7): 1174−1178. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2997999
[107] Wang R R, Wang B N, Xiang M S, et al. Simultaneous time-varying vibration and nonlinearity compensation for one-period triangular-FMCW lidar signal[J]. Remote Sens, 2021, 13(9): 1731. doi: 10.3390/rs13091731
[108] 汪丙南, 赵娟莹, 李威, 等. 阵列激光合成孔径雷达高分辨成像技术研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 1110−1118. doi: 10.12000/JR22204
Wang B N, Zhao J Y, Li W, et al. Array synthetic aperture ladar with high spatial resolution technology[J]. J Radars, 2022, 11(6): 1110−1118. doi: 10.12000/JR22204
[109] Xu C, Jin K, Jiang C C, et al. Amplitude compensation using homodyne detection for inverse synthetic aperture LADAR[J]. Appl Opt, 2021, 60(34): 10594−10599. doi: 10.1364/AO.440764
[110] Hong K, Jin K, Song A P, et al. Low sampling rate digital dechirp for Inverse Synthetic Aperture Ladar imaging processing[J]. Opt Commun, 2023, 540: 129482. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2023.129482
[111] Brown W M, Palermo C J. Theory of coherent systems[J]. IRE Trans Mil Electron, 1962, MIL-6(2): 187−196. doi: 10.1109/IRET-MIL.1962.5008427
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: