Retinal vascular segmentation combined with PCNN and morphological matching enhancement
-
摘要
针对人工手动提取视网膜血管工作量大,主观性强等问题,本文提出了一种将区域生长思想、脉冲耦合神经网络(PCNN)、高斯滤波器组及Gabor滤波器相结合的视网膜血管分割方法。首先将二维高斯滤波器组、二维Gabor匹配滤波器相结合,对视网膜血管区域进行形态匹配增强,提升血管与背景的对比度。然后将带有快速连接机制的PCNN与区域生长思想相结合,每次从未处理的像素点中选取亮度最大的作为种子,使用自适应的连接系数及停止条件,实现眼底图像中血管的自动分割。整个算法在DRIVE眼底数据库上的实验结果显示,平均准确度、灵敏度、特异性分别达到93.96%、78.64%、95.64%,分割结果中血管断点少,微小血管清晰,具有较好的应用前景。

Abstract
Aiming at the problem of large workload and strong subjectivity for manual retinal vessels extraction, this paper proposes a retinal vessel segmentation method that combines regional growing strategy, pulse coupled neural network (PCNN), a Gaussian filter bank and a Gabor filter. First, 2D Gaussian filter bank and 2D Gabor filter are combined to enhance the shape retinal blood vessel region and strengthen the contrast between the blood vessel and the background. Then, PCNN with fast linking mechanism and region growing idea is implemented to achieve automatic retinal vessel segmentation in which the unprocessed pixel with highest intensity is set as the seed, and the adaptive linking weight and stop conditions are adopted. The experimental results on the DRIVE fundus database show that the average accuracy, sensitivity and specificity are 93.96%, 78.64%, 95.64%, respectively. The segmentation results have less vascular breakpoints and clear micro-vessels. This work has promising application value.
-
Overview

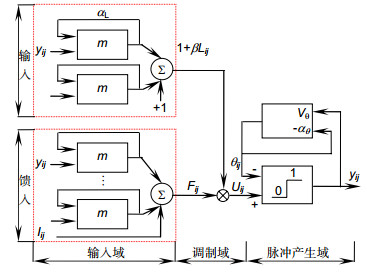
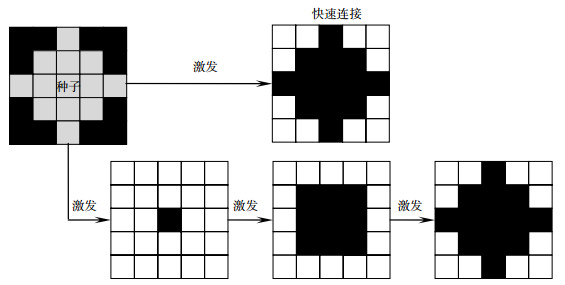
Overview: Studies indicate that retinal blood vessels are the only deep micro-vessels in a human body that can be observed directly in a non-invasive way. The variation of color or the morphological structure of vascular networks can reflect the effects on human health of various eye diseases and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Therefore, the extraction and analysis of retinal vascular is of great significance for medical personnel to diagnose and treat these diseases as early as possible. Due to the limitation of image acquisition equipment and the complex structure of retinal blood vessels, manual extraction of retinal blood vessels has problems of heavy workload and strong subjectivity. Aiming at the problem, this paper proposes a novel automatic retinal vessel image segmentation algorithm based on matched filter enhancement and region growth pulse coupled neural network. Firstly, the original fundus image is pre-processed with a 2D Gaussian filter bank and a 2D Gabor matched filter bank to achieve the contrast enhancement and denoising. By combining these two kinds of filters, the final fused retina image can present more details and less artifact noisy micro-vessels. Secondly, a modified regional growing pulse coupled neural network with fast linking mechanism is adopted. The pixel with the highest brightness is selected as the seed, and adaptive connection coefficients and specially designed terminating conditions are employed to control the growth of the candidate blood vessel area. Operating in this way can overcome the shortcomings of the regular region-growing technique requiring fixed preselected seeds and the traditional PCNN not being able to terminate automatically. In order to evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithm, the DRIVE image dataset, which has been widely used for retina image processing, is adopted. The dataset was acquired using a Canon CR5 non-mydriatic 3CCD camera and each image was captured using 8 bits per color plane at 768 pixelsx584 pixels. The dataset of 40 images has been divided into a training set and a test set, both containing 20 images. The experimental results demonstrate that the algorithm can maintain the consistency of the segmented results and meanwhile achieve the multi-value segmentation of fundus vascular images. The whole algorithm performs well in the DRIVE fundus database. The average accuracy, sensitivity and specificity of the algorithm respectively are 93.96%, 78.64% and 95.64% in DRIVE fundus database. There are fewer vascular breakpoints in the segmentation results, and the micro-vessels are clear. We believe that this work has good application prospects.
-

-
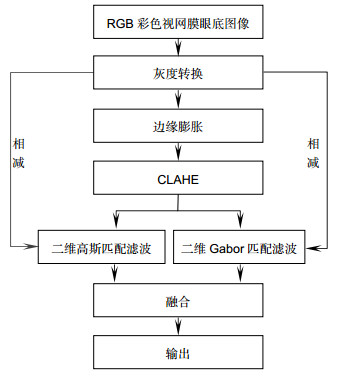
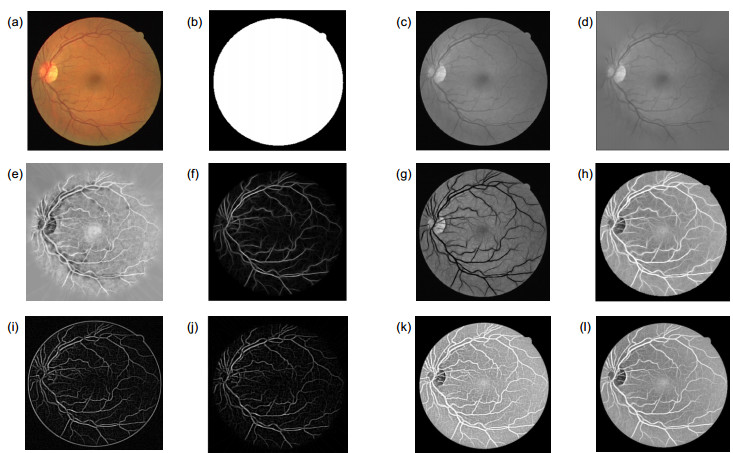
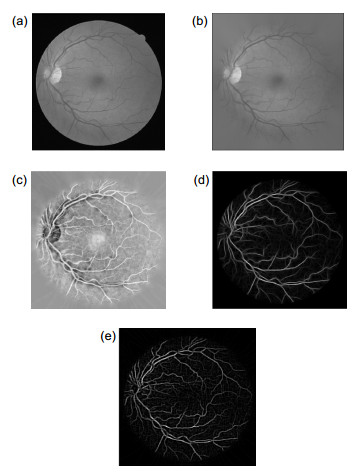
图 6 预处理结果。(a)原图;(b)掩膜;(c)灰度处理;(d)边缘膨胀;(e) CLAHE处理;(f) Gabor滤波;(g) 图 6(d)和6(f)相减;(h) 图 6(g)取反;(i)不进行边缘膨胀处理时匹配滤波的结果;(j)高斯滤波;(k) 图 6(d)和6(j)相减之后取反;(l)最终融合结果
Figure 6. Pre-processing results. (a) Original image; (b) Mask; (c) Grayscale processing; (d) Edge expansion; (e) CLAHE processing; (f) Gabor filtering; (g) Subtraction of (d) and (f); (h) Inverse-color of (g); (i) Matching filtering results without edge expansion; (j) Gaussian filtering; (k) Subtracting (d) from (j) and taking the opposite; (l) Fusion of filtering results
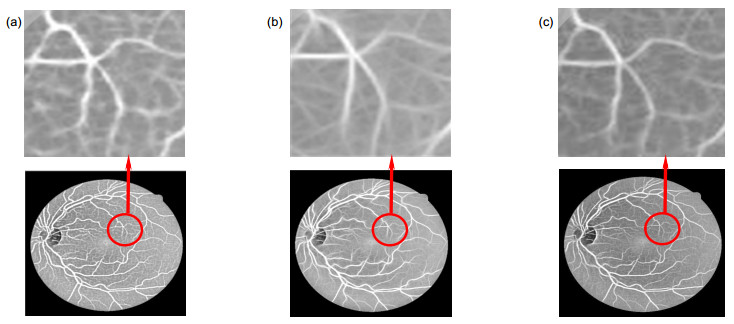
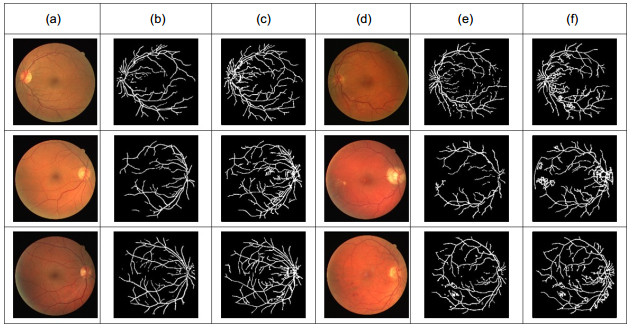
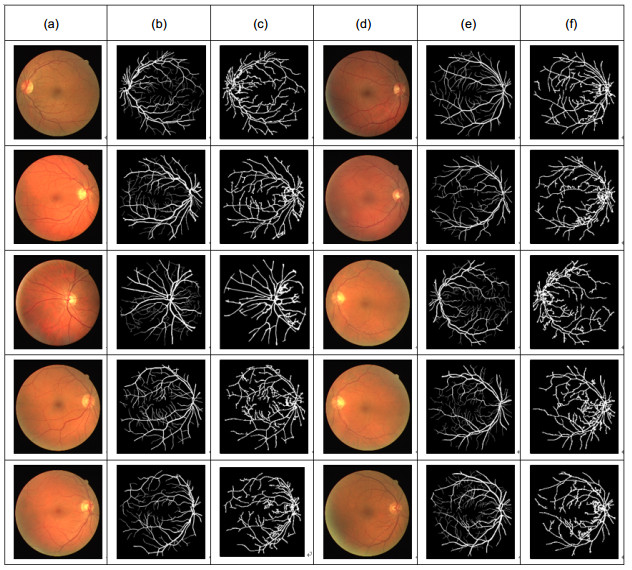
图 8 与文献[27]中分割结果的对比。(a)健康原图;(b)文献[27]对健康图像处理结果;(c)本文对健康图像处理结果;(d)不健康原图;(e)文献[27]对不健康图像处理结果;(f)本文对不健康图像处理结果
Figure 8. Comparison with the segmentation results of ref. [27]. (a) Normal images; (b) The processing results of healthy images in ref. [27]; (c) The processing results of the proposed method on healthy images; (d) Abnormal images; (e) The processing results of abnormal images in ref. [27]; (f) The processing results of the proposed method on abnormal images
表 1 测试图像预处理过程中的参数设置
Table 1. Parameter settings of test images pre-processing
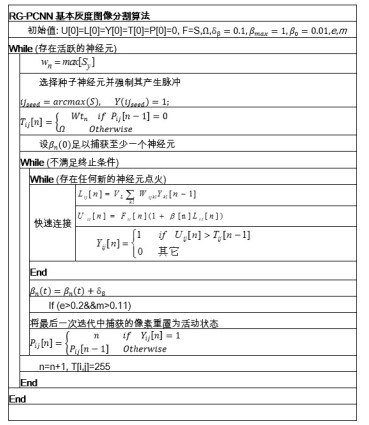
直方图均衡化参数 二维高斯滤波器参数 二维Gabor滤波器参数 子块数 裁剪值 θ1 σ L1 θ2 L2 40 0.02 15 1 9 5 2.9 表 2 测试图像分割算法的参数设置
Table 2. Parameter settings of segmentation algorithm used in test images
β0 δβ βmax e m T 0.01 0.1 1 0.2 0.11 255 表 3 血管分割结果中的四种情况
Table 3. Four cases of blood vessel segmentation results
分类像素点 实际为血管点 实际为背景点 检测为血管点 真阳性 假阳性 检测为背景点 真阴性 假阴性 表 4 Gabor滤波的结果
Table 4. Gabor filtering results
对象 Acc Sen Spe 01 93.71 79.46 95.11 02 94.03 75.89 96.10 04 93.08 70.87 95.54 16 93.73 76.58 95.44 18 93.24 77.88 94.57 19 94.15 81.25 95.31 20 93.56 81.05 94.55 09 93.40 77.63 94.79 10 93.08 75.86 94.63 06 92.75 72.06 94.98 表 5 高斯滤波的结果
Table 5. Gaussian filtering results
对象 Acc Sen Spe 01 94.05 78.53 95.57 02 93.58 72.43 96.00 04 93.02 71.86 95.17 16 93.65 76.17 95.38 18 93.49 78.66 94.76 19 94.21 81.56 95.35 20 93.77 82.51 94.66 09 92.76 73.44 94.46 10 92.89 73.70 94.61 06 92.79 69.52 95.30 表 6 Gabor滤波与高斯滤波融合的结果
Table 6. Results of combining Gabor filtering with Gaussian filtering
对象 Acc Sen Spe 01 94.43 80.67 95.78 02 94.11 75.79 96.20 04 93.20 72.83 95.26 16 94.23 79.08 95.74 18 94.37 83.88 95.27 19 94.56 83.69 95.54 20 94.13 84.95 94.85 09 93.44 77.45 94.85 10 93.41 77.18 94.87 06 93.30 72.16 95.58 表 7 不同算法的性能比较
Table 7. Performance comparison among different algorithms
-
参考文献
[1] Marin D, Aquino A, Gegunde-Zarias M E, et al. A new supervised method for blood vessel segmentation in retinal images by using gray-level and moment invariants-based features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2011, 30(1):146-158. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2010.2064333
[2] Zhao Y Q, Wang X H, Wang X F, et al. Retinal vessels segmentation based on level set and region growing[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2014, 47(7):2437-2446. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2014.01.006
[3] 顾晓东, 郭仕德, 余道衡.一种基于PCNN的图像去噪新方法[J].电子与信息报, 2002, 24(10):1304-1309. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkxxk200210002
Gu X D, Guo S D, Yu D H. New approach for noise reducing of image based on PCNN[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2002, 24(10):1304-1309. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkxxk200210002
[4] Chaudhuri S, Chatterjee S, Katz N, et al. Detection of blood vessels in retinal images using two-dimensional matched filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 1989, 8(3):263-269. doi: 10.1109/42.34715
[5] Jiang X Y, Mojon D. Adaptive local thresholding by verification-based multithreshold probing with application to vessel detection in retinal images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2003, 25(1):131-137. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2003.1159954
[6] Gang L, Chutatape O, Krishnan S M. Detection and measurement of retinal vessels in fundus images using amplitude modified second-order Gaussian filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2002, 49(2):168-172. doi: 10.1109/10.979356
[7] Zhang B, Zhang L, Zhang L, et al. Retinal vessel extraction by matched filter with first-order derivative of Gaussian[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2010, 40(4):438-445. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2010.02.008
[8] Soares J V B, Leandro J J G, Cesar R M, et al. Retinal vessel segmentation using the 2-D Gabor wavelet and supervised classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2006, 25(9):1214-1222. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2006.879967
[9] Gwetu M V, Tapamo J R, Viriri S. Segmentation of retinal blood vessels using normalized Gabor filters and automatic thresholding[J]. South African Computer Journal, 2014, 55(1):12-24. doi: 10.18489/sacj.v55i0.228
[10] Zhang L, Fisher M, Wang W J. Retinal vessel segmentation using multi-scale textons derived from keypoints[J]. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 2015, 45:47-56. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2015.07.006
[11] Zou P, Chan P, Rockett P. A model-based consecutive scanline tracking method for extracting vascular networks from 2-D digital subtraction angiograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2009, 28(2):241-249. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2008.929100
[12] Vlachos M, Dermatas E. Multi-scale retinal vessel segmentation using line tracking[J]. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 2010, 34(3):213-227. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2009.09.006
[13] Zana F, Klein J C. Segmentation of vessel-like patterns using mathematical morphology and curvature evaluation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Process, 2001, 10(7):1010-1019. doi: 10.1109/83.931095
[14] Espona L, Carreira M J, Penedo M G, et al. Retinal vessel tree segmentation using a deformable contour model[C]//Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, 2008: 1-4.
[15] 于江波, 陈后金. PCNN模型的改进及其在医学图像处理中的应用[J].电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(10):2316-2320. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkxxk200710008
Yu J B, Chen H J. Improvement of PCNN model and its application to medical image processing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2007, 29(10):2316-2320. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkxxk200710008
[16] 祝双武, 郝重阳.一种基于改进型PCNN的织物疵点图像自适应分割方法[J].电子学报, 2012, 40(3):611-616. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.03.034
Zhu S W, Hao C Y. An approach for fabric defect image segmentation based on the improved conventional PCNN model[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2012, 40(3):611-616. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.03.034
[17] 姚畅, 陈后金, 荆涛, 等.一种基于改进的PCNN的视网膜血管树提取方法[J].光电子·激光, 2011, 22(11):1745-1750. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdzjg201111035
Yao C, Chen H J, Jing T, et al. Extraction of blood vessel tree in retinal image based on improved PCNN[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics·Laser, 2011, 22(11):1745-1750. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdzjg201111035
[18] Jiang W, Zhou H Y, Shen Y, et al. Image segmentation with pulse-coupled neural network and Canny operators[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2015, 46:528-538. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2015.03.028
[19] Lu Y F, Miao J, Duan L J, et al. A new approach to image segmentation based on simplified region growing PCNN[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2008, 205(2):807-814. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2008.05.029
[20] 陈萌梦, 熊兴良, 张琰, 等. 1种视网膜眼底图像增强的新方法[J].重庆医科大学学报, 2014, 39(8):1087-1090. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cqykdxxb201408011
Chen M M, Xiong X L, Zhang Y, et al. A new method for retinal fundus image enhancement[J]. Journal of Chongqing Medical University, 2014, 39(8):1087-1090. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cqykdxxb201408011
[21] Oloumi F, Rangayyan R M, Oloumi F, et al. Digital image processing and pattern recognition techniques for the analysis of fundus images of the retina[R]. Alberta, Canada: Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Calgary, 2010: 8.
[22] Reza A M. Realization of the contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) for real-time image enhancement[J]. Journal of VLSI Signal Processing Systems for Signal, Image and Video Technology, 2004, 38(1):35-44. doi: 10.1023/B:VLSI.0000028532.53893.82
[23] Gwetu M V, Tapamo J R, Viriri S. Segmentation of retinal blood vessels using normalized Gabor filters and automatic thresholding[J]. South African Computer Journal, 2014, 53(55):12-24. doi: 10.18489/sacj.v55i0.228
[24] 姚畅, 陈后金.病变视网膜图像血管网络的自动分割[J].电子学报, 2010, 38(5):1226-1233. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dianzixb201005042
Yao C, Chen H J. Automated blood vessel network segmentation in pathological retinal images[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2010, 38(5):1226-1233. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dianzixb201005042
[25] 托马斯·林德布拉德, 詹森·金赛.图像处理与脉冲耦合神经网络: 基于Python的实现[M].徐光柱, 马义德, 雷帮军, 译. 3版.北京: 国防工业大学出版社, 2017: 1.
Lindblad T, Kinser J M. Image Processing Using Pulse-Coupled Neural Networks: Applications in Python[M]. Xu G X, Ma Y D, Lei B J, trans. 3rd ed. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017: 1.
[26] 毕英伟, 邱天爽.一种基于简化PCNN的自适应图像分割方法[J].电子学报, 2005, 33(4):647-650. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2005.04.014
Bi Y W, Qiu T S. An adaptive image segmentation method based on a simplified PCNN[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2005, 33(4):647-650. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2005.04.014
[27] 徐光柱, 张柳, 邹耀斌, 等.自适应脉冲耦合神经网络与匹配滤波器相结合的视网膜血管分割[J].光学 精密工程, 2017, 25(3):756-764. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172503.0756
Xu G Z, Zhang L, Zou Y B, et al. Retinal blood segmentation with adaptive PCNN and matched filter[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2017, 25(3):756-764. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172503.0756
[28] Stewart R D, Fermin I, Opper M. Region growing with pulse-coupled neural networks:an alternative to seeded region growing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2002, 13(6):1557-1562. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2002.804229
[29] 马义德, 戴若兰, 李廉.一种基于脉冲耦合神经网络和图像熵的自动图像分割方法[J].通信学报, 2002, 23(1):46-51. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-436X.2002.01.007
Ma Y D, Dai R L, Li L. Automated image segmentation using pulse coupled neural networks and image's entropy[J]. Journal of China Institute of Communications, 2002, 23(1):46-51. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-436X.2002.01.007
[30] 姚畅, 陈后金, 李居朋.基于过渡区提取的视网膜血管分割方法[J].电子学报, 2008, 36(5):974-978. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2008.05.025
Yao C, Chen H J, Li J P. Segmentation of retinal blood vessels based on transition region extraction[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2008, 36(5):974-978. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2008.05.025
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: