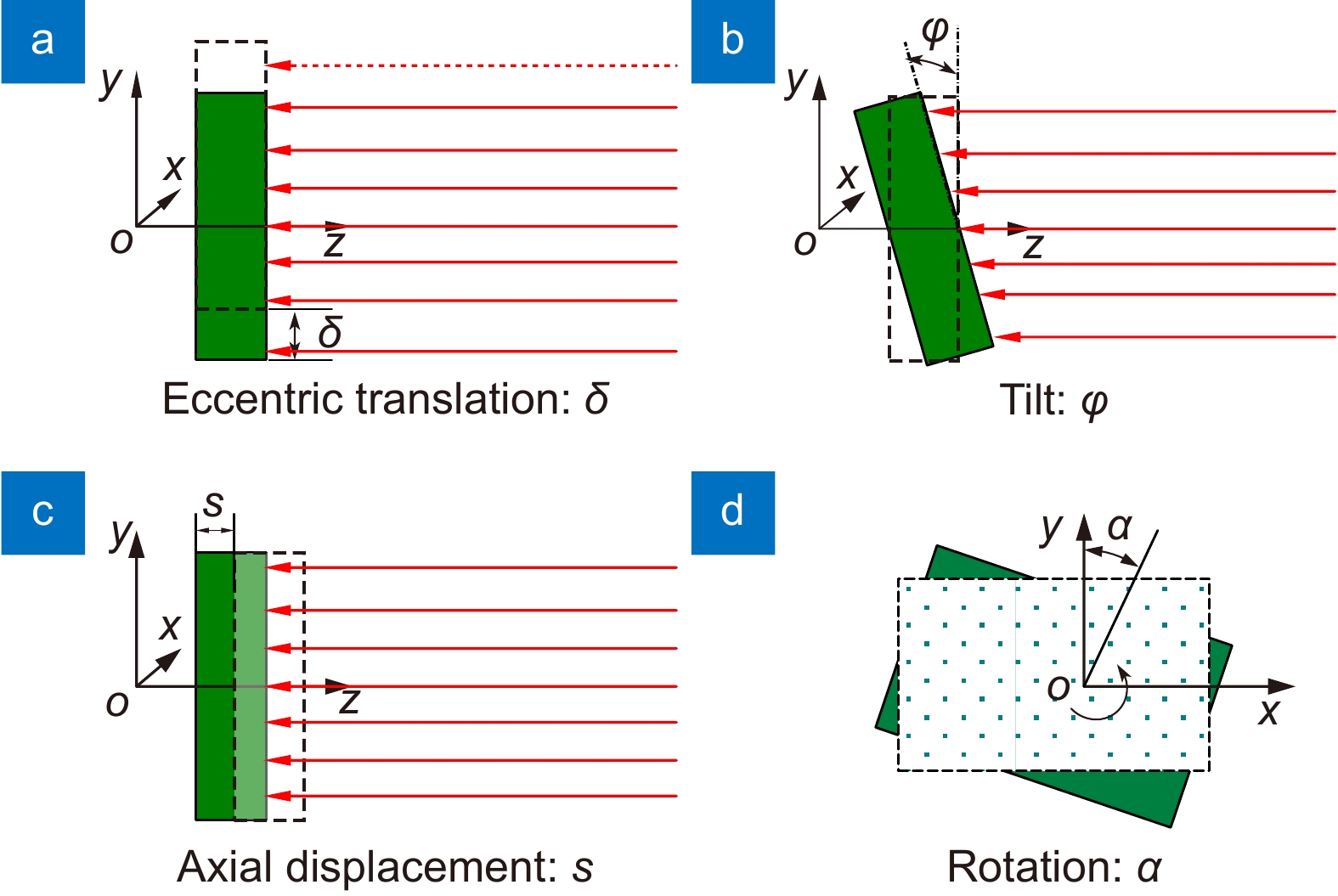
Design of optical path stability measurement scheme and theoretical analysis of noise in telescope
-
摘要:
空间引力波探测对望远镜提出了高稳定性要求。为实现望远镜光程稳定性精度的独立测量与标定,开展了相应测量方法的研究。基于外差干涉测量原理,设计了高共模抑制干涉测量方案,建立了光程噪声理论模型。根据1 pm/Hz1/2@1 mHz光程稳定性指标需求,分配测量系统组成部分光程噪声水平。为验证方案的可行性和噪声理论模型的准确性,搭建了望远镜前端干涉测量系统。根据实验仪器及光学组件相关参数,理论评估系统光程噪声水平为7.319 nm/Hz1/2@10 mHz,与实验测量结果3 nm/Hz1/2@10 mHz基本一致,表明干涉光路具有较好的噪声共模抑制特性,验证了噪声理论模型的准确性。当测试环境及仪器精度满足光程噪声指标分配要求时,该测量方案有望实现引力波望远镜光程稳定性测量。
Abstract:Gravitational wave detection imposes high stability requirements on telescopes in space. To achieve independent measurement and calibration of the optical path stability accuracy of the telescope, the research was conducted on corresponding measurement methods. Based on the principle of heterodyne interferometric measurement, a high common-mode suppression interferometric measurement scheme was designed, and an optical path noise theoretical model was established. According to the requirement of 1 pm/Hz1/2@1 mHz for optical path stability indicators, the optical path noise level of the measurement system components was allocated. To verify the feasibility of the scheme and the accuracy of the noise theoretical model, an interferometric measurement system was constructed at the front end of the telescope. According to the relevant parameters of the experimental instruments and optical components, the theoretical evaluation of the system's optical path noise level was 7.319 nm/Hz1/2@10 mHz. The experimental measurement result of 3 nm/Hz1/2@10 mHz was consistent with the theoretical evaluation, indicating that the interferometric path has good noise common-mode suppression characteristics, and verifying the accuracy of the noise theoretical model. When the testing environment and instrument accuracy meet the requirements for optical path noise allocation, this measurement scheme is expected to achieve the measurement of the optical path stability of gravitational wave telescope.
-
Overview: Gravitational wave detection imposes high stability requirements on telescopes in space. To achieve independent measurement and calibration of the optical path stability accuracy of the telescope, research was conducted on corresponding measurement methods. Based on the heterodyne interference measurement principle, a high common mode suppression interferometic measurement scheme was designed, using the phase difference information between the measuring interferometer and the reference interferometer to characterize the optical path changes of the measurement system. By conducting theoretical analysis on the optical path noise characteristics of each component module of the entire measurement system, a theoretical model of the optical path noise of the measurement system was established. The main sources of optical path noise are determined to be the front end optical path coupling noise, temperature optical path coupling noise, and standard plane mirror position misalignment noise. According to the requirement of 1 pm/Hz1/2@1 mHz for optical path stability indicators, the optical path noise level of the measurement system components was allocated. To verify the feasibility of the scheme and the accuracy of the noise theoretical model, an interferometric measurement system was constructed at the front end of the telescope. Firstly, based on the relevant parameters of the experimental instrument and optical components, the optical path noise level of the system was theoretically evaluated to be 7.319 nm/Hz1/2@10 mHz. Then, the optical path noise level measurement experiment was carried out on the constructed measurement system. The experimental results showed that the optical path noise background of the measurement system was less than 3 nm/Hz1/2@10 mHz. Finally, through the comparison and analysis of optical path noise theory and experimental results, it is known that the designed interference optical path in this paper has good noise common mode suppression characteristics, which further verifies the accuracy of the optical path noise theory model. When the testing environment and instrument accuracy meet the requirements of the optical path noise index allocation, this measurement scheme is expected to achieve the high-precision optical path stability measurement of the gravitational wave telescope.
-

-
表 1 望远镜光程稳定性测量光程噪声指标分配及要求
Table 1. Allocation and requirements of optical path noise indicators for distance stability measurement in telescopes
测量系统组成模块 主要噪声源 噪声分配/(pm/Hz1/2@1 mHz) 要求 激光光源模块 激光频率噪声 0.19 激光频率噪声$\delta f$≤10 Hz/Hz1/2@1 mHz 外差调制模块 前端光程耦合噪声 0.5 温度波动$\delta T $≤0.1 mK/Hz1/2@1 mHz 一体化干涉平台 温度光程耦合噪声 0.5 温度光程耦合系数dS/dT=5 nm/K,
测试环境温度波动$\delta T $≤0.1 mK/Hz1/2@1 mHz相位采集模块 探测器耦合噪声 0.2 高增益、低带宽、高响应度 相位读取噪声 0.1 高采样位数和高采样率 标准平面镜 位置失调噪声 0.5 标准平面镜长期角度不稳定性φ优于35 nrad/Hz1/2@1 mHz 待测望远镜 环境波动噪声 0.4 温度波动$\delta T $≤0.1 mK/Hz1/2@1 mHz;真空度≤0.1 mPa 测量系统总体噪声 1 表 2 望远镜前端干涉测量系统光程噪声理论水平
Table 2. Theoretical level of optical path noise for the interferometric measurement system at the front end of the telescope
测量系统组成模块 主要噪声 等效光程噪声@10mHz 激光光源模块 激光频率噪声 3.4 pm/Hz1/2 外差调制模块 前端光程耦合噪声 0.5 nm/Hz1/2 一体化干涉平台 温度光程耦合噪声 7.28 nm/Hz1/2 相位采集模块 探测器耦合噪声 0.56 nm/Hz1/2 相位读取噪声 1 pm/Hz1/2 总体噪声 7.319 nm/Hz1/2 -
[1] Baker J, Bellovary J, Bender P L, et al. The laser interferometer space antenna: unveiling the millihertz gravitational wave sky[Z]. arXiv: 1907.06482, 2019. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1907.06482.
[2] Luo J, Chen L S, Duan H Z, et al. TianQin: a space-borne gravitational wave detector[J]. Class Quantum Grav, 2016, 33(3): 035010. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/33/3/035010
[3] 胡一鸣, 梅健伟, 罗俊. 天琴计划与国际合作[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(24): 2475−2483. doi: 10.1360/N972019-00046
Hu Y M, Mei J W, Luo J. TianQin project and international collaboration[J]. Chin Sci Bull, 2019, 64(24): 2475−2483. doi: 10.1360/N972019-00046
[4] 罗俊, 艾凌皓, 艾艳丽, 等. 天琴计划简介[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 60(1-2): 1−19. doi: 10.13471/j.cnki.acta.snus.2020.12.23.2020B154
Luo J, Ai L H, Ai Y L, et al. A brief introduction to the TianQin project[J]. Acta Sci Nat Univ Sunyatseni, 2021, 60(1-2): 1−19. doi: 10.13471/j.cnki.acta.snus.2020.12.23.2020B154
[5] 罗子人, 白姗, 边星, 等. 空间激光干涉引力波探测[J]. 力学进展, 2013, 43(4): 415−447. doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-13-044
Luo Z R, Bai S, Bian X, et al. Gravitational wave detection by space laser interferometry[J]. Adv Mech, 2013, 43(4): 415−447. doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-13-044
[6] 罗子人, 张敏, 靳刚, 等. 中国空间引力波探测“太极计划”及“太极1号”在轨测试[J]. 深空探测学报, 2020, 7(1): 3−10. doi: 10.15982/j.issn.2095-7777.2020.20191230001
Luo Z R, Zhang M, Jin G, et al. Introduction of Chinese space-borne gravitational wave detection program “Taiji” and “Taiji-1” satellite mission[J]. J Deep Space Explor, 2020, 7(1): 3−10. doi: 10.15982/j.issn.2095-7777.2020.20191230001
[7] 范纹彤, 赵宏超, 范磊, 等. 空间引力波探测望远镜系统技术初步分析[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 60(1-2): 178−185. doi: 10.13471/j.cnki.acta.snus.2020.11.02.2020b111
Fan W T, Zhao H C, Fan L, et al. Preliminary analysis of space gravitational wave detection telescope system technology[J]. Acta Sci Nat Univ Sunyatseni, 2021, 60(1-2): 178−185. doi: 10.13471/j.cnki.acta.snus.2020.11.02.2020b111
[8] Lucarelli S, Scheulen D, Kemper D, et al. The breadboard model of the LISA telescope assembly[J]. Proc SPIE, 2017, 10564: 105640J. doi: 10.1117/12.2309050
[9] Verlaan A L, Hogenhuis H, Pijnenburg J, et al. LISA telescope assembly optical stability characterization for ESA[J]. Proc SPIE, 2017, 10564: 105640K. doi: 10.1117/12.2309058
[10] Sanjuán J, Korytov D, Mueller G, et al. Note: silicon carbide telescope dimensional stability for space-based gravitational wave detectors[J]. Rev Sci Instrum, 2012, 83(11): 116107. doi: 10.1063/1.4767247
[11] Kulkarni S, Umińska A A, Sanjuán J, et al. Characterization of dimensional stability for materials used in ultra-stable structures[J]. Proc SPIE, 2021, 11820: 1182008. doi: 10.1117/12.2594661
[12] Umińska A A, Kulkarni S, Sanjuan J, et al. Ground testing of the LISA telescope[J]. Proc SPIE, 2021, 11820: 118200I. doi: 10.1117/12.2594605
[13] Kitamoto K, Kamiya T, Mizutani T. Evaluation of dimensional stability of metering truss structure using built-in laser interferometric dilatometer[J]. Eng Res Express, 2020, 2(4): 045023. doi: 10.1088/2631-8695/abc9cf
[14] Jersey K, Zhang YQ, Harley-Trochimczyk I, et al. Design, fabrication, and testing of an optical truss interferometer for the LISA telescope[J]. Proc SPIE, 2021, 11820: 118200L. doi: 10.1117/12.2594738
[15] Sang B L, Deng X Q, Peng B, et al. Dimensional stability ground test and in-orbit prediction of SiC telescope frame for space gravitational wave detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 21041−21047. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3152490
[16] Watchi J, Cooper S, Ding B L, et al. Contributed review: a review of compact interferometers[J]. Rev Sci Instrum, 2018, 89(12): 121501. doi: 10.1063/1.5052042
[17] Lieser M D. LISA optical bench development: experimental investigation of tilt-to-length coupling for a spaceborne gravitational wave detector[D]. Hannover: Leibniz University Hannover, 2017.
[18] Dehne M. Construction and noise behaviour of ultra-stable optical systems for space interferometers[D]. Hannover: Leibniz University Hannover, 2012.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
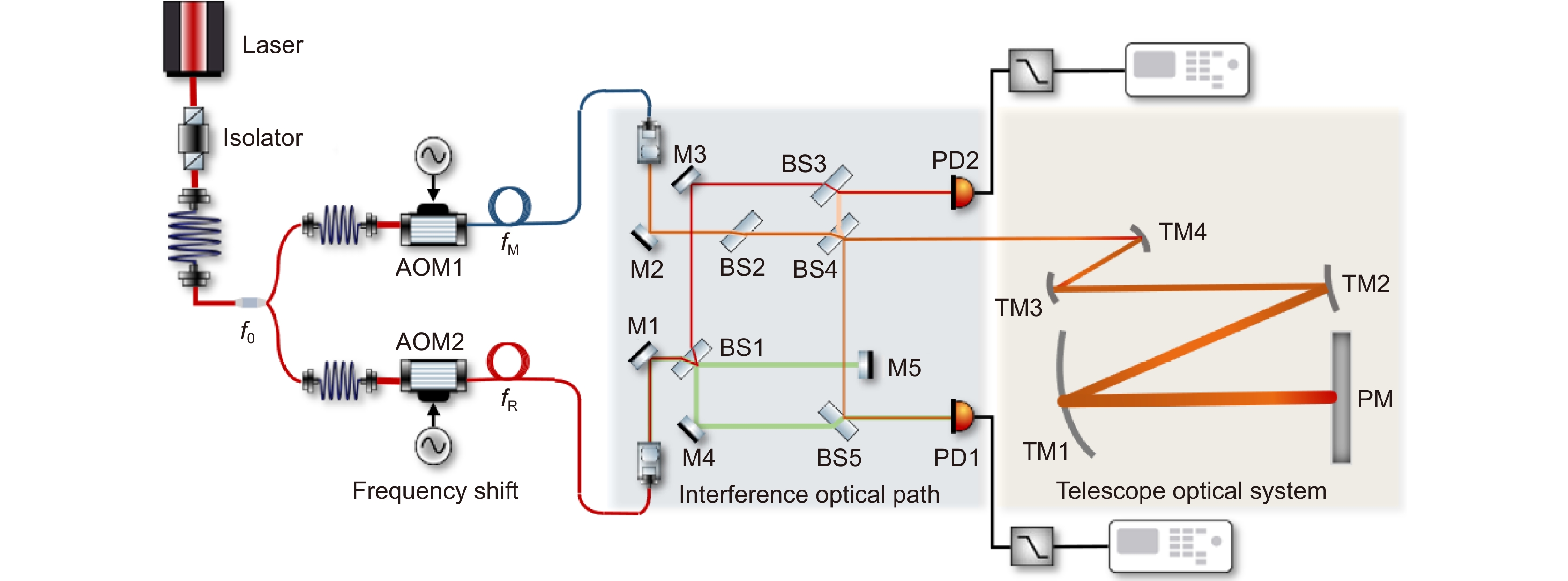
 下载:
下载: