-
摘要:
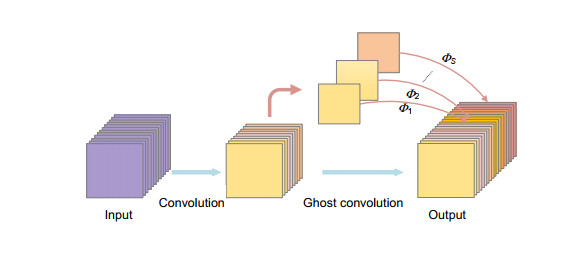
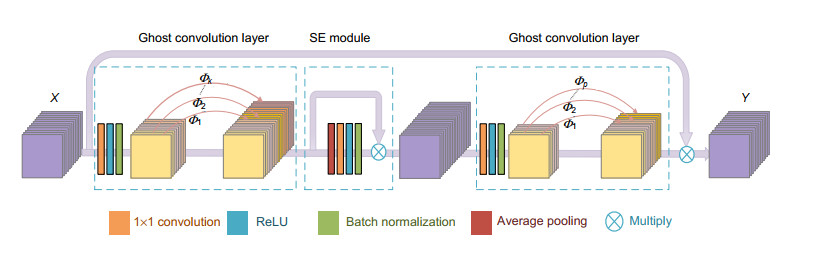
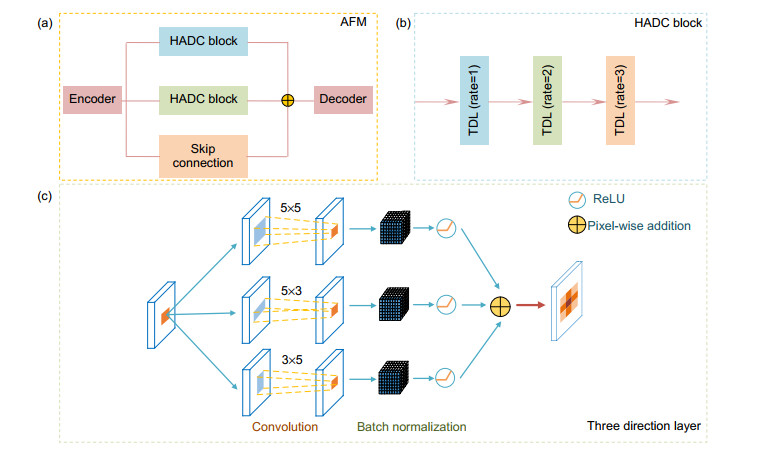
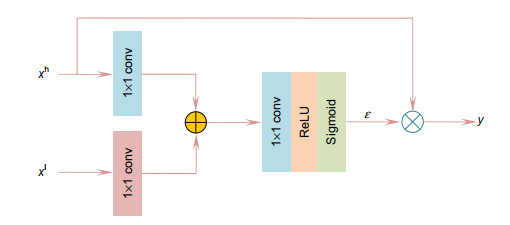
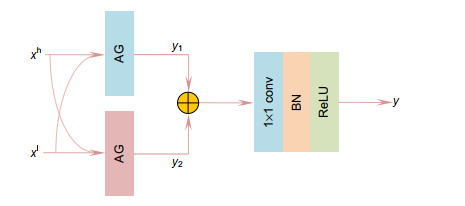
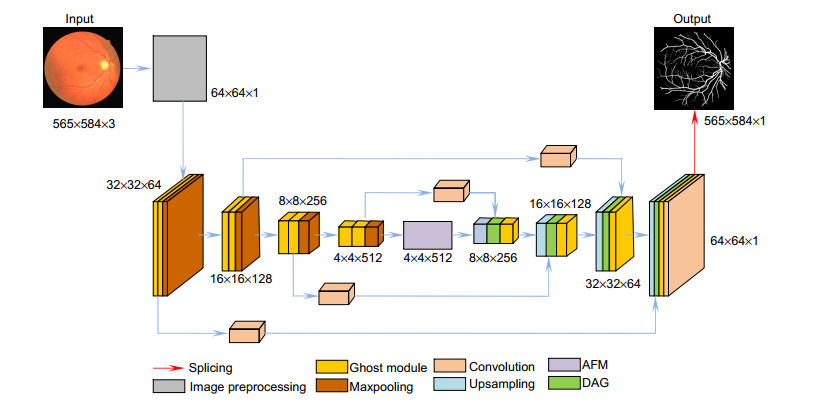
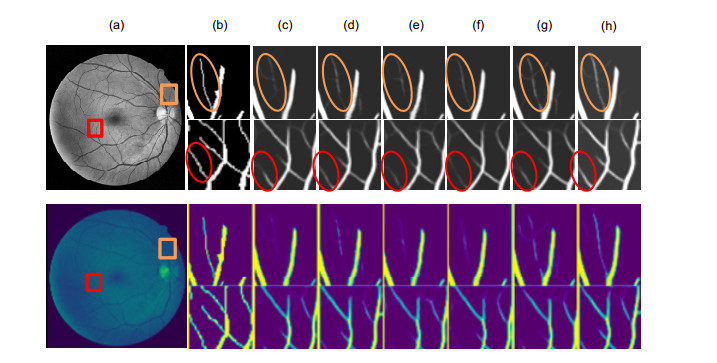
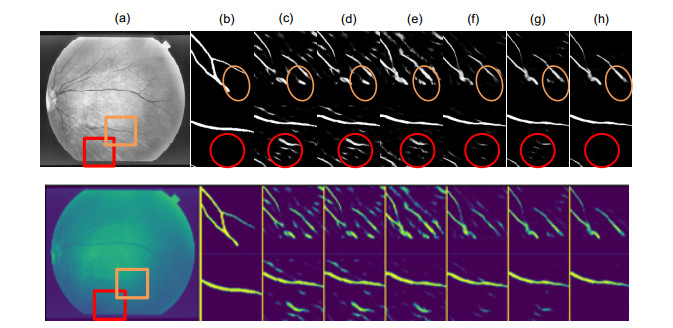
针对视网膜血管分割存在主血管轮廓模糊、微细血管断裂和视盘边界误分割等问题,提出一种鬼影卷积自适应视网膜血管分割算法。算法一是用鬼影卷积替代神经网络中普通卷积,鬼影卷积生成丰富的血管特征图,使目标特征提取充分进行。二是将生成的特征图进行自适应融合并输入至解码层分类,自适应融合能够多尺度捕获图像信息和高质量保存细节。三是在精确定位血管像素与解决图像纹理损失过程中,构建双路径注意力引导结构将网络底层特征图与高层特征图有效结合,提高血管分割准确率。同时引入Cross-Dice Loss函数来抑制正负样本不均问题,减少因血管像素占比少而引起的分割误差,在DRIVE与STARE数据集上进行实验,其准确率分别为96.56%和97.32%,敏感度分别为84.52%和83.12%,特异性分别为98.25%和98.96%,具有较好的分割效果。

-
关键词:
- 视网膜血管 /
- 鬼影卷积 /
- 自适应融合模块 /
- 双路径注意力引导结构
Abstract:In order to solve the problems in retinal vessel segmentation, such as blurred main vessel profile, broken micro-vessels, and missegmented optic disc boundary, a ghost convolution adaptive retinal vessel segmentation algorithm is proposed. The first algorithm uses ghost convolution to replace the common convolution in neural network, and the ghost convolution generates rich vascular feature maps to make the target feature extraction fully carried out. Secondly, the generated feature images are adaptive fusion and input to the decoding layer for classification. Adaptive fusion can capture image information at multiple scales and save details with high quality. Thirdly, in the process of accurately locating vascular pixels and solving image texture loss, a dual-pathway attention guiding structure is constructed to effectively combine the feature map at the bottom and the feature map at the top of the network to improve the accuracy of vascular segmentation. At the same time, Cross-Dice Loss function was introduced to suppress the problem of uneven positive and negative samples and reduce the segmentation error caused by the small proportion of vascular pixels. Experiments were conducted on DRIVE and STARE datasets. The accuracy was 96.56% and 97.32%, the sensitivity was 84.52% and 83.12%, and the specificity was 98.25% and 98.96%, respectively, which proves the good segmentation effect.
-

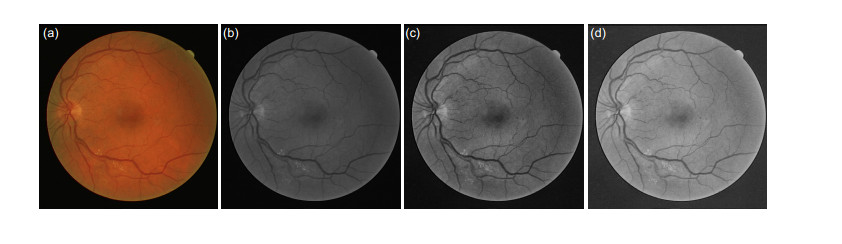
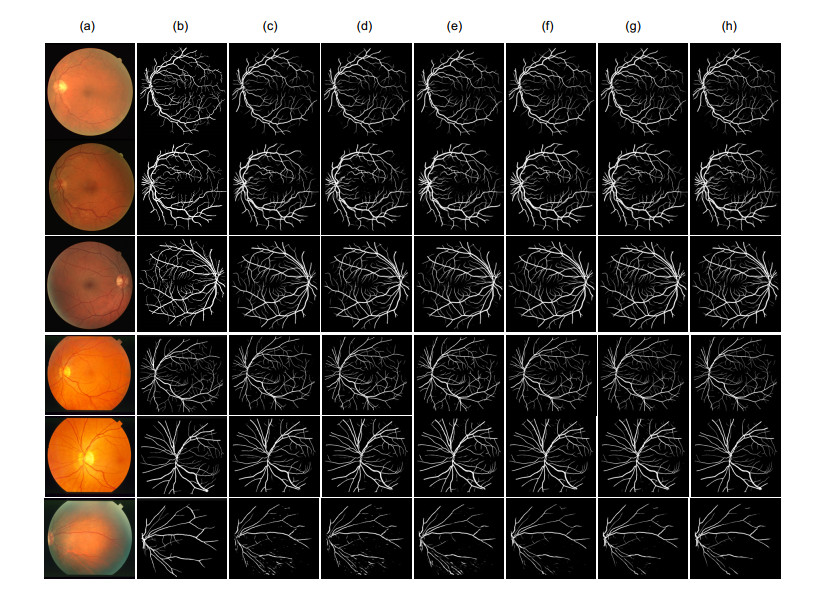
Overview: Retinal vascular morphology is an important indicator of human health, and its image processing and segmentation are of great significance for the early detection and treatment of glaucoma, cardiovascular disease, and venous obstruction. At present, retinal vessel segmentation algorithms are mainly divided into unsupervised and supervised learning methods. Unsupervised learning method mainly focuses on the original information of fundus blood vessels and uses matching filtering, mathematical morphology and vascular tracking to segment fundus images. Supervised learning requires prior label information, and the classifier is trained and extracted by manually labeled Label image, and then the retinal vessels are segmented. However, the existing retinal vessel segmentation algorithm has some problems, such as blurred main vessel contour, micro-vessel fracture, and optic disc boundary missegmentation. To solve the above problems, a ghost convolution adaptive retinal vessel segmentation algorithm was proposed. First, color fundus images were separated by RGB (Red, Green, Blue) channels and Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization to enhance the contrast between retinal blood vessels and background, and to reduce the influence of light intensity and color channel on the segmentation effect. Then the fundus images were input into the ghoul convolution adaptive network for training to extract the vascular features. The algorithm uses ghoul convolution to replace the common convolution in the neural network, and the ghoul convolution can generate rich vascular feature maps to fully extract the target features. The features are classified and predicted by the adaptive fusion module input into the decoding layer, and the adaptive fusion can capture the image information at multiple scales and preserve the vascular details with high quality. In the process of accurately locating vascular pixels and solving the loss of image texture, a dual-pathway attention guiding structure is constructed to effectively combine the feature maps at the bottom and the high level of the network, which solves the information loss at the pooling layer, achieves global semantic transmission, better retains vascular pixels, and makes the edge details of the segmented image more complete. At the same time, Cross-Dice Loss function is introduced to suppress the problem of uneven positive and negative samples and reduce the segmentation error caused by the small proportion of foreground. The experiment was carried out on DRIVE and STARE datasets. The DRIVE dataset contains 40 color fundus images, which were manually divided into training sets and test sets by the authorities. The STARE database contains 20 color fundus images, which were evenly divided into five parts, and the experiment was carried out in a 50% fold cross validation method. Experimental results: the accuracy rate was 96.56% and 97.32%, sensitivity was 84.52% and 83.12%, specificity was 98.25% and 98.96%, respectively. In the segmentation results, the main vessels were less broken and the microvessels were clear, which has certain medical clinical application value.
-

-
表 1 不同算法对比结果
Table 1. Comparison results of different algorithms
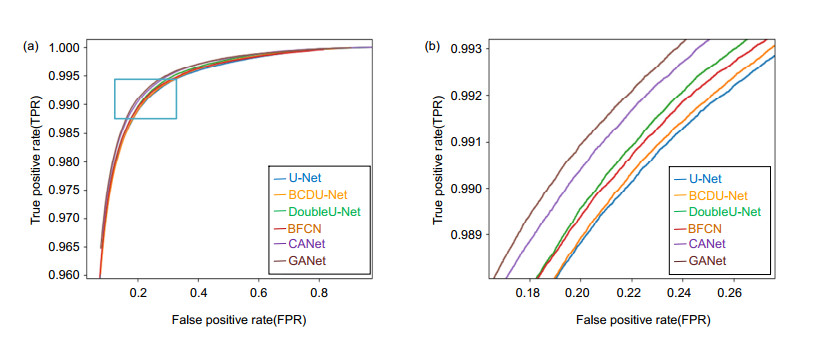
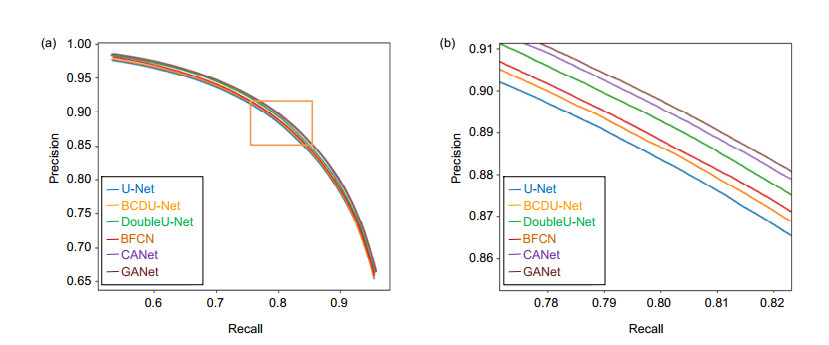
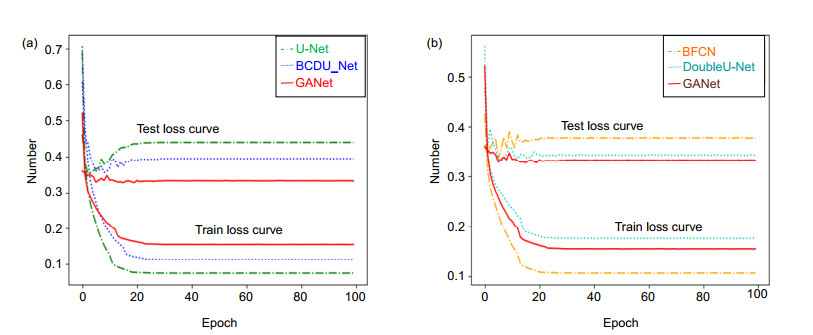
Method DRIVE STARE Parameters Time/s Acc Sen Spe AUC Acc Sen Spe AUC U-Net 0.9637 0.8250 0.9830 0.9856 0.9653 0.7958 0.9857 0.9831 28245825 152 BCDU-Net 0.9638 0.8292 0.9826 0.9857 0.9659 0.8054 0.9791 0.9878 29288325 286 DoubleU-Net 0.9642 0.8201 0.9843 0.9862 0.9667 0.7991 0.9854 0.9851 31837850 294 BFCN 0.9639 0.8313 0.9824 0.9859 0.9687 0.8227 0.9862 0.9893 48224433 422 CANet 0.9645 0.8374 0.9822 0.9867 0.9729 0.8185 0.9873 0.9901 36232127 348 GANet 0.9656 0.8452 0.9825 0.9869 0.9732 0.8312 0.9896 0.9900 27400454 244 表 2 不同算法客观性对比结果
Table 2. Objective comparison results of different algorithms
Method DRIVE STARE Acc Sen Spe AUC Acc Sen Spe AUC Ref.[15] 0.9542 0.7653 0.9818 0.9752 0.9612 0.7581 0.9846 0.9801 Ref.[16] 0.9557 0.7890 0.9799 0.9774 0.9620 0.7798 0.9822 0.9791 Ref.[17] 0.9566 0.7963 0.9800 0.9802 0.9641 0.7595 0.9878 0.9832 Ref.[18] 0.9568 0.7921 0.9810 0.9806 0.9678 0.8352 0.9823 0.9875 Ref.[19] 0.9574 0.8083 0.9790 0.9822 0.9695 0.8162 0.9869 0.9898 Ref.[20] 0.9576 0.8039 0.9804 0.9821 0.9694 0.8315 0.9858 0.9905 Ref.[21] 0.9582 0.7996 0.9813 0.9830 0.9672 0.7963 0.9863 0.9875 Ref.[22] 0.9667 0.8221 0.9817 0.9853 0.9724 0.8210 0.9859 0.9897 Ref.[23] 0.9554 0.8160 0.9756 0.9799 0.9723 0.7551 0.9903 0.9863 Ref.[24] 0.9609 0.8282 0.9738 0.9786 0.9646 0.8979 0.9701 0.9892 GANet 0.9656 0.8452 0.9825 0.9869 0.9732 0.8312 0.9896 0.9900 表 3 各模块消融研究
Table 3. Ablation study of each module
Method DRIVE STARE Acc Sen Spe AUC Acc Sen Spe AUC GANet_1 0.9645 0.8374 0.9822 0.9867 0.9729 0.8185 0.9873 0.9901 GANet_2 0.9650 0.8506 0.9801 0.9868 0.9730 0.8336 0.9892 0.9906 GANet_3 0.9607 0.7865 0.9851 0.9823 0.9699 0.8171 0.9929 0.9892 GANet 0.9656 0.8452 0.9825 0.9869 0.9732 0.8312 0.9896 0.9900 -
[1] 徐光柱, 王亚文, 胡松, 等. PCNN与形态匹配增强相结合的视网膜血管分割[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(4): 180466. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180466
Xu G Z, Wang Y W, Hu S, et al. Retinal vascular segmentation combined with PCNN and morphological matching enhancement[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2019, 46(4): 180466. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.180466
[2] Liu X M, Cao J, Fu T Y, et al. Semi-supervised automatic segmentation of layer and fluid region in retinal optical coherence tomography images using adversarial learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 7: 3046–3061. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8586858/
[3] 佘黎煌, 郭一蓉, 张石. 基于方向分数和Frangi滤波器的视网膜血管分割算法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 41(2): 182–187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBDX202002005.htm
She L H, Guo Y R, Zhang S. Retinal vessel segmentation algorithm based on orientation scores and Frangi filter[J]. J Northeast Univ (Natl Sci), 2020, 41(2): 182–187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBDX202002005.htm
[4] 梁礼明, 盛校棋, 蓝智敏, 等. 自适应尺度信息的U型视网膜血管分割算法[J]. 光学学报, 2019, 39(08): 126–140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB201908016.htm
Liang L M, Sheng X Q, Lan Z M, et al. U-shaped retinal vessel segmentation algorithm based on adaptive scale information[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(08): 126–140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB201908016.htm
[5] Wang D Y, Haytham A, Pottenburgh J, et al. Hard attention net for automatic retinal vessel segmentation[J]. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 2020, 24(12): 3384–3396. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.3002985
[6] Han K, Wang Y H, Tian Q, et al. GhostNet: more features from cheap operations[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2020: 1577–1586.
[7] Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2018: 7132–7141.
[8] Zheng X W, Huan L X, Xia G S, et al. Parsing very high resolution urban scene images by learning deep ConvNets with edge-aware loss[J]. ISPRS J Photogrammetry Remote Sens, 2020, 170: 15–28. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.09.019
[9] Zhang S D, He F Z. DRCDN: learning deep residual convolutional dehazing networks[J]. Vis Comput, 2020, 36(9): 1797–1808. doi: 10.1007/s00371-019-01774-8
[10] Wang Y J, Hu S Y, Wang G D, et al. Multi-scale dilated convolution of convolutional neural network for crowd counting[J]. Multimed Tools Appl, 2020, 79(1–2): 1057–1073. doi: 10.1007/s11042-019-08208-6
[11] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention. 2015: 234–241.
[12] Azad R, Asadi-Aghbolaghi M, Fathy M, et al. Bi-directional ConvLSTM U-Net with densley connected convolutions[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. 2019: 406–415.
[13] Jha D, Riegler M A, Johansen D, et al. DoubleU-Net: a deep convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation[C]//2020 IEEE 33rd International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS). 2020: 558–564.
[14] Jiang Y, Wang F L, Gao J, et al. Efficient BFCN for automatic retinal vessel segmentation[J]. J Ophthalmol, 2020, 2020: 6439407. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9119750
[15] Yan Z Q, Yang X, Cheng K T. Joint segment-level and pixel-wise losses for deep learning based retinal vessel segmentation[J]. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2018, 65(9): 1912–1923. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2018.2828137
[16] Li H, Wang Y K, Wan C, et al. MAU-Net: a retinal vessels segmentation method[C]//2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC). 2020: 1958–1961.
[17] Jin Q G, Meng Z P, Pham T D, et al. DUNet: a deformable network for retinal vessel segmentation[J]. Knowl Based Syst, 2019, 178: 149–162. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2019.04.025
[18] Li X, Jiang Y C, Li M L, et al. Lightweight attention convolutional neural network for retinal vessel image segmentation[J]. IEEE Trans Industr Inform, 2021, 17(3): 1958–1967. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.2993842
[19] Tang P, Liang Q K, Yan X T, et al. Multi-proportion channel ensemble model for retinal vessel segmentation[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2019, 111: 103352. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.103352
[20] Oliveira A, Pereira S, Silva C A. Retinal vessel segmentation based on fully convolutional neural networks[J]. Expert Syst Appl, 2018, 112: 229–242. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2018.06.034
[21] Wu Y C, Xia Y, Song Y, et al. NFN+: a novel network followed network for retinal vessel segmentation[J]. Neural Netw, 2020, 126: 153–162. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2020.02.018
[22] Guo F, Li W Q, Kuang Z H, et al. MES-Net: a new network for retinal image segmentation[J]. Multimed Tools Appl, 2021, 80(10): 14767–14788. doi: 10.1007/s11042-021-10580-1
[23] Tang Y, Rui Z Y, Yan C F, et al. ResWnet for retinal small vessel segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 198265–198274. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3032453
[24] Samuel P M, Veeramalai T. Multilevel and multiscale deep neural network for retinal blood vessel segmentation[J]. Symmetry, 2019, 11(7): 946. doi: 10.3390/sym11070946
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: