Longitudinal super-resolution spherical multi-focus array based on column vector light modulation
-
摘要:
激光多焦点阵列以兼具更高的光场操控自由度和焦斑单元高空间分辨率的特点,被广泛应用在光学诱捕以及飞秒激光微纳制造等领域。然而由于阵列中焦斑的纵向分辨率弱于横向分辨率,在激光加工应用中限制了其对各向同性结构的加工能力。因此,本文提出一种基于柱矢量光调控生成纵向超分辨准球形多焦点阵列的方法。利用对柱矢量光的两组基径向偏振光和角向偏振光分别进行聚焦调控,结合环形衰减调制可形成纵向超分辨焦斑,再将两种偏振光场以适当的振幅比例在焦区叠加,从而合成准球形多焦点阵列。实验结果表明,10×10的多焦点阵列中各焦斑尺寸均一,具有近球形光强分布。其中,阵列中所有焦点的纵向半高全宽的平均值为0.76
λ 、标准差为0.005λ ,横向半高全宽的平均值为0.76λ 、标准差为0.019λ 。该具有高尺寸均一性的准球形多焦点阵列可为激光微纳加工精准制备微纳器件提供新的途径。Abstract:Featured by the capability of multi degree-of-freedom light-field manipulations while reserving high spatial resolution, multifocal laser arrays have been widely applied in femtosecond laser micro/nanofabrication, optical trapping, and so forth. Yet, due to the relatively lower axial resolution of single focuses within the array in comparison with the lateral resolution of their own, multifocal laser array has been refrained from isotropic 3D nanofabrication. Herein, we propose a feasible method for generation of axially super-resolved multifocal array with quasi-spherical focal spots. In particular, quasi-spherical multifocal array is optically synthesized via precise modulation on the coherent superposition of the orthogonal radially polarized beam (RPB) and azimuthally polarized beam (APB) states in the focal region based on annular amplitude modulation. We show theoretically the generation of quasi-spherical multifocal array with a high uniformity up to 99%. The average axial and lateral full-width-half maximum (FWHM) of the focal array are measured to be 0.76
λ with the standard deviations in the axial and lateral directions being 0.005λ and 0.019λ , respectively. The presented strategy for synthesis of quasi-spherical multifocal array with high uniformity paves the way for high-precision laser fabrication of 3D micro/nano devices. -
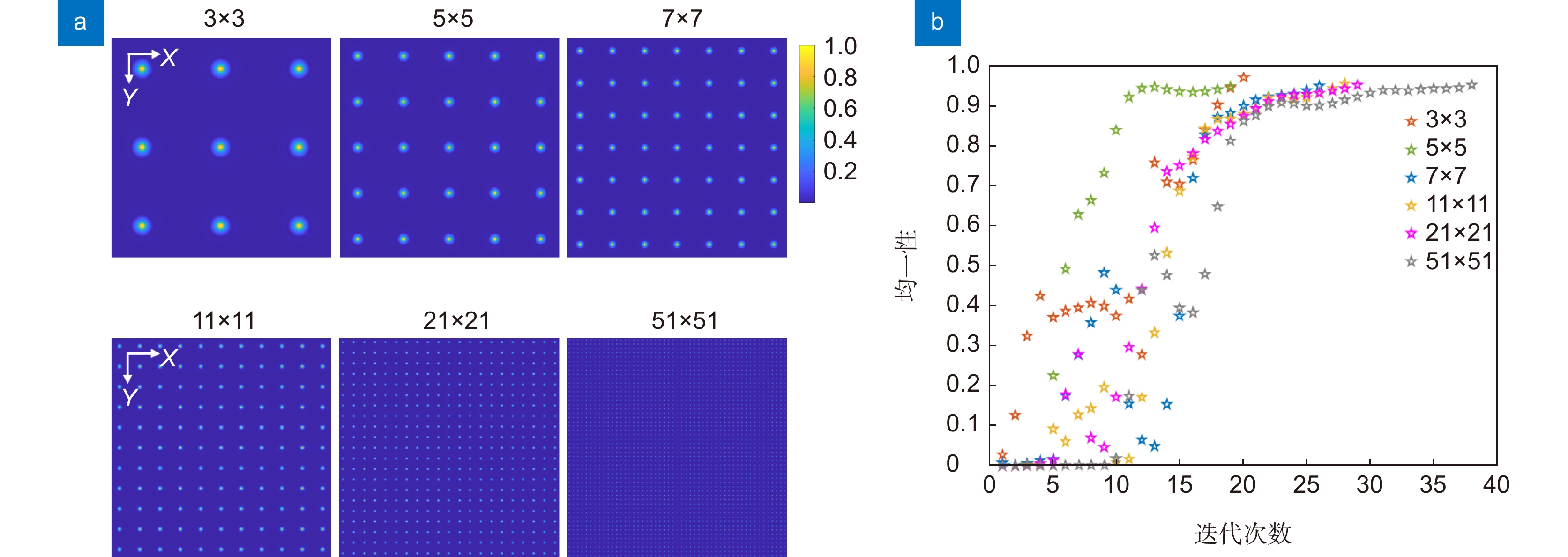
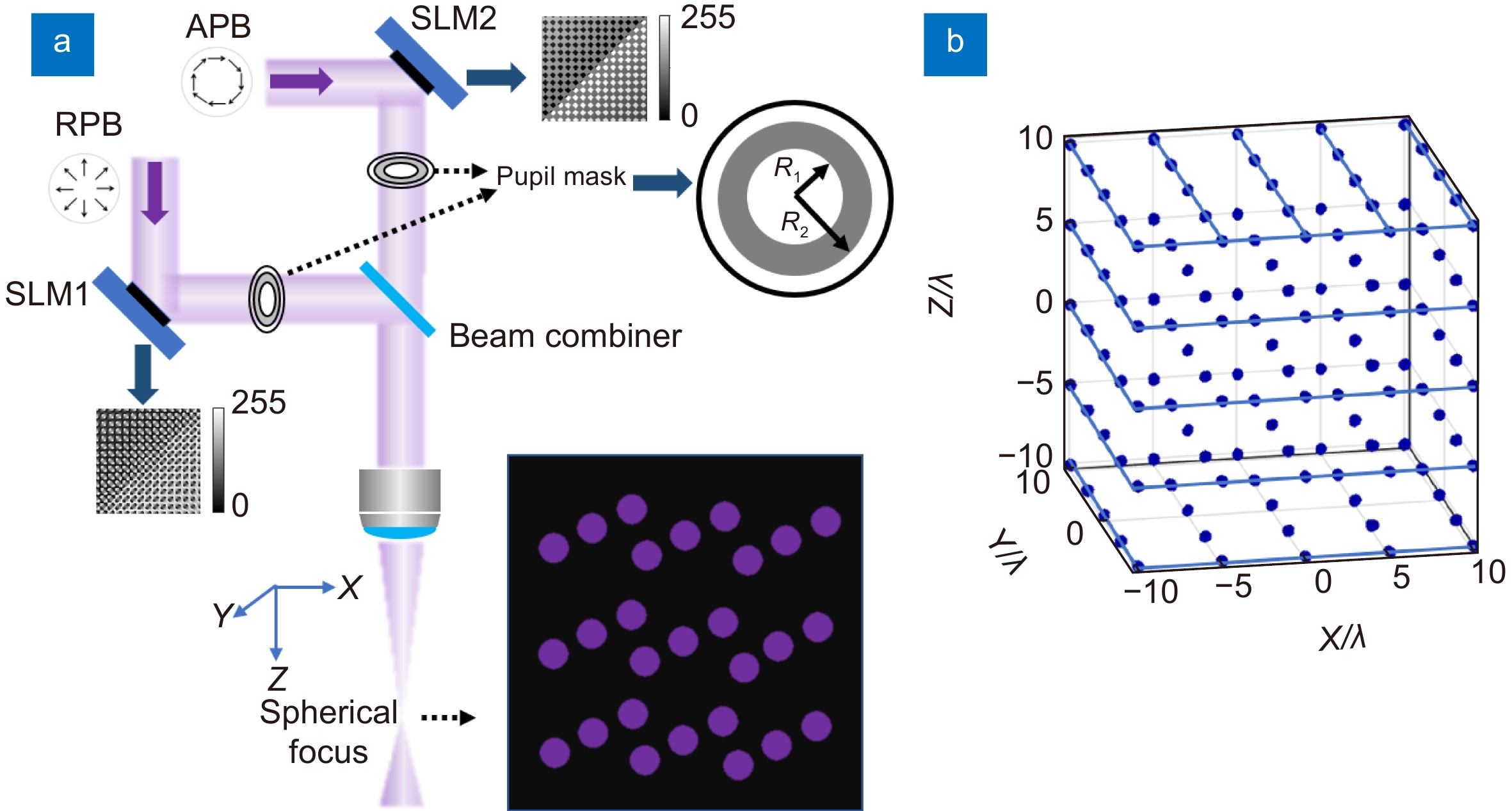
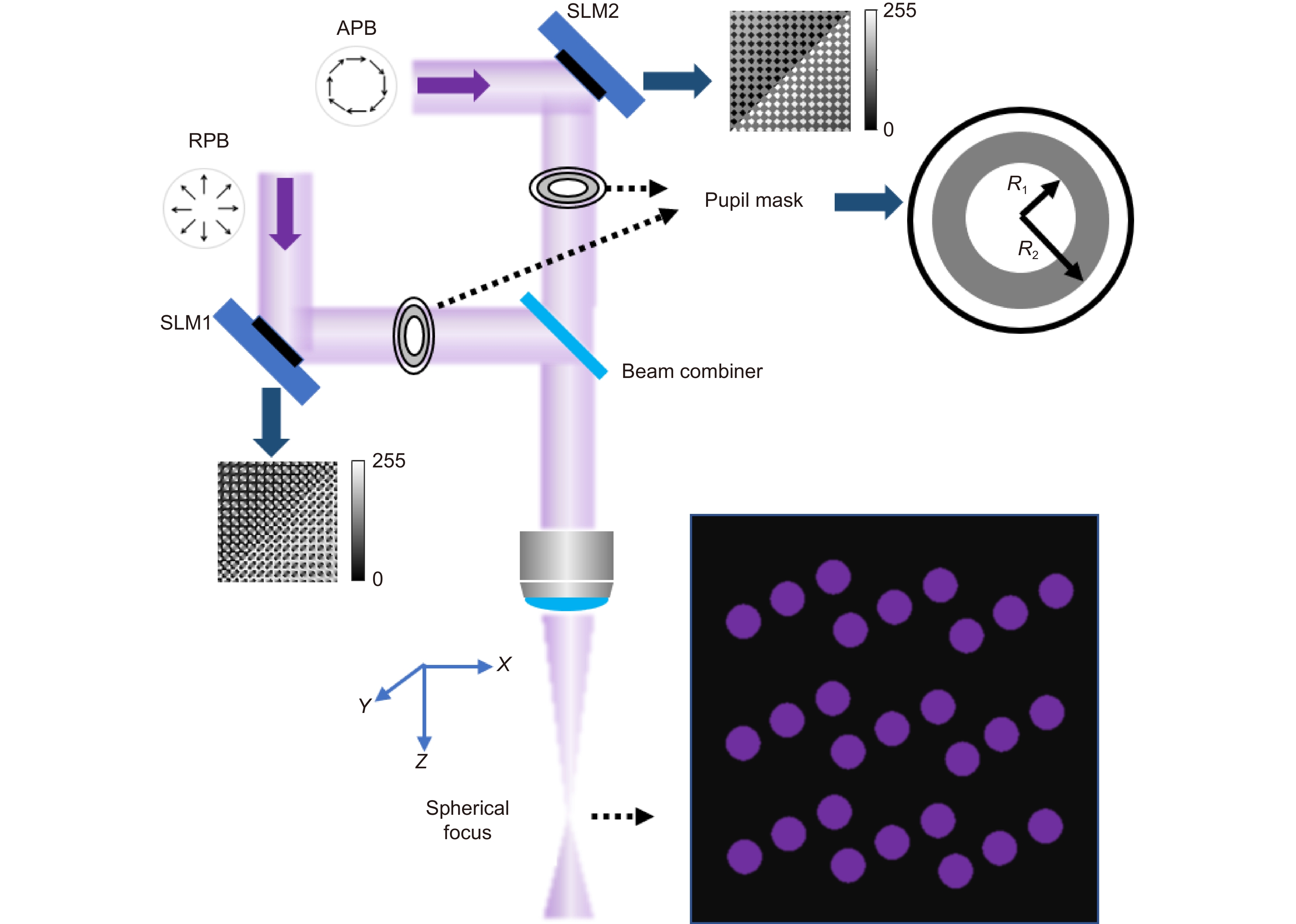
Overview: Featured by the capability of multi degree-of-freedom light-field manipulations while reserving high spatial resolution, multifocal laser arrays have been widely applied in femtosecond laser micro/nanofabrication, optical trapping, etc. However, for lens diffraction, the smaller momentum spread along the optical axis with respect to that in the transverse direction could introduce a larger position spread in real space, which in turn leads to lower axial resolution than the transverse resolution. The anisotropy of the focused laser beam, inherent regardless of paraxial or tight-focusing cases, has been a great hurdle for laser printing of functional microdevices with precise control on feature size and improved mechanical performances. To this end, in this research, a feasible method for generation of isotropic focused laser beam with quasi-spherical 3D point spread function (PSF) is developed based on vectorial light field modulation. We demonstrate that through simultaneous implementation of phase modulation and amplitude modulation, homogeneous multifocal array with quasi-spherical focal spots can be generated. Particularly, with the use of a well-designed annular mask, the suppression on the axial spread of field is accomplished via accurate control on the coherent superposition of the orthogonal radially polarized beam (RPB) and azimuthally polarized beam (APB) in the focal region since the depolarized axial component of the AP beam vanishes in vicinity of the gaussian focus even under tight focusing condition. Using the proposed method, isotropic 3D PSF with identical axial and transverse FWHM of 0.71λ is achieved. Meanwhile, based on iterative phase retrieval algorithm, phase-only holograms are designed and employed transforming the incident wavelet as the summation of sub-wavelets, yielding multiple converging sites in 3D space, thereby generating the multifocal array. We further present the synthesis of quasi-spherical multifocal array. A high uniformity up to 99% for a 10-by-10 multifocal array, in which the single focus elements share near-identical axial and transverse FWHM, being 0.76λ on average. The standard deviation of the axial and transverse FWHM of the multifocal array are evaluated be 0.005λ and 0.019λ, respectively, highlighting the features of high uniformity and isotropy. The reported strategy renders precise control on the axial feature size and is potential for the application in high-precision parallel laser printing technique.
-

-
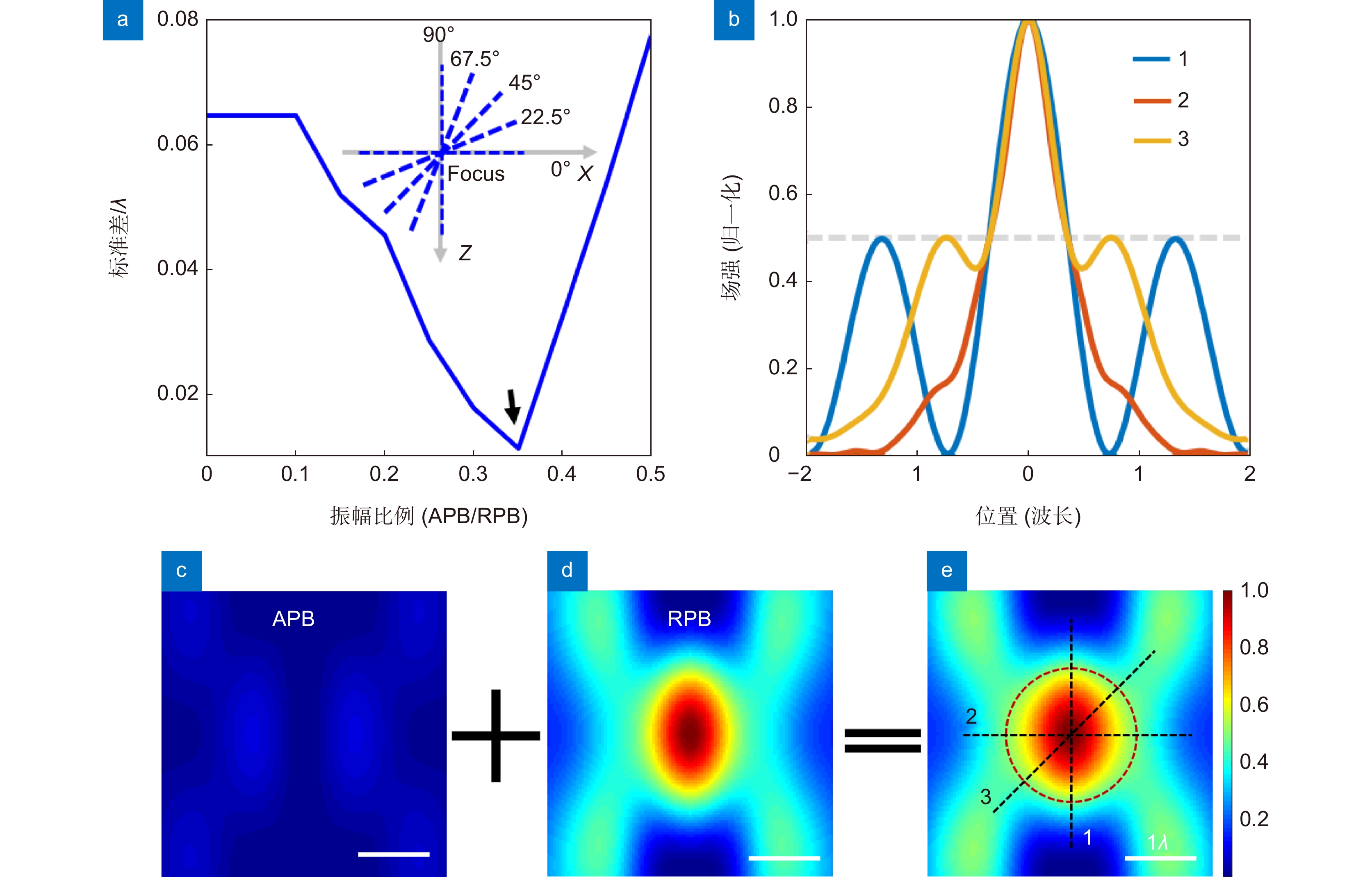
图 2 (a) 在角向偏振光和径向偏振光的不同振幅比下合成焦点的五个方向上的半高全宽的标准差;(b) 合成焦点的强度分布沿不同方向的场强曲线; (c)~(e) 角向偏振光叠加径向偏振光生成合成焦点的二维强度分布
Figure 2. (a) The standard deviation of the full width at half maximum in the five directions of the composite focus under different amplitude ratios of angularly polarized beam and radially polarized beam; (b) Field strength curves of the intensity distribution of the synthetic focus along different directions; (c)~(e) Azimuthal polarized beam superimposed on radially polarized beam to generate a two-dimensional intensity distribution of the composite focus
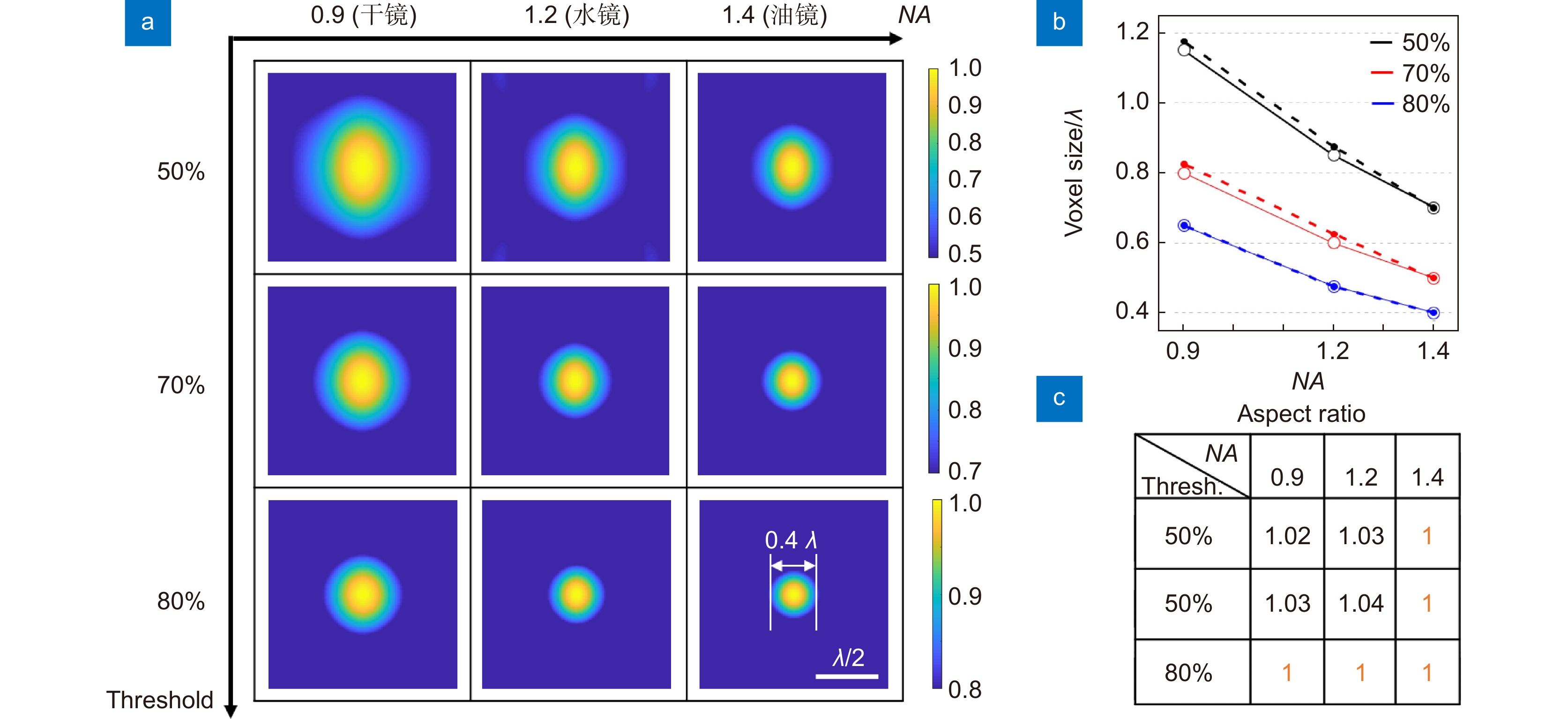
图 3 (a)~(b) x-z平面上叠加生成的球形焦点的二维光场强度分布,以及在不同阈值和不同物镜NAs下的横向和纵向尺寸大小,虚线是纵向尺寸、实线是横向尺寸;(c) 在不同的阈值强度和数值孔径下的角向偏振光与径向偏振光焦点的纵向和横向半高全宽的比值
Figure 3. (a)~(b) Two-dimensional light field intensity distributions of spherical foci generated by superposition in the x-z plane, as well as lateral and longitudinal dimensions at different thresholds and different objective NAs, where the dotted line is the longitudinal dimension and the solid line is the transverse dimension; (c) The ratio of the longitudinal and transverse full width at half maximum of the focal point for angularly polarized light to radially polarized light at different threshold intensities and numerical apertures
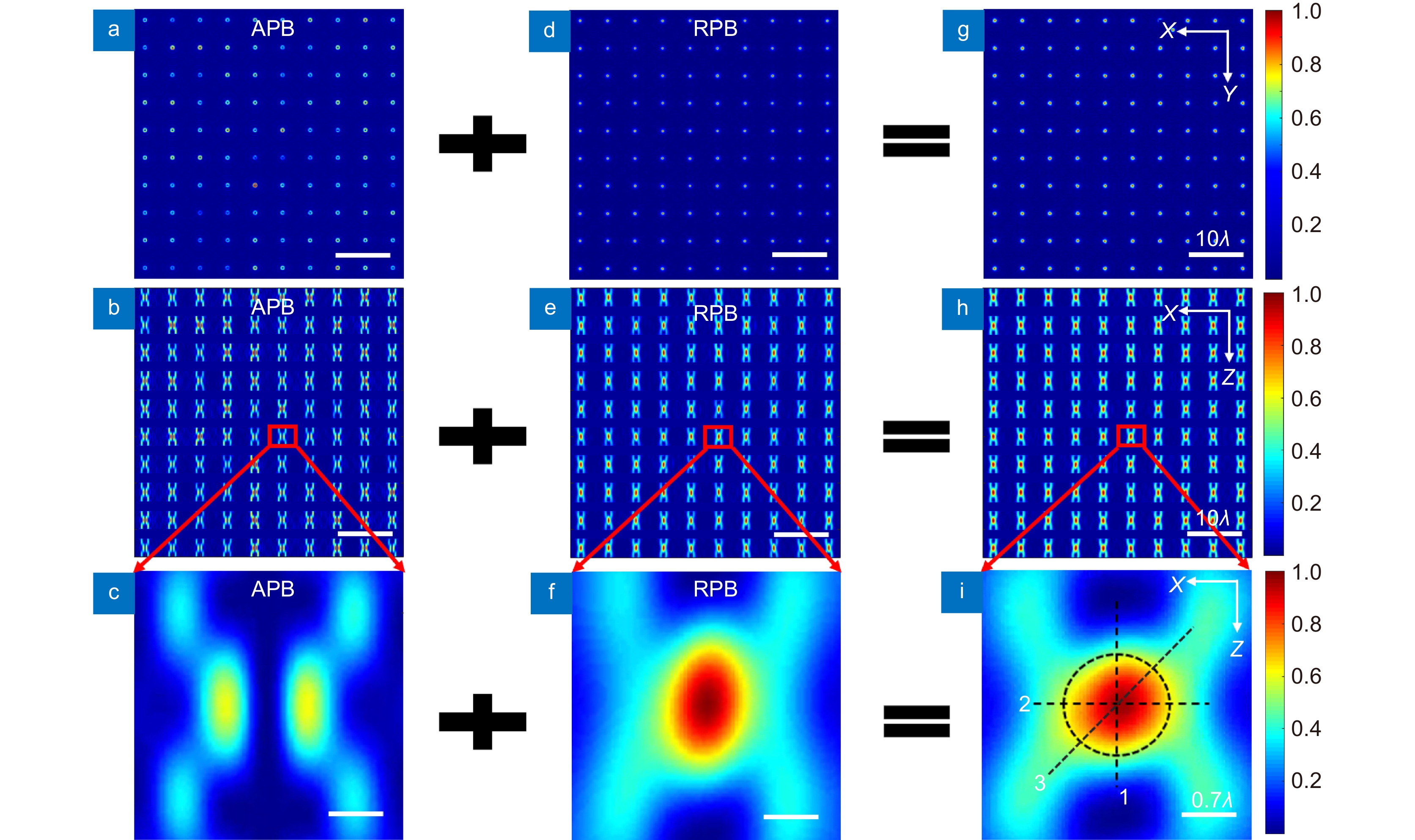
图 5 (a),(d) 调制角向偏振光(a)和调制径向偏振光(d)聚焦叠加得到的准球形多焦点阵列x-y面剖面图(g);(b),(e) 调制角向偏振光(b)和调制径向偏振光(e)聚焦得到的准球形多焦点阵列x-z面剖面图(h);(c),(f),(i) 分别是(b),(e),(h)中标记焦点的放大图
Figure 5. (a), (d) The x-y cross-section (g) of the quasi-spherical multifocal array obtained by focusing and stacking the modulated angularly polarized light (a) and the modulated radially polarized light (d); (b), (e) The x-z profile (h) of the quasi-spherical multifocal array obtained by focusing the modulated angularly polarized light (b) and the modulated radially polarized light (e); (c), (f), (i) are magnifications of the marked foci in (b), (e), (h), respectively
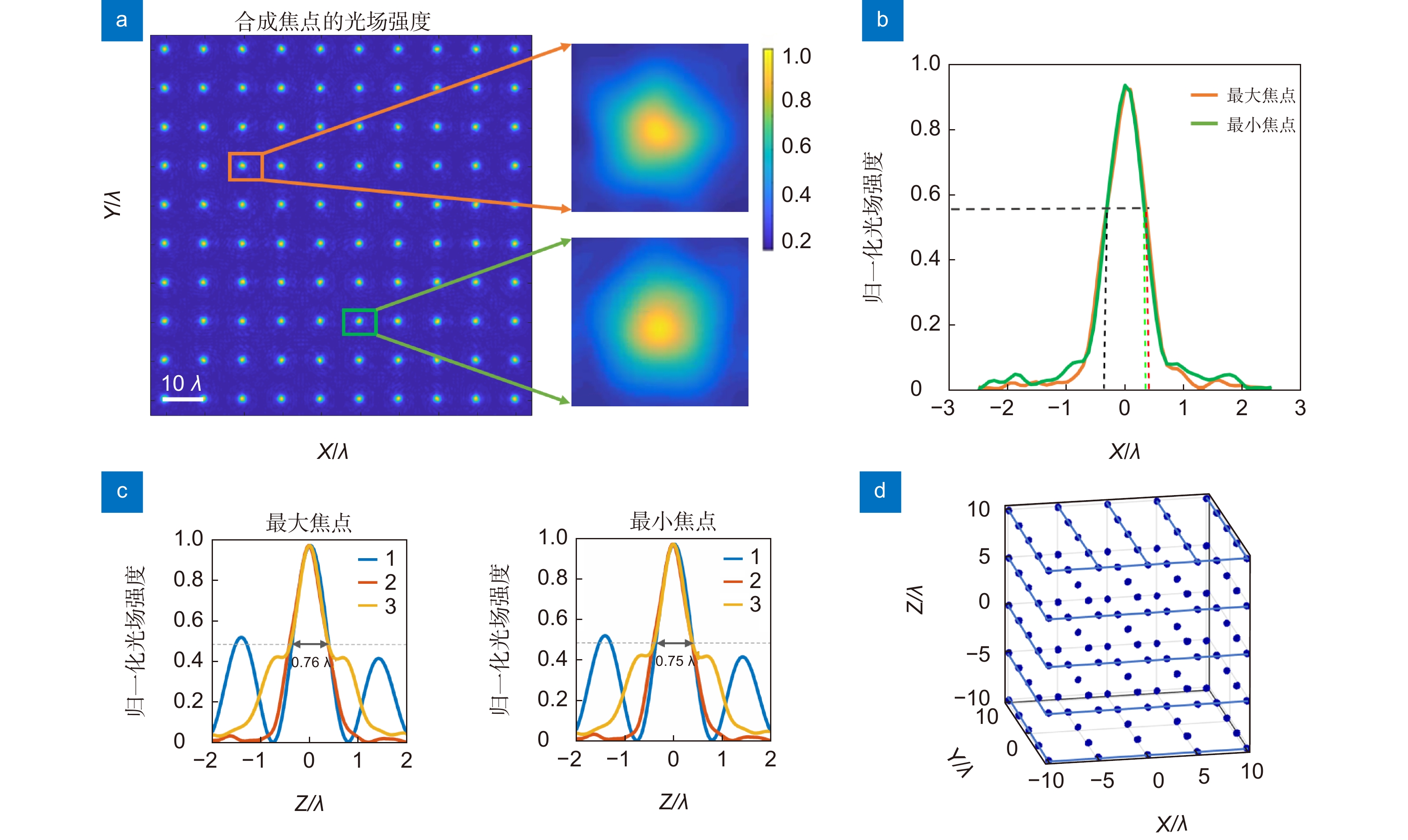
图 6 (a) 合成准球形多焦点阵列焦点横向光场强度分布;(b) x-y面的最大焦点与最小焦点的光场强度曲线对比;(c) x-z面的最大焦点与最小焦点的光场强度分布沿不同方向的场强曲线;(d) 合成纵向超分辨率的准球形多焦点阵列的三维光场强度分布
Figure 6. (a) The lateral light field intensity distribution at the focal point of the synthetic quasi-spherical multifocal array; (b) Comparison of the light field intensity curves of the maximum focus and the minimum focus on the x-y plane; (c) The field intensity curves of the light intensity distribution of the maximum focus and the minimum focus in the x-z plane along different directions; (d) Three-dimensional light intensity distribution of synthetic longitudinal super-resolution quasi-spherical multifocal arrays
-
[1] Kato J I, Takeyasu N, Adachi Y, et al. Multiple-spot parallel processing for laser micronanofabrication[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 86(4): 044102. doi: 10.1063/1.1855404
[2] Yamaji M, Kawashima H, Suzuki J I, et al. Three dimensional micromachining inside a transparent material by single pulse femtosecond laser through a hologram[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 93(4): 041116. doi: 10.1063/1.2965451
[3] Zhang Y L, Chen Q D, Xia H, et al. Designable 3D nanofabrication by femtosecond laser direct writing[J]. Nano Today, 2010, 5(5): 435−448. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2010.08.007
[4] 聂芳松, 姜美玲, 张明偲, 等. 基于迂回相位的轨道角动量Talbot阵列照明器[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(6): 200093. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.200093
Nie F S, Jiang M L, Zhang M S, et al. Orbital angular momentum Talbot array illuminator based on detour phase encoding[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(6): 200093. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.200093
[5] Dufresne E R, Spalding G C, Dearing M T, et al. Computer-generated holographic optical tweezer arrays[J]. Rev Sci Instrum, 2001, 72(3): 1810. doi: 10.1063/1.1344176
[6] Di Leonardo R, Ianni F, Ruocco G. Computer generation of optimal holograms for optical trap arrays[J]. Opt Express, 2007, 15(4): 1913−1922. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.001913
[7] Cai Y N, Yan S H, Wang Z J, et al. Rapid tilted-plane Gerchberg-Saxton algorithm for holographic optical tweezers[J]. Opt Express, 2020, 28(9): 12729−12739. doi: 10.1364/OE.389897
[8] Hasegawa S, Hayasaki Y, Nishida N. Holographic femtosecond laser processing with multiplexed phase Fresnel lenses[J]. Opt Lett, 2006, 31(11): 1705−1707. doi: 10.1364/OL.31.001705
[9] Hasegawa S, Hayasaki Y. Holographic femtosecond laser processing with multiplexed phase Fresnel lenses displayed on a liquid crystal spatial light modulator[J]. Opt Rev, 2007, 14(4): 208−213. doi: 10.1007/s10043-007-0208-9
[10] Salter P S, Booth M J. Addressable microlens array for parallel laser microfabrication[J]. Opt Lett, 2011, 36(12): 2302−2304. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.002302
[11] Zandrini T, Shan O M, Parodi V, et al. Multi-foci laser microfabrication of 3D polymeric scaffolds for stem cell expansion in regenerative medicine[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 11761. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48080-w
[12] Geng Q, Wang D E, Chen P F, et al. Ultrafast multi-focus 3-D nano-fabrication based on two-photon polymerization[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 2179. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10249-2
[13] Skelton S E, Sergides M, Saija R, et al. Trapping volume control in optical tweezers using cylindrical vector beams[J]. Opt Lett, 2013, 38(1): 28−30. doi: 10.1364/OL.38.000028
[14] Biss D P, Youngworth K S, Brown T G. Dark-field imaging with cylindrical-vector beams[J]. Appl Opt, 2006, 45(3): 470−479. doi: 10.1364/AO.45.000470
[15] Feng Z X, Cheng D W, Wang Y T. Iterative freeform lens design for prescribed irradiance on curved target[J]. Opto-Electron Adv, 2020, 3(7): 200010. doi: 10.29026/oea.2020.200010
[16] 欧阳旭, 徐毅, 冼铭聪, 等. 基于无序金纳米棒编码的多维光信息存储[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(3): 180584. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180584
Ouyang X, Xu Y, Xian M C, et al. Encoding disorder gold nanorods for multi-dimensional optical data storage[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2019, 46(3): 180584. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180584
[17] Ouyang X, Xu Y, Xian M C, et al. Synthetic helical dichroism for six-dimensional optical orbital angular momentum multiplexing[J]. Nat Photonics, 2021, 15(12): 901−907. doi: 10.1038/s41566-021-00880-1
[18] 姜美玲, 张明偲, 李向平, 等. 超分辨光存储研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(3): 180649. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180649
Jiang M L, Zhang M S, Li X P, et al. Research progress of super-resolution optical data storage[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2019, 46(3): 180649. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180649
[19] Wang J Y, Tan X D, Qi P L, et al. Linear polarization holography[J]. Opto-Electron Sci, 2022, 1(2): 210009. doi: 10.29026/oes.2022.210009
[20] Meier M, Romano V, Feurer T. Material processing with pulsed radially and azimuthally polarized laser radiation[J]. Appl Phys A, 2007, 86(3): 329−334. doi: 10.1007/s00339-006-3784-9
[21] 曹耀宇, 谢飞, 张鹏达, 等. 双光束超分辨激光直写纳米加工技术[J]. 光电工程, 2017, 44(12): 1133−1145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.12.001
Cao Y Y, Xie F, Zhang P D, et al. Dual-beam super-resolution direct laser writing nanofabrication technology[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2017, 44(12): 1133−1145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.12.001
[22] Qin L, Huang Y Q, Xia F, et al. 5 nm nanogap electrodes and arrays by super-resolution laser lithography[J]. Nano Lett, 2020, 20(7): 4916−4923. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c00978
[23] Youngworth K S, Brown T G. Focusing of high numerical aperture cylindrical-vector beams[J]. Opt Express, 2000, 7(2): 77−87. doi: 10.1364/OE.7.000077
[24] Yun M J, Liu L R, Sun J F, et al. Transverse or axial superresolution with radial birefringent filter[J]. J Opt Soc Am A, 2004, 21(10): 1869−1874. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.21.001869
[25] Waller E H, Renner M, von Freymann G. Active aberration-and point-spread-function control in direct laser writing[J]. Opt Express, 2012, 20(22): 24949−24956. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.024949
[26] Ovsianikov A, Viertl J, Chichkov B, et al. Ultra-low shrinkage hybrid photosensitive material for two-photon polymerization microfabrication[J]. ACS Nano, 2008, 2(11): 2257−2262. doi: 10.1021/nn800451w
[27] Lin H, Jia B H, Gu M. Generation of an axially super-resolved quasi-spherical focal spot using an amplitude-modulated radially polarized beam[J]. Opt Lett, 2011, 36(13): 2471−2473. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.002471
[28] Neil M A A, Juškaitis R, Wilson T, et al. Optimized pupil-plane filters for confocal microscope point-spread function engineering[J]. Opt Lett, 2000, 25(4): 245−247. doi: 10.1364/OL.25.000245
[29] Martínez-Corral M, Ibáñez-López C, Saavedra G, et al. Axial gain resolution in optical sectioning fluorescence microscopy by shaded-ring filters[J]. Opt Express, 2003, 11(15): 1740−1745. doi: 10.1364/OE.11.001740
[30] Ibáñez-López C, Saavedra G, Boyer G, et al. Quasi-isotropic 3-D resolution in two-photon scanning microscopy[J]. Opt Express, 2005, 13(16): 6168−6174. doi: 10.1364/OPEX.13.006168
[31] de Juana D M, Oti J E, Canales V F, et al. Transverse or axial superresolution in a 4Pi-confocal microscope by phase-only filters[J]. J Opt Soc Am A, 2003, 20(11): 2172−2178. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.20.002172
[32] 蔡建文. 飞秒激光微加工中轴向超分辨相位板的设计及仿真[J]. 应用光学, 2014, 35(5): 908−911. doi: 10.5768/JAO201435.0507003
Cai J W. Design and simulation of axial super-resolved phase plate in femtosecond laser microfabrication[J]. J Appl Opt, 2014, 35(5): 908−911. doi: 10.5768/JAO201435.0507003
[33] Gu M. Advanced Optical Imaging Theory[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2000.
[34] Lin J, Rodríguez-Herrera O G, Kenny F, et al. Fast vectorial calculation of the volumetric focused field distribution by using a three-dimensional Fourier transform[J]. Opt Express, 2012, 20(2): 1060−1069. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.001060
[35] Jenness N J, Wulff K D, Johannes M S, et al. Three-dimensional parallel holographic micropatterning using a spatial light modulator[J]. Opt Express, 2008, 16(20): 15942−15948. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.015942
[36] Leutenegger M, Rao R, Leitgeb R A, et al. Fast focus field calculations[J]. Opt Express, 2006, 14(23): 11277−11291. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.011277
[37] 吕清花, 程壮, 翟中生, 等. 基于计算全息的无衍射光莫尔条纹三自由度测量方法研究[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(2): 190331. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190331
Lv Q H, Cheng Z, Zhai Z S, et al. 3-DOF measurement method for non-diffracting Moiré fringes based on CGH[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(2): 190331. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190331
[38] Xue Y, Kuang C F, Li S, et al. Sharper fluorescent super-resolution spot generated by azimuthally polarized beam in STED microscopy[J]. Opt Express, 2012, 20(16): 17653−17666. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.017653
[39] Xian M C, Xu Y, Ouyang X, et al. Segmented cylindrical vector beams for massively-encoded optical data storage[J]. Sci Bull, 2020, 65(24): 2072−2079. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2020.07.016
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: