Gauss-Lorenz hybrid prior super resolution reconstruction with mixed sparse representation
-
摘要:
为了得到置信度更高的超分辨率先验模型,实现重建结果在噪声和细节之间的平衡,建立了基于混合稀疏表达框架下的高斯⎯洛伦兹混合先验模型。研究了该先验模型在超分算法中的应用优势和具体的应用方案。首先,根据先验信息的类型介绍了一些超分辨率算法的优势和问题。接着,提出对图像不同分量的统计特点进行单独建模的应用方法。然后,在分析了混合稀疏框架、高斯吉布斯先验和洛伦兹先验的基础上,说明了基于群稀疏框架下的高斯⎯洛伦兹混合先验的超分辨率算法。最后,介绍了具体实现环节和最终迭代方案。实验结果表明,本文基本完成了在重建过程中保持细节的同时抑制噪声的改进目标,可以用于更多复杂环境的超分辨率重建要求。
Abstract:In order to obtain a super-resolution prior model with higher confidence and balance the reconstructed results between noise and details, this paper establishes a Gauss-Lorenz hybrid prior model based on the mixed sparse representation framework. This prior model's advantages and specific application schemes are studied. Firstly, according to the type of prior information, the advantages and problems of some traditional algorithms are introduced. Next, the statistical characteristics of different components of the image are modeled separately. Then, based on the analysis of the mixed sparse framework, the Gauss-Gibbs prior and the Lorenz prior, the super-resolution algorithm based on the Gauss-Lorenz hybrid prior under the group sparse framework is illustrated. Finally, the implementation and the final iteration scheme are introduced. The aim of noise suppression while maintaining details in the reconstruction process has been completed, which can be used for in more complex environments with super-resolution resconstruction.
-

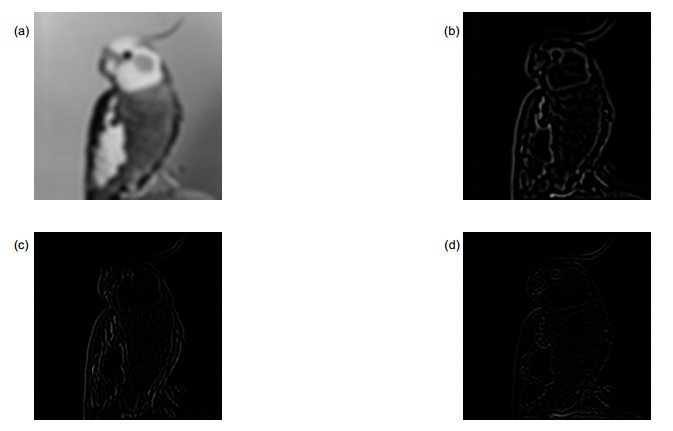
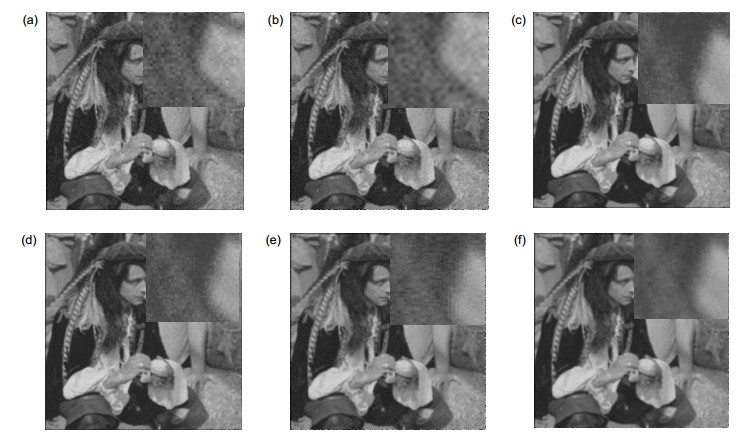
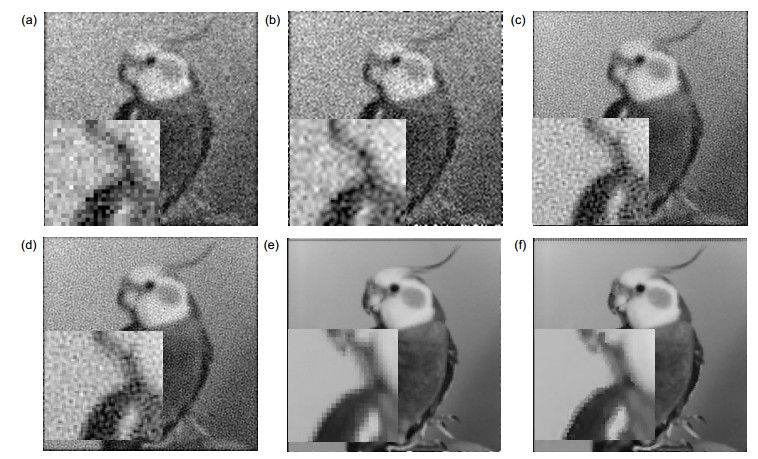
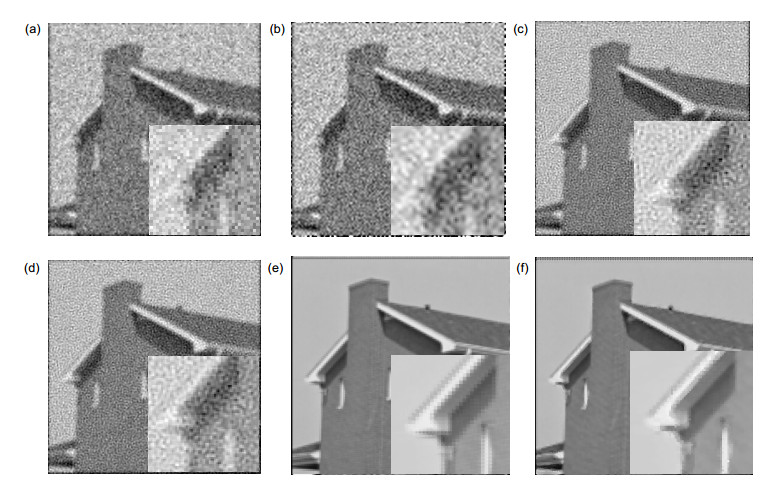
Overview: The optimization function of a super-resolution algorithm consists of two parts: a data consistency term that is dependent on input images and a prior term that is derived from a prior model. The data consistency term introduces non-redundant information between images, but it also exacerbates the noise and causes overfitting. Therefore, the selection of the prior model is crucial for optimizing the performance of the image reconstruction. In order to obtain a higher confidence super-resolution prior model and balance the reconstructed results between noise and details, this paper establishes a Gauss-Lorenz hybrid prior model based on the mixed sparse representation framework. This prior model's advantages and specific application scheme are studied. Firstly, according to the type of prior information, the advantages and problems of some traditional algorithms are introduced. Next, the statistical characteristics of different components of the image are modeled separately. Then, based on the analysis the mixed sparse framework, the Gauss-Gibbs prior and the Lorenz prior, the super-resolution algorithm based on the Gauss-Lorenz hybrid prior under the group sparse framework is illustrated. Finally, the implementation and the final iteration scheme are introduced. The aim of noise suppression while maintaining details in the reconstruction process has been completed, which can be used for more complex environments with super-resolution reconstruction requirements. This paper has three main innovations. 1) We use the group sparse framework as the basic framework of the prior model. In this paper, different components of the natural images are projected into spatial, wavelet, and curved domains respectively. The image is divided into three components: point, line, and surface. We get constraints that are closer to natural images and improve the prior confidence. 2) Line component, that is, the edge component of an image, is closer to Lorenz distribution in statistical derivation than Gaussian distribution, so Lorenz model is used to model the edge component in the curved domain; Gaussian-Gibbs model is used to model the point and area components, which can suppress noise. The three components are continuously and alternately optimized in iteration to achieve a balance. 3) The pixel residuals threshold in the convex set projection iteration method is used as the iteration termination condition to solve the problem that the optimization progress and the optimization step are not uniform in different domains. We use four detection methods: structural similarity, maximum absolute error, noise level detection and peak signal-to-noise ratio to evaluate the results of the algorithm. Whether it is the evaluation method with or without reference, the algorithm proposed in this paper obtains better evaluation results than other algorithms.
-

-
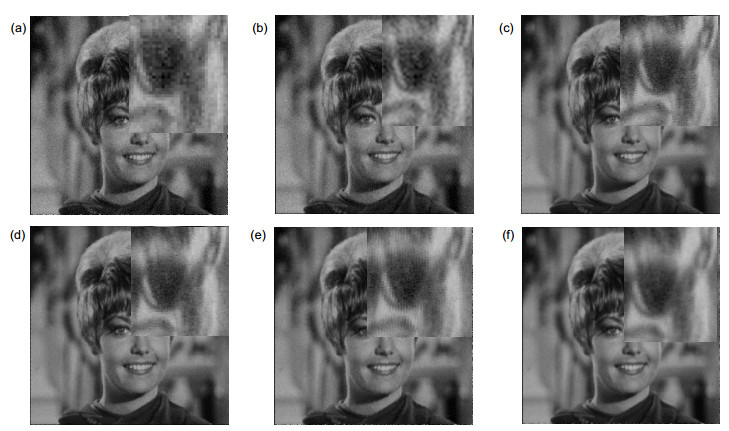
表 1 配准结果
Table 1. Results of registration
参考帧 光流估计结果 乘上采样因子倍数取整 X轴 Y轴 X轴 Y轴 0 0 0 0 1 0.9255 -0.0114 2 0 2 0.0349 -0.4805 0 -1 3 1.0520 -0.5131 2 -1 4 0.5041 -0.5497 1 -1 5 -0.0253 0.3150 0 1 6 0.4791 0.3778 1 1 7 1.0110 0.3719 2 1 表 2 SSIM参数评价结果
Table 2. Results of SSIM evaluation
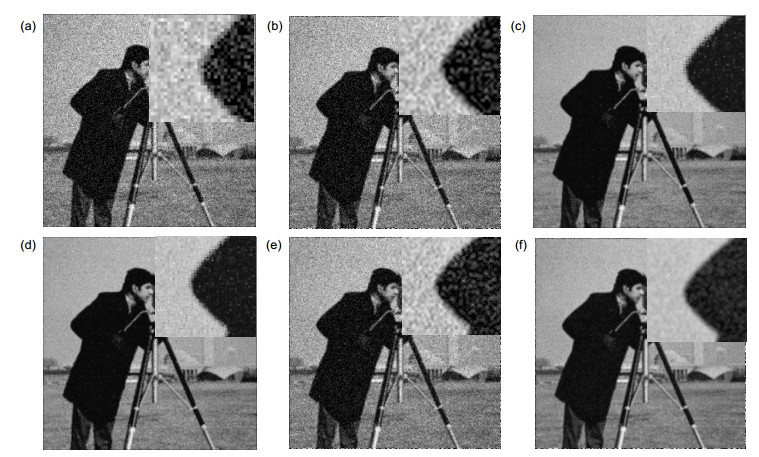
MAP L1 TV GLMSR Zelda 0.8650 0.8198 0.8311 0.8932 Man 0.6954 0.7126 0.7090 0.7282 Cameraman 0.3959 0.5893 0.5880 0.7004 Coco 0.8217 0.2170 0.2286 0.8273 House 0.6740 0.2283 0.2440 0.6982 表 3 MAE参数评价结果
Table 3. Results of MAE evaluation
MAP L1 TV GLMSR Zelda 8.1551 29.2648 29.0016 6.1974 Man 12.7265 12.9196 13.2840 11.2340 Cameraman 18.5889 12.8681 12.8269 9.8238 Coco 7.4278 18.9194 18.2419 7.5007 House 10.2257 20.3483 19.2766 10.1467 表 4 PSNR评价结果
Table 4. Results of PSNR evaluation
MAP L1 TV GLMSR Zelda 22.9272 23.9469 24.7402 24.8186 Man 21.6447 22.6163 23.9956 24.0214 Cameraman 19.7764 23.5189 23.5414 23.9116 Coco 20.1809 18.5350 18.8461 21.0835 House 19.6762 18.8256 19.2512 20.5463 -
[1] 周春平, 宫辉力. 实用卫星遥感超分辨率理论及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 6.
Zhou C P, Gong H L. Theory and Application of Superresolution for Practical Satellite Remote Sensing[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016: 6.
[2] 赵圆圆, 施圣贤. 融合多尺度特征的光场图像超分辨率方法[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(12): 54–64. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.200007
Zhao Y Y, Shi S X. Light-field image super-resolution based on multi-scale feature fusion[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(12): 54–64. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.200007
[3] 于淑侠, 胡良梅, 张旭东, 等. 彩色图像多尺度引导的深度图像超分辨率重建[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(4): 42–51. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190260
Yu S X, Hu L M, Zhang X D, et al. Multi-scale guided depth image super-resolution reconstruction[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(4): 42–51. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190260
[4] 朱福珍, 刘越, 黄鑫, 等. 改进的稀疏表示遥感图像超分辨重建[J]. 光学精密工程, 2019, 27(3): 718–725. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM201903026.htm
Zhu F Z, Liu Y, Huang X, et al. Remote sensing image super-resolution based on improved sparse representation[J]. Opt Precis Eng, 2019, 27(3): 718–725. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM201903026.htm
[5] Fu B, Li Y, Wang X H, et al. Image super-resolution using TV priori guided convolutional network[J]. Patt Recognit Lett, 2019, 125: 780–784. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2019.06.022
[6] Xu T, Huang T Z, Deng L J, et al. Hyperspectral image superresolution using unidirectional total variation with tucker decomposition[J]. IEEE J Select Top Appl Earth Observat Remote Sens, 2020, 13: 4381–4398. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3012566
[7] Farsiu S, Robinson M D, Elad M, et al. Fast and robust multiframe super resolution[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2004, 13(10): 1327–1344. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2004.834669
[8] 代少升, 崔俊杰, 张德洲. 基于自适应阈值HMRF的红外超分辨率重建[J]. 半导体光电, 2017, 38(4): 577–579, 613. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BDTG201704027.htm
Dai S S, Cui J J, Zhang D Z. Infrared super-resolution reconstruction based on adaptive threshold HMRF[J]. Semicond Optoelectr, 2017, 38(4): 577–579, 613. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BDTG201704027.htm
[9] Rezayi H, Seyedin S A. Huber Markov random field for joint super resolution[C]//2017 10th Iranian Conference on Machine Vision and Image Processing (MVIP), Isfahan, Iran, 2017: 93–98.
[10] Shao Z F, Wang L, Wang Z Y, Deng J. Remote sensing image super-resolution using sparse representation and coupled sparse autoencoder[J]. IEEE J Select Top Appl Earth Observat Remote Sens, 2019, 12(8): 2663–2674. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2925456
[11] Li J, Zhou T, Wang W X, et al. Enhancement method for aviation image based on improved NSCT[C]//2020 Cross Strait Radio Science & Wireless Technology Conference (CSRSWTC), Fuzhou, China, 2020: 1–3.
[12] Li F, Xin L, Guo Y, et al. A framework of mixed sparse representations for remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens, 2017, 55(2): 1210–1221. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2621123
[13] 鲍东星, 李晓明, 李金. 基于洛伦兹范数的医学图像超分辨率重建研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2020, 37(4): 205–208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2020.04.043
Bao D X, Li X M, Li J. Lorentzian norm based super-resolution reconstruction of medical image[J]. Comput Simul, 2020, 37(4): 205–208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2020.04.043
[14] 孙超. 基于混合方法的卫星遥感图像自动配准技术的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018.
Sun C. The research on automatic registration technology of satellite remote sensing images based on hybrid methods[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2018.
[15] Liu L, Huang W, Wang C, et al. SAR image super-resolution based on TV-regularization using gradient profile prior[C]//2016 CIE International Conference on Radar (RADAR), Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–4.
[16] 李志明. 基于L1范数的全变分正则化超分辨重构算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2016, 52(15): 212–216. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1511-0286
Li Z M. Super resolution reconstruction algorithm based on L1 norm of total variation regularization[J]. Comput Eng Appl, 2016, 52(15): 212–216. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1511-0286
[17] 薛翠红, 于明, 杨宇皓, 等. 基于学习的马尔科夫超分辨率复原[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(S1): 406–409. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY2013S1086.htm
Xue C H, Yu M, Yang Y H, et al. MRF reconstruction based on the markov network[J]. J Jilin Univ (Eng Ed), 2013, 43(S1): 406–409. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY2013S1086.htm
[18] Liu X H, Tanaka M, Okutomi M. Noise level estimation using weak textured patches of a single noisy image[C]//2012 19th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Orlando, FL, USA, 2013.
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: