-
摘要
无线光通信信道复杂多变,喷泉码作为一种新兴的无速率编码无需信道的先验信息即可实现不同信道环境下的自适应传输,与传统编码相比更能提升无线传输的质量。本文首先总结了喷泉码应用于无线光通信的优势以及国内外喷泉码的发展现状,然后深入研究了两类喷泉码编码方案的设计以及对喷泉码性能影响重大的度分布函数的设计,总结了一种喷泉码即(LT)码的译码方法以及近些年不断提出优化的方案,同时指出了喷泉码设计中亟需解决的关键难点,最后提出了喷泉码应用于无线光通信的必要技术和探索方向。
Abstract
The optical wireless communication channel is complex and changeable. Fountain codes as an emerging rateless coding can achieve adaptive transmission in different channel environments without a priori information of the channel. Compared with traditional coding, it can improve the quality of wireless transmission. In this paper, we first summarize the advantages of fountain codes applied to optical wireless communication and the domestic and foreign researches on the development status of fountain codes. Then we deeply study the design of two kinds of fountain codes coding schemes, as well as the degree distribution function which has significant influence on the performance of fountain code. Soon we put forward one kind of fountain codes, namely Luby transform (LT) codes, and introduce the optimization schemes in recent years. Meanwhile, the key difficulties that need to be solved in the fountain codes design are pointed out. Finally, the necessary technologies and explorations direction of fountain codes for wireless optical communication are proposed.
-
Overview

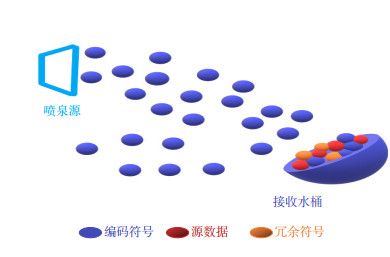
Overview: Fountain codes is a typical rateless coding scheme, which can also provide reliable guarantee for data transmission without channel feedback or channel estimation, and exhibit excellent adaptability to complex and variable optical wireless communication (OWC) channels. This paper reviews the development of fountain codes proposed nearly three decades ago. In 1998, Luby and other scholars proposed the concept of digital fountain in the context of solving large-scale data reliability transmission and broadcasting or multicast. Until 2002, Luby and his team designed the first practical fountain codes which be called Luby transform (LT) codes. In the theory of LT codes, robust soliton distribution (RSD) is innovatively proposed to regularize the choice of source symbols. In 2004, in order to solve the disadvantages of LT codes such as the high complexity and disability of realizing linear-time encoding or decoding, Shokrollahi et al. proposed a novel encoding scheme named Raptor (rapid tornado) codes that creatively concatenates linear block codes and LT codes together. They also optimized the fixed distribution function of Raptor codes for different information lengths. After that, some new digital fountain codes such as system fountain codes, incremental codes, spinal codes and Kite codes were successively proposed these years. Although the fountain codes was originally proposed for erasure channels, since it has great adaptivity in various channel conditions, the research of fountain code has been extended to the wireless channel in 2006, and the soft decision decoding algorithm for the fountain codes under wireless channels was obtained. At present, the fountain codes has been widely applied in wireless communication relay, space diversity, wireless cooperative transmission, etc. Thanks to its rateless characteristics, any number of coded packets can be adaptively generated according to channel conditions, producing excellent performance under erasure channel. However, when fountain codes are used in wireless channels, the design of the coding and degree distribution need to be reconsidered, which often causes the problem of high complexity and error floor. Therefore, the research hotspot of the fountain code under optical wireless communication is to cascade it with the channel coding schemes with capability of error detection, so that the fountain code can also exert its advantages under the noise channel. In short, the application prospects of fountain codes in OWC will be promising. This review focuses on the principle of fountain code and the fountain code with excellent performance, and it sheds some light on the future application of fountain code in scenario of OWC.
-

-
表 1 国内外喷泉码的研究进展
Table 1. Research progress of fountain codes abroad
年份 研究者 研究进展 1998 Byers和Luby 首次提出了数字喷泉的概念[7] 2002 Luby 提出了第一种实用的喷泉码—LT(Luby Transform)码 2004 Shokrollahi 构造了具有线性时间复杂度的Raptor码 2005 Luby和Shokrollahi 成立了数字喷泉公司,提出的多项方案成为了3GPP多媒体广播业务的标准方案 2006 Puducherry 提出了分布式编码方案及其性能[16-17] 2007 Hyytia 研究了短码长下LT码度分布的优化设计[18] 2009 Sejdinovic 利用加窗的方式构造了具有不等差错保护特性的喷泉码[19] 2009 Bioglio 提出了即时高斯消元法(OFG)译码算法降低了译码复杂度和译码时延[20] 2012 Sorensen 研究了在AWGN信道下LT码ripple的设计[21] 2015 雷维嘉 提出了修正二进制-鲁棒孤子分布 2016 姚伟清 提出了鲁棒泊松度分布[22] 2017 牛芳琳 提出了基于部分信息度分布构造喷泉码的方法 2017 张勋 比较了转移鲁棒孤子分布下LT码与LDPC码性能[23] 2018 曹阳 将LT码与奇偶校检码级联降低了MIMO系统误码扩散的问题[24] 表 2 PRSD和RSD的性能对比
Table 2. Performance comparison between PRSD and RSD
输入符号 平均译码开销/(%) 平均度值 译码耗时/s K RSD PRSD RSD PRSD RSD PRSD 500 24.27 9.42 9.50 5.76 3.81 2.17 1000 20.46 7.56 10.72 6.30 17.48 8.08 2000 16.80 5.82 11.63 6.51 47.21 25.21 表 3 不同码长下优化出Raptor码的度分布
Table 3. Optimizing the degree distribution of Raptor codes under different code length
K 65536 80000 100000 120000 Ω1 0.007969 0.007544 0.006495 0.004807 Ω2 0.493570 0.493610 0.495044 0.496472 … … … … … Ω66 0.03135 0.010479 0.016298 0.009100 Ω67 \ 0.017365 0.010777 \ ε 0.038 0.035 0.028 0.02 α 5.87 5.91 5.85 5.83 -
参考文献
[1] 许国良, 张旭苹, 徐伟弘, 等.自由空间光通信[J].光电子技术, 2002, 22(4): 198-205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-488X.2002.04.003
Xu G L, Zhang X P, Xu W H, et al. Free space optical communication[J]. Optoelectronic Technology, 2002, 22(4): 198-205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-488X.2002.04.003
[2] Hayajneh K F, Yousefi S. Overlapped LT codes over the binary erasure channel: analysis and design[J]. IET Communications, 2019, 13(16): 2567-2572. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2018.5273
[3] 徐大专, 许生凯, 华洁, 等.数字喷泉码度分布优化设计的最新研究进展[J].数据采集与处理, 2015, 30(4): 733-746. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sjcjycl201504004
Xu D Z, Xu S K, Hua J, et al. Recent progress on optimization design of degree distributions in digital fountain codes[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2015, 30(4): 733-746. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sjcjycl201504004
[4] Xiong K, Zhang Y, Fan P Y, et al. Evaluation framework for user experience in 5G systems: on systematic rateless-coded transmissions[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 9108-9118. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2644106
[5] Luby M. LT codes[C]//Proceedings of the 43rd Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, 2002: 271-280.
[6] Byers J W, Luby M, Mitzenmacher M. A digital fountain approach to asynchronous reliable multicast[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2002, 20(8): 1528-1540. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2002.803996
[7] Luby M G, Mitzenmacher M, Shokrollahi M A, et al. Practical loss-resilient codes[C]//Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, 1997: 150-159.
[8] Mirrezaei S M, Faez K, Yousefi S. Towards fountain codes[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2014, 77(2): 1533-1562. doi: 10.1007/s11277-013-1597-7
[9] Byers J W, Luby M, Mitzenmacher M. A digital fountain retrospective[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2019, 49(5): 82-85. doi: 10.1145/3371934.3371960
[10] Palanki R, Yedidia J S. Rateless codes on noisy channels[C]//Proceedings of International Symposium onInformation Theory, 2004: 37.
[11] Castura J, Mao Y. Rateless coding over fading channels[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2006, 10(1): 46-48. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2006.1576565
[12] Jiao J, Qinyu Z, Hui L. Design of Concatenated Fountain Code in Deep Space Communication[C]// 5th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, IEEE, 2009.
[13] Rahnavard N, Vellambi B N, Fekri F. Rateless codes with unequal error protection property[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(4): 1521-1532. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2007.892814
[14] Wu G, Yang C Y, Li S Q, et al. Recent advances in energy-efficient networks and their application in 5G systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2015, 22(2): 145-151. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2015.7096297
[15] 张勋, 曹阳, 彭小峰, 等. MIMO-FSO系统中LT码的性能分析[J].激光杂志, 2017, 38(3): 61-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jgzz201703015
Zhang X, Cao Y, Peng X F, et al. Performance analysis of LT codes in MIMO-FSO system[J]. Laser Journal, 2017, 38(3): 61-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jgzz201703015
[16] Puducheri S, Kliewer J, Fuja T E. Distributed LT codes[C]//Proceedings of 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, 2006: 987-991.
[17] Puducheri S, Kliewer J, Fuja T E. The design and performance of distributed LT codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(10): 3740-3754. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2007.904982
[18] Hyytia E, Tirronen T, Virtamo J. Optimal Degree Distribution for LT Codes with Small Message Length[C]// INFOCOM 2007. 26th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, 2007.
[19] Sejdinovic D, Vukobratovic D, Doufexi A, et al. Expanding window fountain codes for unequal error protection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2009, 57(9): 2510-2516. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2009.09.070616
[20] Bioglio V, Grangetto M, Gaeta R, et al. On the fly gaussian elimination for LT codes[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2009, 13(12): 953-955. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2009.12.091824
[21] Sorensen J H, Koike-Akino T, Orlik P, et al. Ripple design of LT codes for BIAWGN channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2014, 62(2): 434-441. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2013.122013.130116
[22] Yao W Q, Yi B S, Huang T Q, et al. Poisson robust soliton distribution for LT codes[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(8): 1499-1502. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2578920
[23] 张勋.大气激光通信中喷泉码及其级联码技术研究[D].重庆: 重庆理工大学, 2018.
Zhang X. Research on fountain code and its cascade over atmospheric laser communication[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University of Technology, 2018.
[24] 曹阳, 张勋, 彭小峰, 等.空间光通信中基于多输入多输出的级联码方案研究[J].光学学报, 2018, 38(1): 0106003. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201801009
Cao Y, Zhang X, Peng X F, et al. Cascade scheme based on multiple-input multiple-output in spatial optical communication[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(1): 0106003. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201801009
[25] Lázaro F, Liva G, Bauch G. Inactivation decoding of LT and Raptor codes: analysis and code design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2017, 65(10): 4114-4127.
[26] Byers J W, Luby M, Mitzenmacher M, et al. A digital fountain approach to reliable distribution of bulk data[C]//Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM '98 Conference on Applications, Technologies, Architectures, and Protocols for Computer Communication, 1998: 56-67.
[27] MacKay D J C. Fountain codes[J]. IEE Proceedings Communications, 2005, 152(6): 1062-1068. doi: 10.1049/ip-com:20050237
[28] Liang M S, Duan J J, Zhao D F. Optimal redundancy control strategy for fountain code-based underwater acoustic communication[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 69321-69334. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2879911
[29] MacKay D J C. Information Theory, Inference, and Learning Algorithms[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003.
[30] Li G T, Wu H K, Lee H C, et al. Systematic physical-layer raptor coding to attain low decoding complexity[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(6): 1124-1127. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2828857
[31] Karp R, Luby M, Shokrollahi A. Finite length analysis of LT codes[C]//Proceedings of International Symposium on Information Theory, 2004: 39.
[32] Di C Y, Proietti D, Telatar I E, et al. Finite-length analysis of low-density parity-check codes on the binary erasure channel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2002, 48(6): 1570-1579. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2002.1003839
[33] Xu S K, Xu D Z. Design of degree distributions for finite length LT codes[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2018, 98(2): 2251-2260. doi: 10.1007/s11277-017-4972-y
[34] Abbas R, Shirvanimoghaddam M, Huang T, et al. Novel design for short analog fountain codes[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(8): 1306-1309. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2910517
[35] Huang W Z. Investigation on digital fountain codes over erasure channels and additive white Gaussian noise channels[D]. Columbus: Ohio University, 2012.
[36] Khonsari H, Okpotse T, Valipour M, et al. Analysis of ripple size evolution in the LT process[J]. IET Communications, 2018, 12(14): 1686-1693. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2017.1352
[37] Kim S, Ko K, Chung S Y. Incremental Gaussian elimination decoding of raptor codes over BEC[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2008, 12(4): 307-309. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2008.072141
[38] Etesami O, Shokrollahi A. Raptor codes on binary memoryless symmetric channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(5): 2033-2051. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.872855
[39] Palanki R. Iterative decoding for wireless networks[D]. Pasadena, California: California Institute of Technology, 2004.
[40] Castura J, Mao Y Y. When is a message decodable over fading channels?[C]//Proceedings of the 23rd Biennial Symposium on Communications, 2006: 59-62.
[41] He J G, Hussain I, Li Y, et al. Distributed LT codes with improved error floor performance[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 8102-8110. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2890452
[42] Auguste, Poulliat C, Declercq D. Jointly Decoded Raptor Codes: Analysis and Design for the BIAWGN Channel[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2009, 2009:1-11. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_465e3ba52cfea4a1cf68dadec24d3485
[43] Liu X, Lim T J. Fountain codes over fading relay channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2009, 8(6): 3278-3287. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2009.081102
[44] Subhagya A A M, Kaythry P, Kishore R. LT code based forward error control for wireless multimedia sensor networks[C]//Proceedings of 2017 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking, 2017: 1612-1616.
[45] Borkotoky S S, Pursley M B. Fountain-coded broadcast distribution in multiple-hop packet radio networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2019, 27(1): 29-41. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2018.2882303
[46] Spencer J, Hayajneh K F, Yousefi S. Robust quaternary fountain codes in AWGN interference[J]. IET Communications, 2018, 12(20): 2561-2567. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2018.5491
[47] Deng D C, Xu D Z, Xu S K. Optimisation design of systematic LT codes over AWGN multiple access channel[J]. IET Communications, 2018, 12(11): 1351-1358. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2017.1063
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: