-
摘要
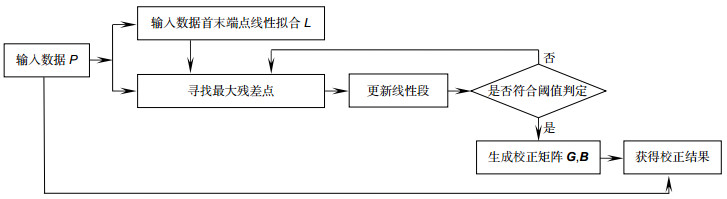
为改善sCMOS读出电路工艺偏差导致的非均匀性问题,本文提出了自适应多点非均匀性校正方法。算法首先以搜寻最小范数点、阈值比较的方式分别确定最优分段点的位置以及最佳分段数量,然后再根据这些分段信息在各区间段分别进行两点校正。通过该自适应方法可有效改善传统多点法中由于分段参数选择不当导致的校正性能下降。同时,为实现实时的非均匀性校正,文中根据自适应多点法的算法特点,提出了一种与之匹配的嵌入式数据串流校正方案,可在不影响现有相机采集结构以及采集速率的情况下实现非均匀性的校正。
Abstract
In order to improve the nonuniformity caused by the process bias of sCMOS readout circuit, an adaptive multipoint nonuniformity correction method is presented. The algorithm first determines the location of the optimal segment point and the optimal number of segments by searching for the minimum norm point and threshold comparison, then corrects two points in each interval segment according to the segment information. This adaptive method can effectively improve the correction performance of traditional multipoint methods, which is caused by improper selection of segment parameters. At the same time, in order to achieve real-time non-uniformity correction, a matching embedded data series correction scheme is proposed based on the algorithm characteristics of adaptive multipoint method, which can achieve non-uniformity correction without affecting the existing camera acquisition structure and acquisition rate.
-
Key words:
- non-uniformity /
- multipoint /
- adaptive /
- real-time processing
-
Overview

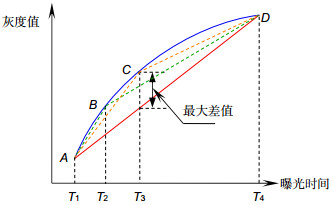
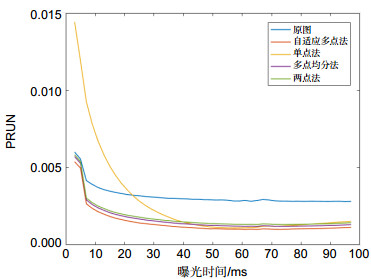
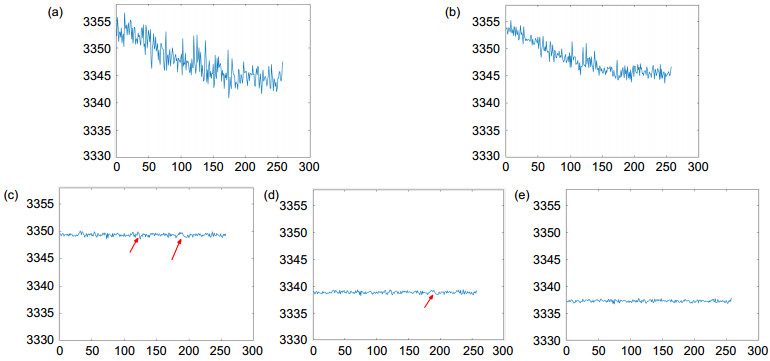
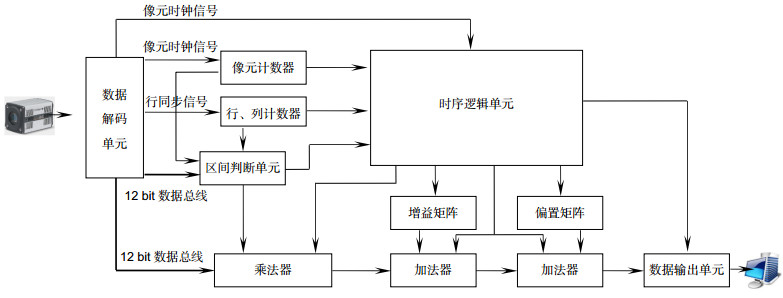
Overview: sCMOS is a photoelectric detection device widely used in scientific research field today. The parameter mismatch between the column amplifiers may occur due to its process, which leads to the nonuniformity problem. The methods for nonuniformity correction can be divided into scene-based and calibration-based methods. In the real-time application scenarios, the calibration-based multipoint nonuniformity correction method is widely used in engineering because of its simple calculation and high accuracy. However, the multipoint correction method has some difficulties in selecting the location and number of segments. The calibration-based adaptive multipoint correction method proposed in this paper can automatically obtain the optimal location and optimal number of segments by searching for the maximum error point and the number of segments closest to the accuracy threshold. This method can effectively avoid the degradation of the correction performance caused by improper selection of segment parameters in traditional multipoint methods. The basic principle is to search for the maximum error point between the non-linear photoelectric response curve of each pixel and the straight line composed of the first and last points as the basis for selecting the segment location, and to calculate the error accuracy of the segment as the basis for selecting the number of segments. After obtaining the segment points and the number of segments, the two-point method can be repeated for each linear segment to correct each segment straight line to the reference line, where the reference curve is obtained by fitting the global average point. Experimental results show that the sCMOS image processed by the adaptive multipoint correction method has better PRUN and more uniform and stable column mean curve than traditional single-point, two-point and average multipoint methods. For an image acquisition system where the acquisition software and the system structure are solidified, an embedded data series correction scheme is presented according to the characteristics of the adaptive multipoint method in order to achieve nonuniformity correction while maintaining the existing acquisition structure. By comparing the decoded data from the sCMOS camera with the lookup table, the offset and gain correction coefficients for the matching segment period and the corresponding period are determined. Subsequent multipliers and adders are used to correct the linear segment to the reference line using a two-point method. Finally, the corrected data is encoded and output in the original data format. With this scheme, a camera with a frame rate of 200 frames per second at the 2k×2k resolution used in the experiment can achieve real-time nonuniformity correction without changing the collection structure, acquisition rate and acquisition software of the existing camera.
-

-
-
参考文献
[1] 韩开亮, 何春芳. 基于两点法的红外图像非均匀性校正算法及其DSP实现[J]. 红外技术, 2007, 29(9): 541–544. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8891.2007.09.012
Han K L, He C F. A nonuniformity correction algorithm for IRFPAs based on two points and it's realization by DSP[J]. Infrared Technol, 2007, 29(9): 541–544. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8891.2007.09.012
[2] Xing S, Zhang J, Sun L, et al. Two-point nonuniformity correction based on LMS[C]//Infrared Components and Their Applications. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2005, 5640: 130–136.
[3] Wang H W, Ma C W, Cao J Z, et al. An adaptive two-point non-uniformity correction algorithm based on shutter and its implementation[C]//Proceedings of 2013 Fifth International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation, 2013: 174–177.
[4] 李言旭, 孙德新, 刘银年. 基于多项式拟合的红外焦平面非均匀性校正[J]. 激光与红外, 2005, 35(2): 104–107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGHW20050200B.htm
Li Y X, Sun D X, Liu Y N. Polynomial fitting based on nonuniformity correction of infrared focal plane arrays[J]. Laser Infrared, 2005, 35(2): 104–107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGHW20050200B.htm
[5] 黄英东, 安建波. 基于改进多项式拟合的红外焦平面非均匀性校正方法[J]. 红外, 2011, 32(3): 29–33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWAI201103009.htm
Huang Y D, An J B. A nonuniformity correction algorithm for IRFPA based on improved polynomial fitting[J]. Infrared, 2011, 32(3): 29–33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWAI201103009.htm
[6] Gadallah F L, Csillag F, Smith E J M. Destriping multisensor imagery with moment matching[J]. Int J Remote Sens, 2000, 21(12): 2505–2511. doi: 10.1080/01431160050030592
[7] 钱润达, 赵东, 周慧鑫, 等. 基于加权引导滤波与时域高通滤波的非均匀性校正算法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2018, 47(12): 1204001.
Qian R D, Zhao D, Zhou H X, et al. Non-uniformity correction algorithm based on weighted guided filter and temporal high-pass filter[J]. Infrared Laser Eng, 2018, 47(12): 1204001.
[8] Scribner D A, Sarkady K A, Caulfield J T, et al. Nonuniformity correction for staring IR focal plane arrays using scene-based techniques[J]. Proc SPIE, 1990, 1308: 224–233. http://spie.org/Publications/Proceedings/Paper/10.1117/12.21730
[9] 张爽, 周慧鑫, 牛肖雪, 等. 基于非局部均值滤波与时域高通滤波的非均匀性校正算法[J]. 光子学报, 2014, 43(1): 0110003. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZXB201401029.htm
Zhang S, Zhou H X, Niu X X, et al. Temporal high-pass filter nonuniformity correction algorithm based on non-local means filter for infrared focal plane array[J]. Acta Photon Sin, 2014, 43(1): 0110003. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZXB201401029.htm
[10] 李佳, 秦翰林, 延翔, 等. 时空域非线性滤波红外序列图像非均匀性校正[J]. 光子学报, 2015, 44(4): 0410001. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZXB201504017.htm
Li J, Qin H L, Yan X, et al. Temporal-spatial nonlinear filter based non-uniformity correction method for IR image sequence[J]. Acta Photon Sin, 2015, 44(4): 0410001. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZXB201504017.htm
[11] Münch B, Trtik P, Marone F, et al. Stripe and ring artifact removal with combined wavelet—Fourier filtering[J]. Opt Express, 2009, 17(10): 8567–8591. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.008567
[12] Pande-Chhetri R, Abd-Elrahman A. De-striping hyperspectral imagery using wavelet transform and adaptive frequency domain filtering[J]. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens, 2011, 66(5): 620–636. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2011.04.003
[13] Feng Q L, Gong J H. Destriping remotely sensed data using anisotropic diffusion in wavelet domain[C]//Proceedings of 2014 4th IEEE International Conference on Information Science and Technology, 2014.
[14] Vera E, Meza P, Torres S. Total variation approach for adaptive nonuniformity correction in focal-plane arrays[J]. Opt Lett, 2011, 36(2): 172–174. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.000172
[15] Bouali M, Ladjal S. Toward optimal destriping of MODIS data using a unidirectional variational model[J]. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens, 2011, 49(8): 2924–2935. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2119399
[16] Zhou G, Fang H Z, Yan L X, et al. Removal of stripe noise with spatially adaptive unidirectional total variation[J]. Optik, 2014, 125(12): 2756–2762. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2013.11.031
[17] Liu H, Zhang Z L, Liu S Y, et al. Destriping algorithm with L0 sparsity prior for remote sensing images[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, 2015.
[18] Celedón N, Redlich R, Figueroa M. FPGA-based neural network for nonuniformity correction on infrared focal plane arrays[C]//Proceedings of 2012 15th Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design, 2012: 193–200.
[19] Vera E, Torres S. Fast adaptive nonuniformity correction for infrared focal-plane array detectors[J]. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process, 2005, 2005(13): 560759. doi: 10.1155/ASP.2005.1994
[20] 徐文文, 周建勇, 唐遵烈, 等. TDI-CCD多抽头图像合成及非均匀性校正[J]. 半导体光电, 2009, 30(1): 153–155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BDTG200901038.htm
Xu W W, Zhou J Y, Tang Z L, et al. Synthesis and non-uniformity correction of TDI-CCD multi-tap's imaging[J]. Semicond Optoelectron, 2009, 30(1): 153–155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BDTG200901038.htm
[21] 吕雷, 张学峰. 基于FPGA的红外图像实时非均匀性校正[J]. 激光与红外, 2011, 41(6): 641–643. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGHW201106008.htm
Lü L, Zhang X F. Real-time infrared image nonuniformity correction base on FPGA[J]. Laser Infrared, 2011, 41(6): 641–643. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGHW201106008.htm
[22] 程旺, 吕群波, 赵娜. 基于FPGA的科学级CMOS图像传感器非均匀性校正[J]. 半导体光电, 2016, 37(6): 873–875, 889. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BDTG201606024.htm
Cheng W, Lv Q B, Zhao N. Non-uniformity correction of scientific CMOS image sensor based on FPGA[J]. Semicond Optoelectron, 2016, 37(6): 873–875, 889. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BDTG201606024.htm
[23] 夏候耀涛, 王万平, 黄涛. 基于FPGA的CMOS图像实时非均匀性校正方法[J]. 电子设计工程, 2019, 27(1): 184–188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWDZ201901036.htm
Xiahou Y T, Wang W P, Huang T. The real-time non-uniformity correction method on multichannel CMOS images based on FPGA[J]. Electron Des Eng, 2019, 27(1): 184–188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWDZ201901036.htm
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: