Research on resonance characteristics of photoelastic modulators and self-tracking of resonant frequency
-
摘要
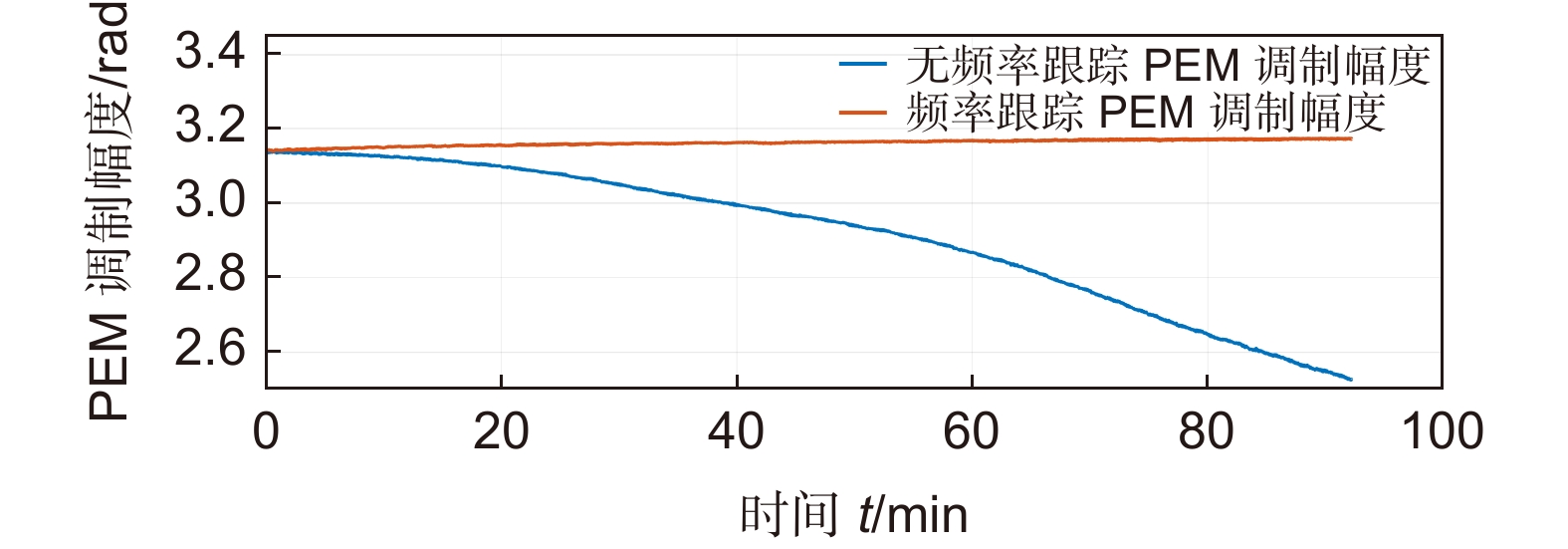
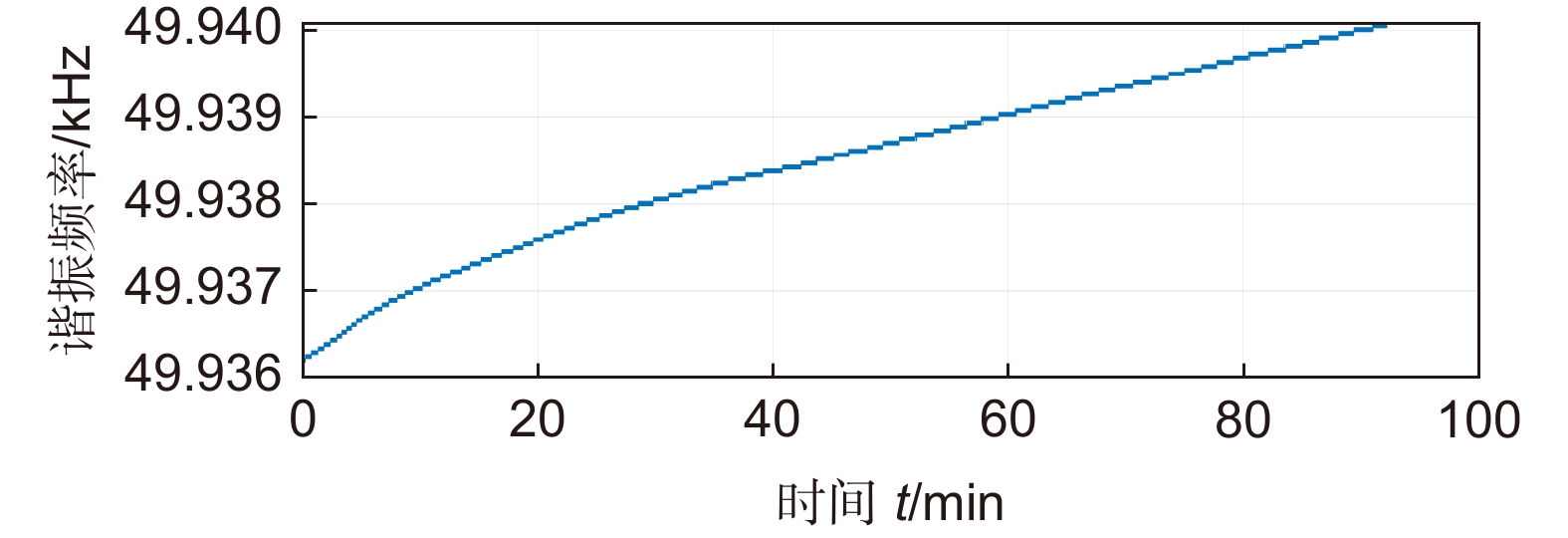
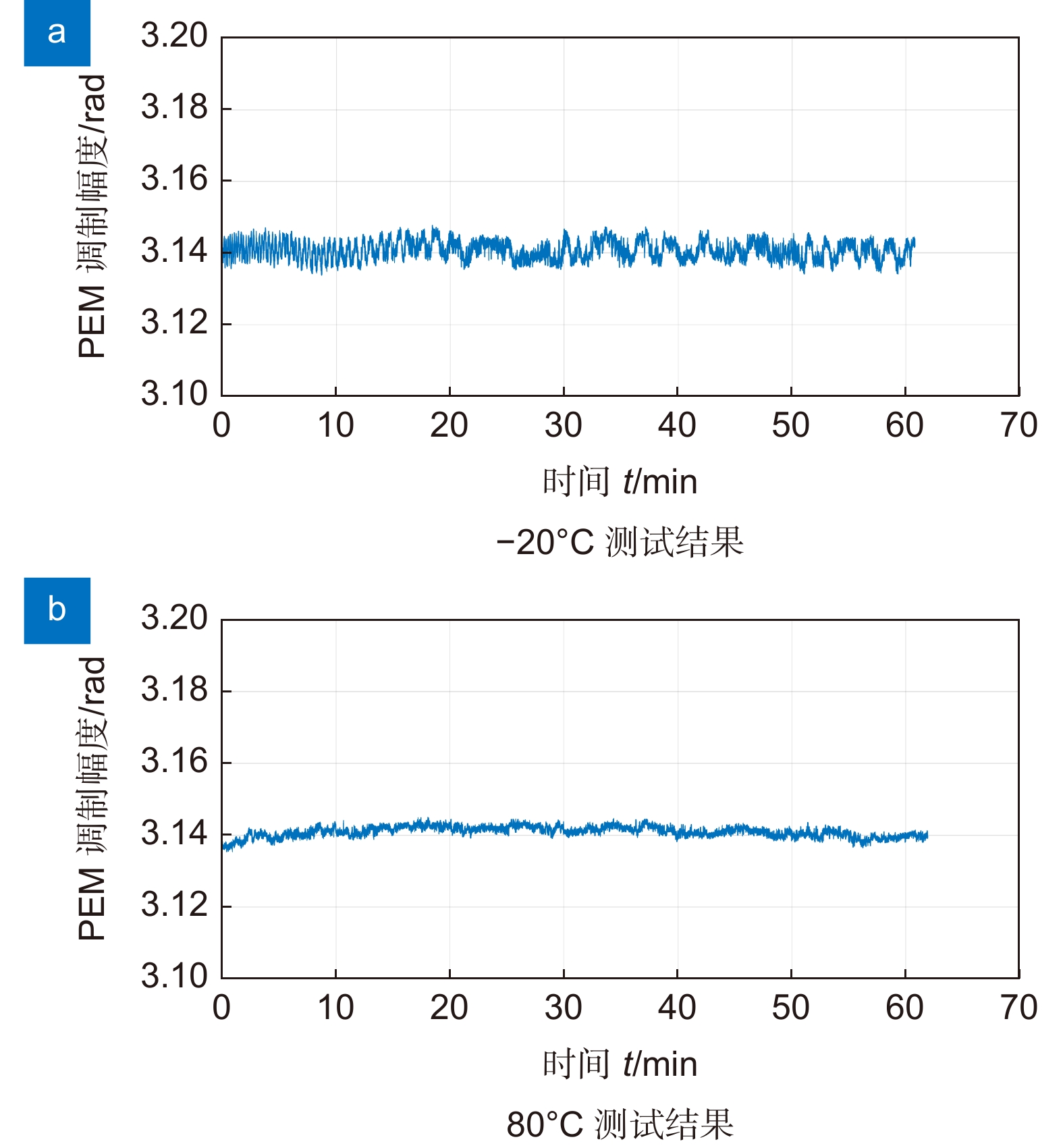
弹光调制器是一种由各向同性的弹光晶体和压电晶体组成的高品质因数热机电耦合器件,广泛用于偏振测量、光谱测量等诸多领域。但是在高压谐振状态下,其谐振频率会随着温度变化出现漂移,导致弹光调制器的相位调制幅值不稳定以及驱动效率降低。针对该问题,首先对弹光调制器谐振频率特性进行分析,建立了弹光调制器及其高压谐振驱动电路的复合谐振网络模型,提出了利用谐振网络的幅频特性进行频率跟踪的实现方法,并设计了基于现场可编程门阵列(field programmable gate array,FPGA)的控制测试系统,实现了谐振频率跟踪以及调制幅度的测量。通过测试验证了该方案可有效进行谐振频率跟踪,提高了弹光调制器的稳定性以及驱动效率,测试时长大于90 min,相位调制幅度的标准偏差为0.83% rad。
Abstract
As a kind of high-quality factor thermo-electromechanical coupling device composed of isotropic elastic-optical crystal and piezoelectric crystal, photoelastic modulator (PEM) is widely applied for polarization measurement, spectrum measurement, and many other purposes. However, the resonant frequency tends to drift with temperature changes in the high-voltage resonant state, which destabilizes the phase modulation amplitude of the photoelastic modulator and reduces the driving efficiency. To solve this problem, the resonant frequency characteristics of the photoelastic modulator are analyzed at first. Then, a compound resonant network model of the photoelastic modulator and its high voltage resonant driving circuit is established, and a solution to frequency tracking based on the amplitude-frequency characteristics of the resonant network is proposed. Besides, a control test system based on field programmable gate array (FPGA) is developed to achieve resonant frequency tracking and modulation amplitude measurement. The test results show that this method is applicable to track the resonant frequency effectively and improve the stability and driving efficiency of the elastic light modulator. The duration of the test exceeds 90 min, and the standard deviation of the phase modulation amplitude is 0.83% rad.
-
Overview
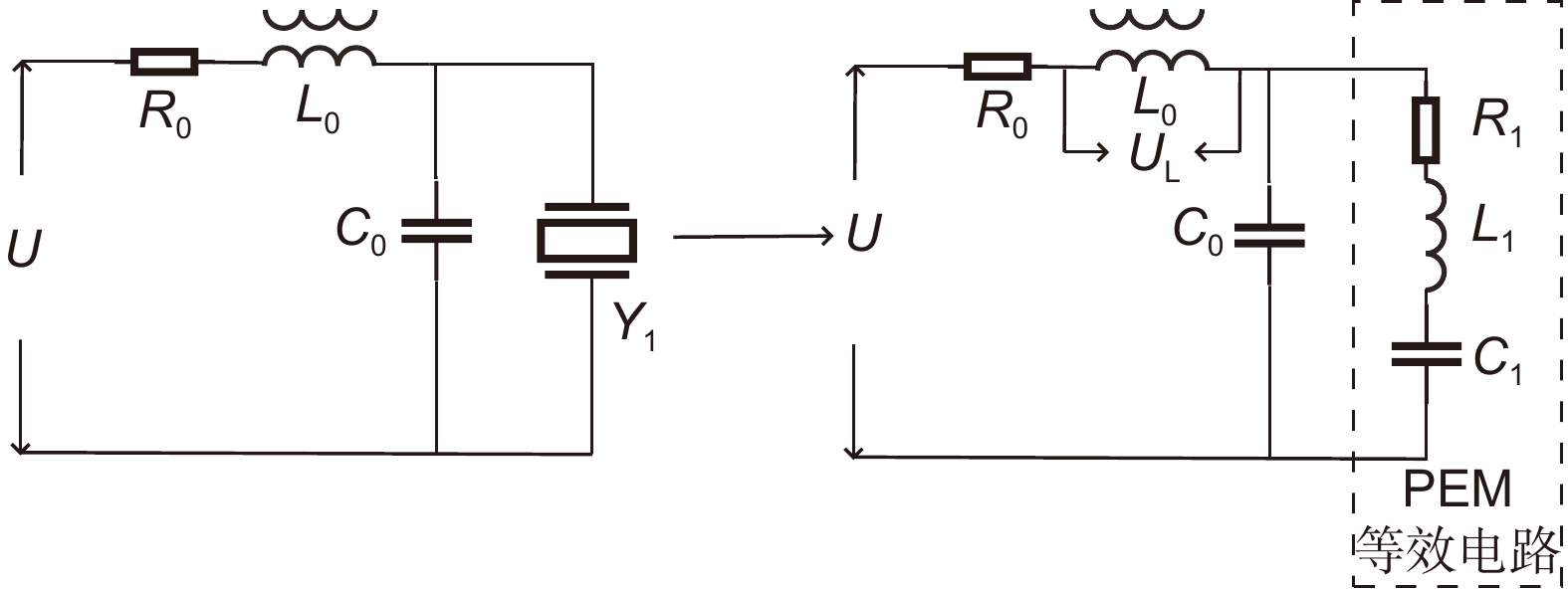
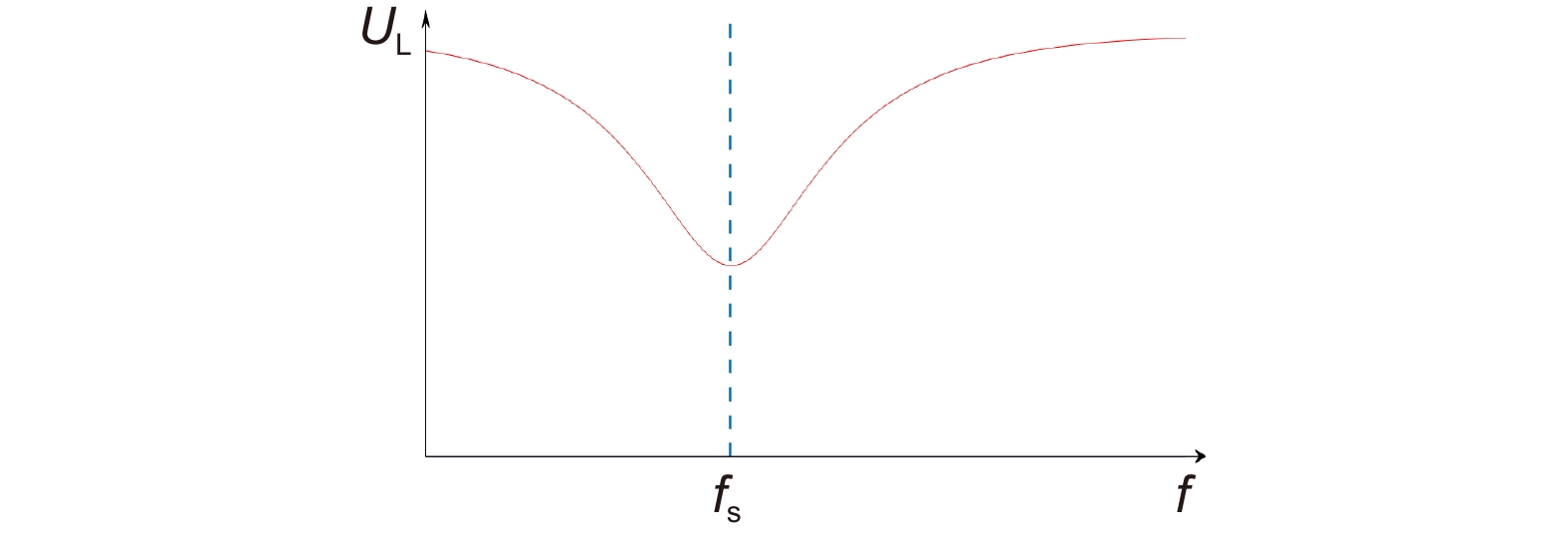
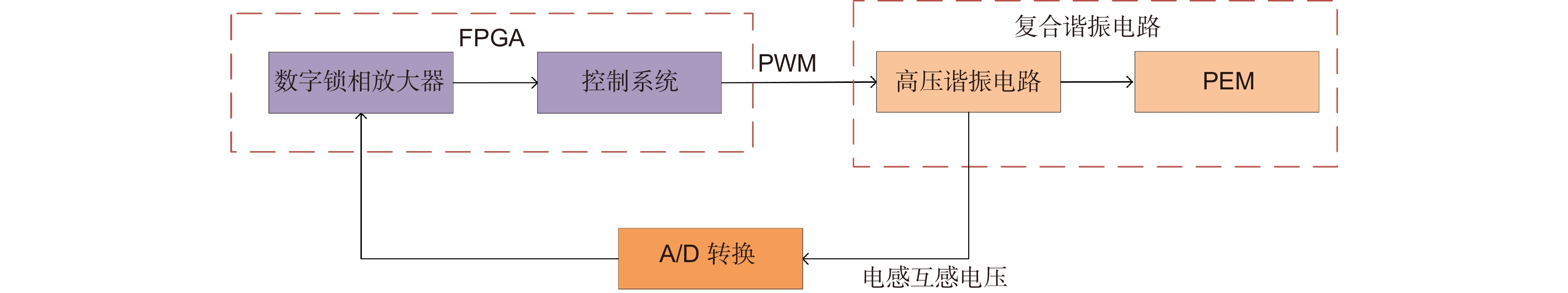
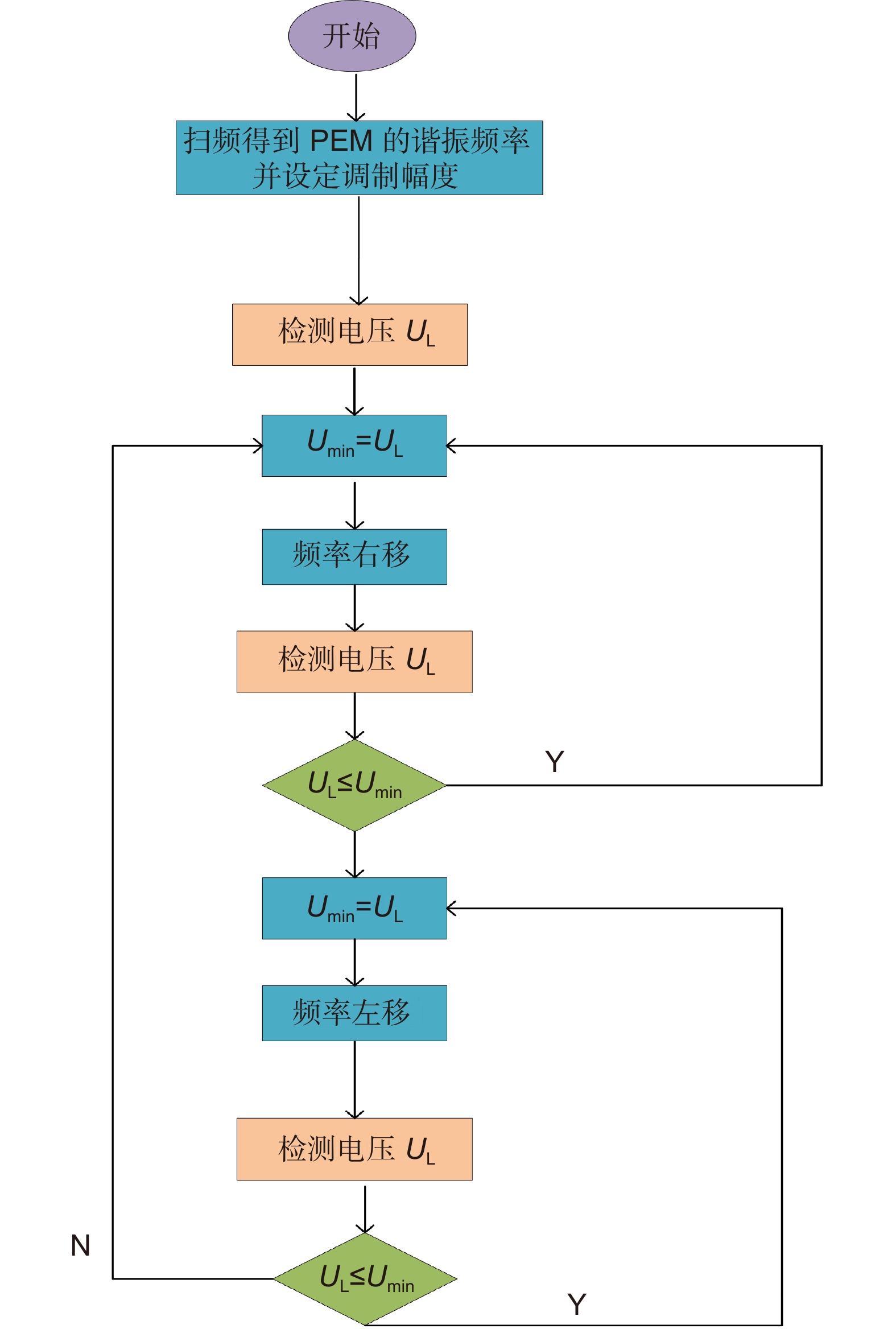
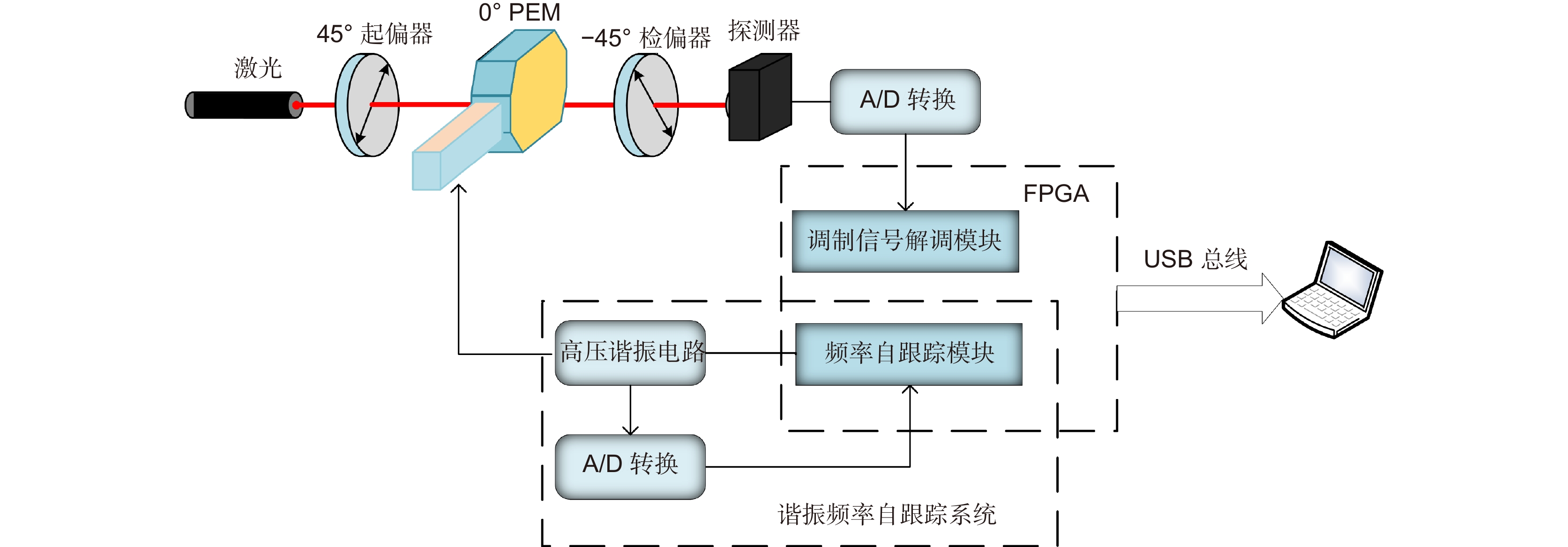
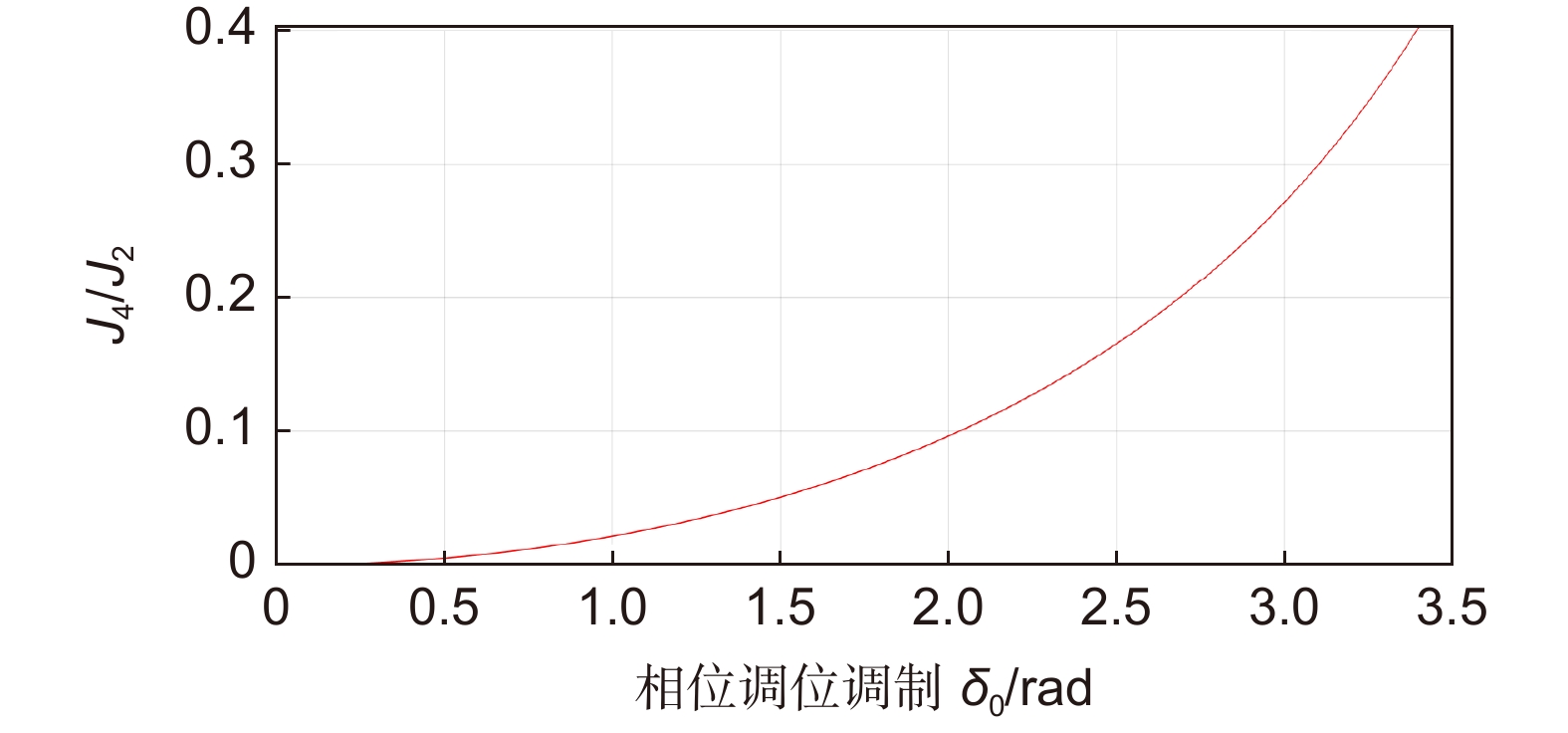
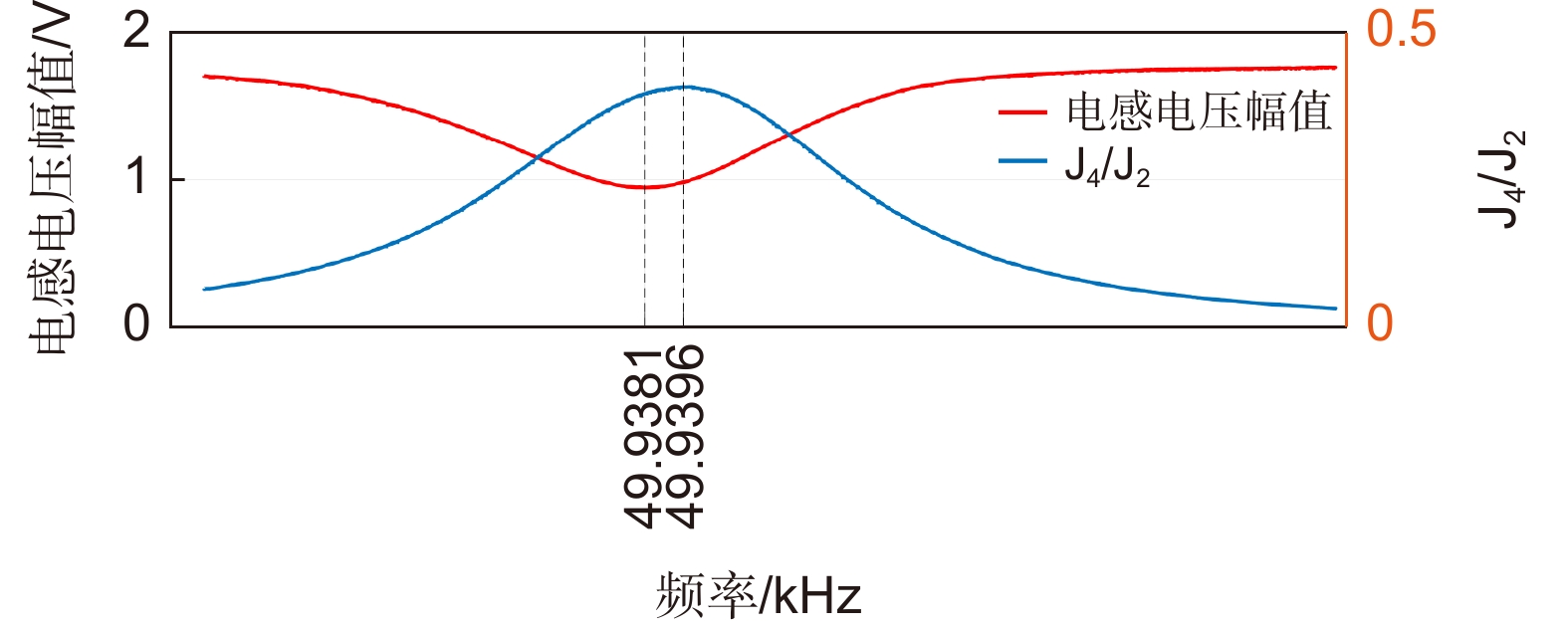
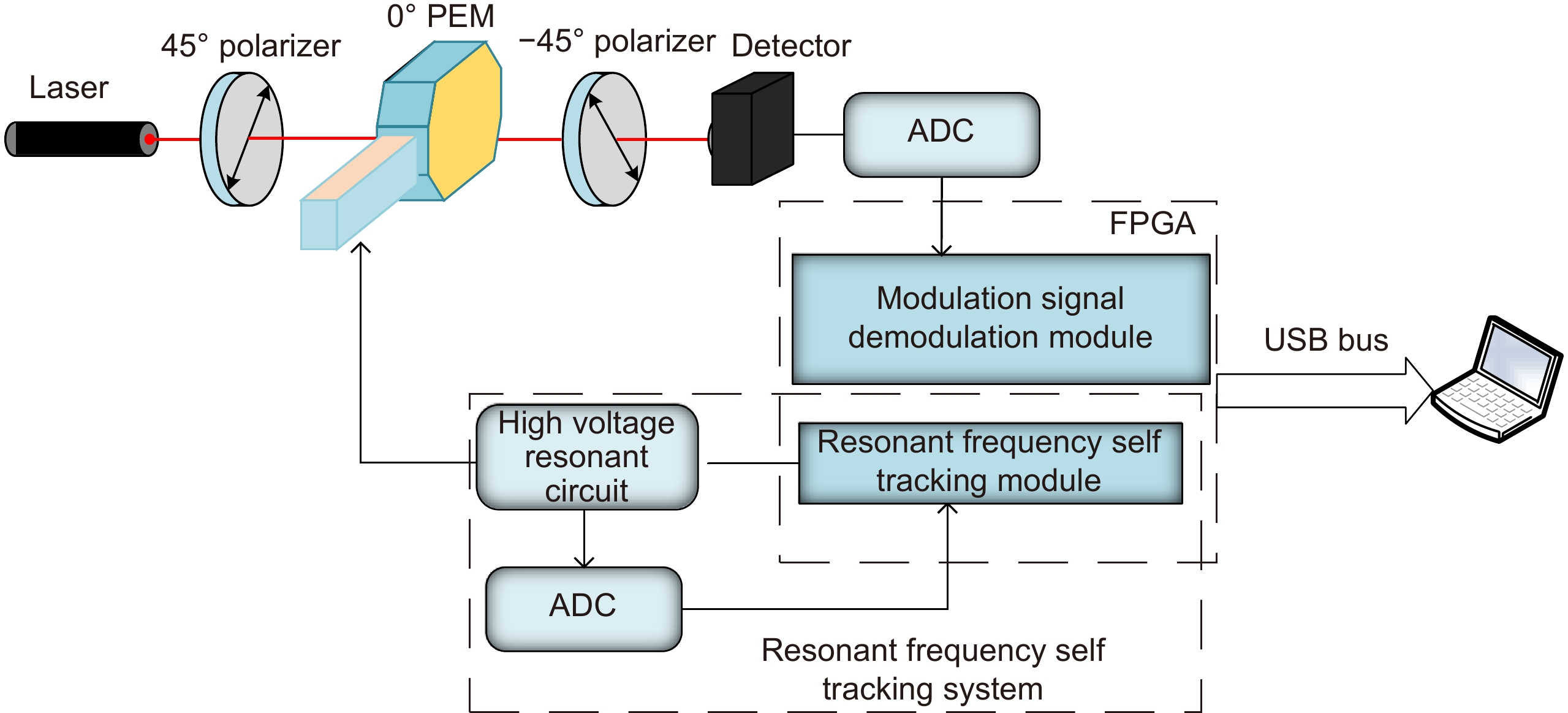
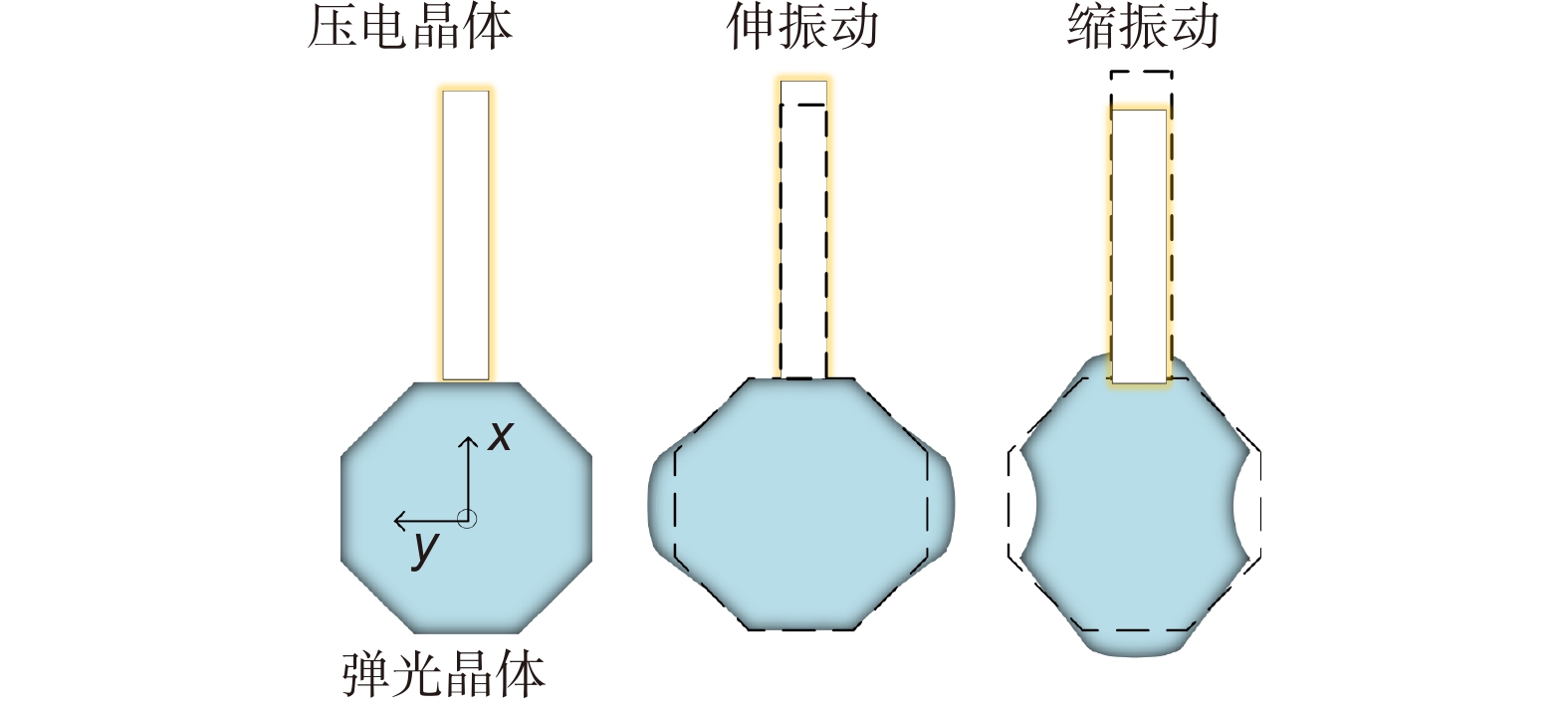
Overview: Overview: Photoelastic modulator, a high-quality thermo-mechanical coupling device composed of isotropic elastic optical crystal and piezoelectric crystal, is widely used in polarization measurement, spectral measurement, and many other fields. A high-voltage resonant circuit is adopted to generate the periodically changing high voltage amplitude, which is applied to both ends of the piezoelectric crystal to drive the photoelastic modulator to perform forced telescopic vibration, thus generating periodic birefringence. Although the quality factor of the photoelastic modulator is as high as 103, the photoelastic crystal in the photoelastic modulator will vibrate in length under the action of the piezoelectric crystal when driven by the high voltage. In addition, there will be thermal dissipation caused by dielectric loss and mechanical loss, some of which exchange heat with the environment, and the rest will raise the temperature of the photoelastic modulator itself. When the heat exchange between the photoelastic modulator and the external environment is happened before the heat balance, the resonant frequency will be changed, which will lead to the reduction of the modulator driving efficiency and the instability of the modulation amplitude. Standing from the perspective of mechanical point, the system can be equivalent to the vibration model of a damped spring-mass system. The system is an underdamped second-order system, and the modulator can also be equivalent to a RLC series resonant circuit from the electrical perspective. Therefore, when the temperature of the modulator changes, its electrical parameters and resonat will also vary. Therefore, this paper first analyzes the resonant frequency characteristics of the photoelastic modulator from the perspective of electricity, and establishes the equivalent circuit model of the photoelastic modulator and the composite resonant network model with the high-voltage resonant drive circuit. Meanwhile, the resonant network is analyzed, and the results show that when the phoyoelastic is in the resonant state, the modulator impedance and the inductance voltage amplitude of the high-voltage resonant circuit are both the smallest. Therefore, this paper designs a control and test system based on field programmable gate array (FPGA) by combining the above mentioned characteristic and applying the amplitude and frequency characteristics of the resonant network. FPGA completes the measurement of the inductance voltage amplitude and the demodulation of the photoelastic modulation signal through the digital phase-locked amplifier. After obtaining the inductance voltage amplitude, the real-time tracking of the minimum value of the inductance voltage amplitude can be obtained by FPGA, so that the tracking of the resonant frequency of the photoelastic modulator can be realized. By demodulating the modulated signal, the calibration optical path system of the photoelastic modulator is also capable of measuring the modulation amplitude of the modulator. Finally, this paper successfully builds the test system, and conducts the frequency sweep test to verify the feasibility of the resonance tracking system. The resonance tracking tests on the modulator are implemented at room temperature - 20℃ & 80℃ respectively. The results show that the test meets the requirements, and the maximum standard deviation of modulation amplitude is lower than 0.83% rad.
-

-
-
参考文献
[1] 张敏娟. 弹光调制傅里叶变换光谱复原高速数据处理技术研究[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2013.
Zhang M J. The research of high-speed data processing technology of the photo-elastic modulation fourier transform spectral reconstruction[D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2013.
[2] Hipps K W, Crosby G A. Applications of the photoelastic modulator to polarization spectroscopy[J]. J Phys Chem, 1979, 83(5): 555−562. doi: 10.1021/j100468a001
[3] Su F, Zhang B W, Li T H. High speed stress measurement technique based on photoelastic modulator (PEM) and galvano-scanner[J]. Opt Lasers Eng, 2021, 136: 106306. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2020.106306
[4] Wang S, Han X, Wang Y N, et al. Dispersion of the retardation of a photoelastic modulator[J]. Appl Sci, 2019, 9(2): 341. doi: 10.3390/app9020341
[5] Quan W, Wang Q H, Zhai Y Y. A dual closed-loop drive and control system of photoelastic modulator for atomic magnetometer[J]. Meas Sci Technol, 2018, 29(6): 065105. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/aab6f4
[6] Hirschy L, Wang B L, Wolf J, et al. Basic optical properties of the photoelastic modulator. Part III: thermal properties[J]. Proc SPIE, 2012, 8486: 848619. doi: 10.1117/12.930285
[7] 梁振坤, 李晓, 王志斌, 等. 基于驱动电压自适应调节的弹光调制[J]. 中国激光, 2021, 48(11): 1104001. doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.1104001
Liang Z K, Li X, Wang Z B, et al. Photo-elastic modulation based on adaptive regulation of driving voltage[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2021, 48(11): 1104001. doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.1104001
[8] 陈光威, 安永泉, 王志斌, 等. 弹光调制的频率自跟踪技术[J]. 光电工程, 2015, 42(10): 21−26,32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2015.10.004
Chen G W, An Y Q, Wang Z B, et al. Self tracking technology of photoelastic modulation frequency[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2015, 42(10): 21−26,32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2015.10.004
[9] Wang B L, Hinds E, Krivoy E. Basic optical properties of the photoelastic modulator part II: residual birefringence in the optical element[J]. Proc SPIE, 2009, 7461: 746110. doi: 10.1117/12.826392
[10] 魏海潮. 弹光调制器及其高压驱动技术研究[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2013.
Wei H C. The study of photoelastic modulator and its high-voltage drive technology[D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2013.
[11] 王艳超. 弹光调制傅里叶变换光谱仪稳定性研究[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2014.
Wang Y C. The research on stability of photoelastic modulation fourier transform spectrometer[D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2014.
[12] 李健. 数字锁相放大器在微弱光电信号检测中的应用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2016.
Li J. Research on the application of digital lock-in amplifier in the detection of weak photoelectric signal[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2016.
[13] 周军. 光弹调制器应用的Mueller矩阵分析[J]. 常熟高专学报, 2001, 15(4): 19−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2794.2001.04.007
Zhou J. Mueller matrix analysis of photoelastic modulator[J]. J Changshu Coll, 2001, 15(4): 19−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2794.2001.04.007
[14] Zeng A J, Huang L H, Dong Z R, et al. Calibration method for a photoelastic modulator with a peak retardation of less than a half-wavelength[J]. Appl Opt, 2007, 46(5): 699−703. doi: 10.1364/AO.46.000699
[15] Wang M W, Tsai F H, Chao Y F. In situ calibration technique for photoelastic modulator in ellipsometry[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2004, 455–456: 78−83. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2003.12.048
[16] 武燕婷, 熊伟, 李超波, 等. 光弹调制器谐振特性的研究及验证[J]. 光学学报, 2021, 41(15): 1523002. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1523002
Wu Y T, Xiong W, Li C B, et al. Research and verification on resonance characteristics of photoelastic modulator[J]. Acta Opt Sin, 2021, 41(15): 1523002. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1523002
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: