-
摘要
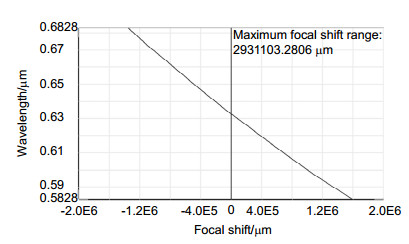
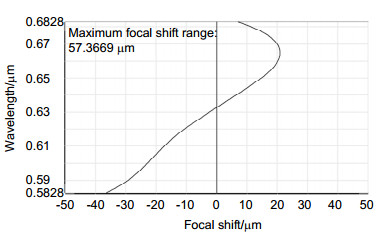
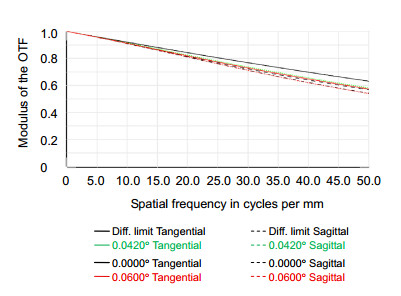
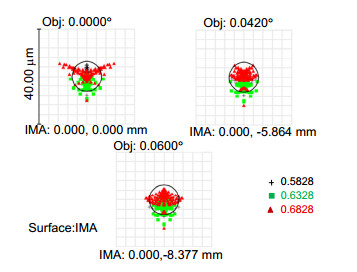
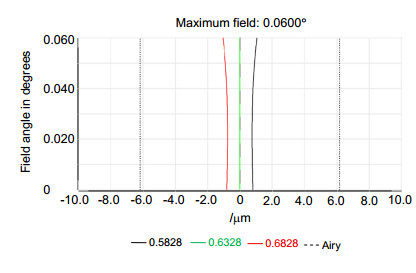
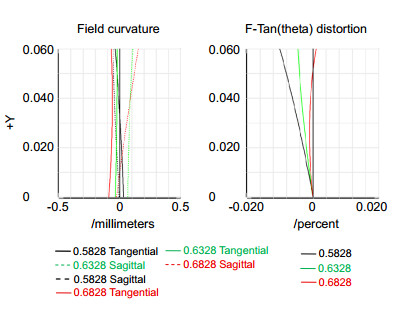
本文基于Schupmann消色差理论,介绍了一种离轴四反射镜衍射成像光学系统设计方法。设计了口径1 m、F数为8、视场0.12°、波段582.8 nm~682.8 nm的离轴四反射镜衍射成像光学系统。设计结果表明,该光学系统的色差得到有效校正,系统调制传递函数(MTF)在50 lp/mm范围内优于0.53,弥散斑半径的均方根值小于艾里斑半径,成像质量接近衍射极限。分析了平面衍射物镜和曲面衍射校正镜可分别采用二元光刻工艺和金刚石车削技术制作的原因。对设计结构进行公差分析,确定公差误差主要来源于中继反射镜的倾斜角度,为装调过程提供指导。设计的系统为宽波段、高像质的反射式衍射成像光学系统发展提供了参考。

Abstract
According to the Schupmann's achromatic theory, a calculation method of off-axis four-mirror diffractive imaging optical system is introduced. By using the method, an optical system which has an aperture of 1 m, F-number of 8, full field of view of 0.12°, waveband of 582.8 nm~682.8 nm is designed. The results show that the chromatic aberration is corrected effectively. The modulation transfer function (MTF) is more than 0.53 in the range of 50 lp/mm, and the RMS radius of diffusion spot is less than the airy radius. It demonstrates that the image quality of this system is close to the diffraction limit. It is analyzed that the processing of diffractive primary lens and diffractive correct mirror can be realized by traditional lithography and diamond turning, respectively. Monte-Carlo simulation of tolerance analysis is carried out, it determined that the tolerance error mainly originates from the tilt angle of relay mirror, which provides guidance for the process of assembling and adjusting. This system has the advantages of broadband, high image quality, which can provide references for the development of reflective diffractive imaging optical system.
-
Key words:
- optical design /
- diffractvie imaging /
- off-axis /
- four-mirror
-
Overview

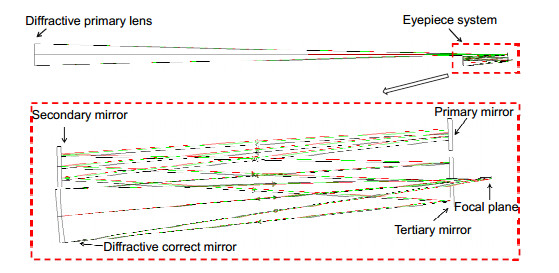
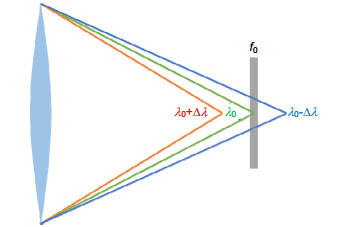
Overview: The most effective way to improve the resolution of space optical telescope is to enlarge the aperture. With the increase of aperture, it has become increasingly difficult for traditional reflective space telescope system considering manufacturing technology, the ability to launch and space expansion as well as adjustment technology. Furthermore, considering the support and control structure, the weight of optical telescope system is proportional to the square of aperture. As a result, the control becomes more complex and the cost of optical system is increasing rapidly. Compared with the reflective telescope optical system, diffractive imaging system based on the thin film material as the objective lens can achieve large diameter, high resolution, light weight structure, space packagable and deployable, loose tolerance and so on. Diffractive imaging technology can save launch and manufacturing costs significantly, and has great potential applications in the field of high orbit high-resolution imaging. The existing eyepiece systems of diffractive telescopes mostly use refractive structure, but it can hardly meet the requirements of large aperture space optical telescope in terms of complexity and quality. The reflective eyepiece system has obvious advantages of high image quality, light weight and wide waveband because of its non-chromatic aberration and deflection of optical path. To realize an off-axis reflective diffractive imaging optical system with broadband and compact structure, we analysis the basic principle of diffractive imaging optical system. According to the Schupmann’s achromatic theory, a calculation method of off-axis four-mirror diffractive imaging optical system is introduced. By using the method, an optical system which has an aperture of 1 m, F-number of 8, waveband of 582.8 nm~682.8 nm and the full field of view of 0.12° is designed. The results show that the chromatic aberration is corrected effectively. The modulation transfer function (MTF) of the full field of view is more than 0.53 in the range of 50 lp/mm, the RMS radius of diffusion spot is less than the airy radius. It demonstrates that the image quality of system is close to the diffraction limit. It is analyzed that the processing of diffractive primary lens and diffractive correct mirror can be realized by traditional lithography and diamond turning, respectively. Monte-Carlo simulation of tolerance analysis is carried out, it determined that the tolerance error mainly originate from the tilt angle of relay mirror, which provides guidance for the process of assembling and adjusting. This system has the advantages of broadband, short optical path, ideal obscuration, which can provide references for the development of reflective diffractive imaging optical system.
-

-
表 1 同轴四反射镜衍射成像光学系统初始结构参量
Table 1. Initial parameters of diffractive imaging optical system based on coaxial four-mirror
Surface Radius/mm Thickness/mm Diffractive objective — 20000.000 Primary mirror -1980.200 -1000.000 Secondary mirror -666.561 1000.000 Tertiary mirror -1004.784 -1000.000 Diffractive correct mirror 100.000 70.000 Image — — 表 2 优化后的离轴四反射镜衍射成像光学系统结构参量
Table 2. Optimized parameters of diffractive imaging optical system based on off-axis four-mirror
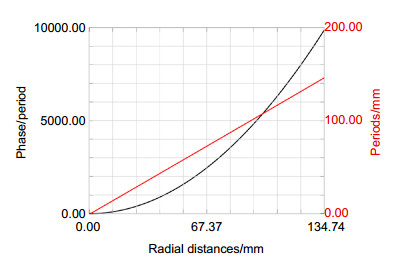
Surface Radius/mm Thickness/mm Conic Diameter/mm Diffractive objective — 20750.000 — 1000 Primary mirror -9925.477 -1938.785 -2.794 160 Secondary mirror 45520.000 1938.785 -4.982 200 Tertiary mirror 153600.000 -1938.785 2.745 250 Diffractive correct mirror 1539.624 2148.094 -0.160 270 Image — — — 17 表 3 衍射面多项式系数
Table 3. Coefficient of diffractive surface
Surface Coefficient Diffractive objective -0.248, 1.551E-010, -1.926E-019, -6.008E-027, 1.026E-032 Diffractive correct mirror 3.411, 3.141E-007, -1.094E-013, 1.392E-017, -4.556E-022 表 4 蒙特卡洛最终分析结果
Table 4. Final Monte-Carlo analysis results
Monte-Carlo analysis MTF value ≥98% 0.111 ≥90% 0.165 ≥80% 0.216 ≥50% 0.302 ≥20% 0.400 ≥10% 0.439 ≥2% 0.481 表 5 最敏感的公差分析结果
Table 5. Results of the most sensitive tolerance analysis
Type Value Criterion Change TETY 3 4 0.00140000 0.32911857 -0.19965035 TETY 3 4 -0.00140000 0.32911857 -0.19965035 TETX 3 4 0.00140000 0.38914889 -0.13962002 TETX 3 4 -0.00140000 0.39516929 -0.13359962 TEDY 3 4 0.01000000 0.49963567 -0.02913324 TEDY 9 9 -0.01000000 0.50957441 -0.01919451 TEDX 3 4 0.01000000 0.51019057 -0.01857834 TEDX 3 4 -0.01000000 0.51019057 -0.01857834 TEZI 5 -1.5820E-005 0.51396962 -0.01479929 TEDX 9 9 0.01000000 0.51761049 -0.01115843 -
参考文献
[1] 于前洋, 曲宏松.实现同步轨道(GEO)高分辨力对地观测的技术途径(上)[J].中国光学, 2008, 1(1): 1–12. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zggxyyygxwz200901001
Yu Q Y, Qu H S. Realization of high-resolution visible earth observation on geostationary earth orbit[J]. Chinese Journal of Optics and Applied Optics, 2008, 1(1): 1–12. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zggxyyygxwz200901001
[2] Whiteaker K L, Marshalek R G, Domber J L, et al. Large aperture diffractive receiver for deep space optical communications[C]//Proceedings of Applications of Lasers for Sensing and Free Space Communications 2015, Arlington, Virginia United States, 2015: LTh3C.3.
[3] Huang W, Ma J Y, Zhu F, et al. Low divergent diffractive optical element for remote detection[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2014, 12(7): 070501. doi: 10.3788/COL201412.070501
[4] 刘韬, 周一鸣, 王景泉, 等.波带片衍射成像技术在对地观测卫星中的应用[J].航天器工程, 2012, 21(3): 88–95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2012.03.035
Liu T, Zhou Y M, Wang J Q, et al. Application of zone plate diffractive imaging technology in earth observation satellites[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2012, 21(3): 88–95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2012.03.035
[5] Rahlves M, Rezem M, Boroz K, et al. Flexible, fast, and low-cost production process for polymer based diffractive optics[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(3): 3614–3622. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.003614
[6] 刘玉凤, 李林.二元光学透镜在资源卫星中的应用[J].光学技术, 2004, 30(5): 590–593. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.2004.05.022
Liu Y F, Li L. Application of binary optical lens in resource satellite[J]. Optical Technique, 2004, 30(5): 590–593. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.2004.05.022
[7] Tullson D, Andersen G. Broadband antihole photon sieve telescope[J]. Applied Optics, 2007, 46(18): 3706–3708. doi: 10.1364/AO.46.003706
[8] 杨伟, 吴时彬, 汪利华, 等.微结构薄膜望远镜研究进展分析[J].光电工程, 2017, 44(5): 475–482. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.05.001
Yang W, Wu S B, Wang L H, et al. Research advances and key technologies of macrostructure membrane telescope[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017, 44(5): 475–482. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.05.001
[9] Li Z L, Kim I, Zhang L, et al. Dielectric meta-holograms enabled with dual magnetic resonances in visible light[J]. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(9): 9382–9389. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b04868
[10] Hyde R A. Eyeglass. 1. Very large aperture diffractive telescopes[J]. Applied Optics, 1999, 38(19): 4198–4212. doi: 10.1364/AO.38.004198
[11] Hyde R A, Dixit S N, Weisberg A H, et al. Eyeglass: a very large aperture diffractive space telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2002, 4849: 28–39. doi: 10.1117/12.460420
[12] Atcheson P D, Stewart C, Domber J, et al. MOIRE: initial demonstration of a transmissive diffractive membrane optic for large lightweight optical telescopes[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2012, 8442: 844221. doi: 10.1117/12.925413
[13] Copp T L, Domber J L, Atcheson P D, et al. MOIRE: membrane material property characterizations, testing and lessons learned[C]//Proceedings of Spacecraft Structures Conference, National Harbor, Maryland, 2014.
[14] Domber J L, Atcheson P D, Kommers J. MOIRE: ground test bed results for a large membrane telescope[C]//Proceedings of Spacecraft Structures Conference, National Harbor, Maryland, 2014.
[15] Atcheson P, Domber J, Whiteaker K, et al. MOIRE: ground demonstration of a large aperture diffractive transmissive telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9143: 91431W. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ024144916/
[16] Britten J A, Dixit S N, DeBruyckere M, et al. Large-aperture fast multilevel Fresnel zone lenses in glass and ultrathin polymer films for visible and near-infrared imaging applications[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(11): 2312–2316. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.002312
[17] Andersen G. Large optical photon sieve[J]. Optics Letters, 2005, 30(22): 2976–2978. doi: 10.1364/OL.30.002976
[18] Andersen G. Membrane photon sieve telescopes[J]. Applied Optics, 2010, 49(33): 6391–6394. doi: 10.1364/AO.49.006391
[19] 张健, 栗孟娟, 阴刚华, 等.用于太空望远镜的大口径薄膜菲涅尔衍射元件[J].光学 精密工程, 2016, 24(6): 1289–1296. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201606008
Zhang J, Li M J, Yin G H, et al. Large-diameter membrane Fresnel diffraction elements for space telescope[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(6): 1289–1296. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxjmgc201606008
[20] 王若秋.基于衍射成像系统的薄膜元件关键技术研究[D].长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2017.
Wang R Q. Research on key technologies of thin film element based on diffractive imaging system[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80139-1017063979.htm [21] 徐琰, 颜树华, 周春雷, 等.宽波段超大孔径反衍望远系统设计[J].半导体光电, 2007, 28(4): 579–592. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5868.2007.04.034
Xu Y, Yan S H, Zhou C L, et al. Design of hybrid reflective-diffractive telescope with very large aperture and broad bandwidth[J]. Semiconductor Optoelectronics, 2007, 28(4): 579–592. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5868.2007.04.034
[22] 任智斌, 胡佳盛, 唐洪浪, 等. 10m大口径薄膜衍射主镜的色差校正技术研究[J].光子学报, 2017, 46(4): 0422004. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gzxb201704004
Ren Z B, Hu J S, Tang H L, et al. Study on chromatic aberration correction of 10 meter large aperture membrane diffractive primary lens[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2017, 46(4): 0422004. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gzxb201704004
[23] 张楠, 卢振武, 李凤有.衍射望远镜光学系统设计[J].红外与激光工程, 2007, 36(1): 106–108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2007.01.026
Zhang N, Lu Z W, Li F Y. Optical design of diffractive telescope[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2007, 36(1): 106–108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2007.01.026
[24] Faklis D, Morris G M. Broadband imaging with holographic lenses[J]. Optical Engineering, 1989, 28(6): 286592. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=CC026097793
[25] 郭永洪.现代红外光学系统研究[D].杭州: 浙江大学, 1999.
http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y323849 [26] 潘君骅.光学非球面的设计、加工与检验[M].苏州:苏州大学出版社, 2004.
Pan J H. The Design, Manufacture and Test of the Aspherical Optical Surfaces[M]. Suzhou: Suzhou University Press, 2004.
[27] ZEMAX Development Corporation. Zemax OpticStudio 17 Help Files[M]. 2016.
[28] 张以谟.现代应用光学[M].北京:电子工业出版社, 2018.
Zhang Y M. Contemporary Applied Optics[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2018.
[29] 王松, 杨伟, 吴时彬, 等.柔性光学聚酰亚胺薄膜折射率均匀性检测方法[J].光电工程, 2016, 43(7): 85–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.07.014
Wang S, Yang W, Wu S B, et al. Refractive index homogeneity measure method of flexible optical polyimide film[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2016, 43(7): 85–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.07.014
[30] 王鹏.衍射光学元件设计及金刚石单点车削技术的研究[D].长春: 长春理工大学, 2007.
Wang P. Research on design and process prameters of diamond turning of diffractive optical elements[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2007.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10186-2007063788.htm -
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: