-
摘要
对焦窗口的选择是实现显微镜自动对焦的关键步骤。针对传统的对焦窗口选取方法不能准确定位目标物体的问题, 本文提出了一种改进的人工鱼群对焦窗口法。以整幅图像中细节最丰富的区域作为对焦窗口的选取依据, 充分利用人工鱼群算法良好的全局寻优能力, 在整幅图像中选取最佳对焦窗口; 将全局优值添加到每条人工鱼的行为更新中, 使其能快速移动到当前最佳位置甚至是全局最优位置。此外, 在算法中引入了淘汰机制, 在保证精度的前提下, 提高算法的收敛速度; 再根据算法中公告板的特点, 结合趋势对比法识别干扰区域, 有效排除非目标区域的影响。实验表明, 该方法得到的对焦窗口, 可以更好地对目标物体进行对焦, 大大提高了自动对焦的精确度, 并且构建对焦窗口的效率较传统方法提高了1.65倍。

Abstract
The selection of the focusing window is the key procedure in achieving precise automatic focus of the microscope. For the traditional focus window selection method, the limitation is that the target object cannot be accurately positioned. This paper proposes an improved artificial fish focusing window method. The method takes the area-of-interest of the whole image as the basis of the selection window. Through utilizing the global optimization ability of the artificial fish swarm algorithm, the best focusing window can be obtained. Adding the global optimal value to the behavior update of each artificial fish makes the artificial fish quickly move to the optimal position. Under the premise of ensuring accuracy, the elimination behavior is introduced to improve the convergence speed of the algorithm in the later period. Furthermore, according to the characteristics of the bulletin board in the algorithm, the interference area is identified with the trend comparison method, and the influence of the non-target area is effectively excluded. Experiment results show that the focusing window obtained by this algorithm can be well-suited for the target object, greatly improve the accuracy of autofocus, and make the efficiency improvement 1.65 times than the traditional method.
-
Overview

Overview: As the computer is developed in acquiring and analyzing images, microscope systems become available to focus automatically. The selection of the focusing window is the key procedure achieving precise autofocus. A suitable focusing window can save time and focus more consistently than the entire image in the focusing process. Traditional focus window selection methods were designed to solve the problem of large amounts data for microscopes. However, the conventional methods cannot position the target object accurately to some extent. This paper proposes an improved artificial fish swarm focusing window method. Firstly, according to the characteristics of the target object often containing more details than the non-interested area, this method takes the area-of-interest of the whole image as the basis of the selection window. Through utilizing the global optimization ability of the artificial fish swarm algorithm, the best focusing window can be obtained. Secondly, adding the global optimal value to the behavior update of each artificial fish makes the artificial fish quickly move to the optimal position while reducing the time for each artificial fish to select and adjust behavior. Thirdly, under the premise of ensuring accuracy, the elimination mechanism is introduced to the algorithm, and the individual fish with poor performance was deleted to decrease unnecessary calculation. Furthermore, the bulletin board in the algorithm always records the state of the optimal artificial fish. By making use of the feature, the influence of the non-target area is effectively excluded. It then compares this method with traditional focus window methods. It is shown that the proposed method gives the best results when tested on several different sets of specimen images. The focusing window obtained by this algorithm can be well-suited for the target object regardless of whether the target is in the center of the image. Experiment results between the defocus images and the focus images demonstrate that proposed method have good performance about the stability of algorithm. The windows captured under different levels of focus images are basically the same. The superiority of this algorithm is greatly improving the accuracy of autofocus, compared with other recently reported artificial fish swarm focusing window algorithms. Moreover, the method improves the convergence speed of the algorithm in the later period and avoids a tedious parameter-tuning procedure. Simulation results verify that the proposed algorithm can make the efficiency improve 1.65 times than the traditional artificial fish swarm algorithm.
-

-
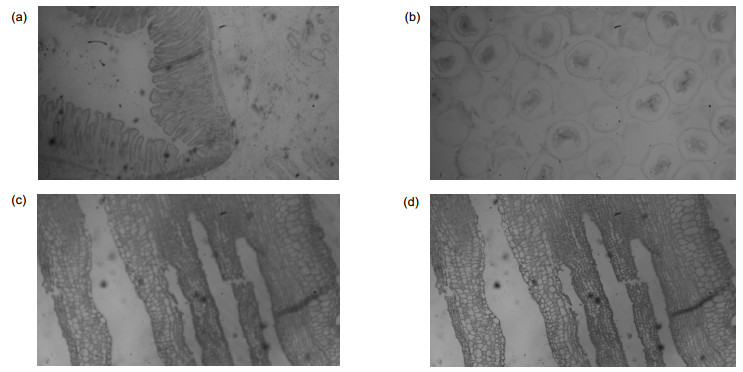
图 2 实验原图。(a)胃壁切片标本对焦图;(b)马蛔虫受精卵有丝分裂标本对焦图;(c)南瓜茎纵切标本离焦图;(d)南瓜茎纵切标本对焦图
Figure 2. The source image of the experiment. (a) Focused image of gastric wall specimen; (b) Focused image of mitotic specimen of maggot fertilized egg cells; (c) Defocused image of longitudinal specimens of pumpkin stem; (d) Focused image of longitudinal specimens of pumpkin stem
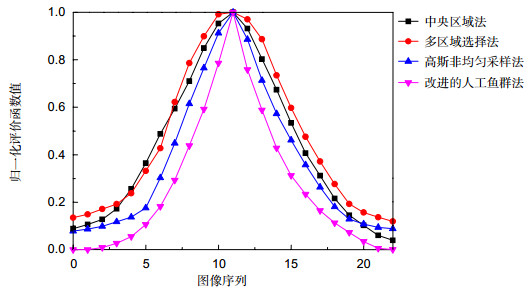
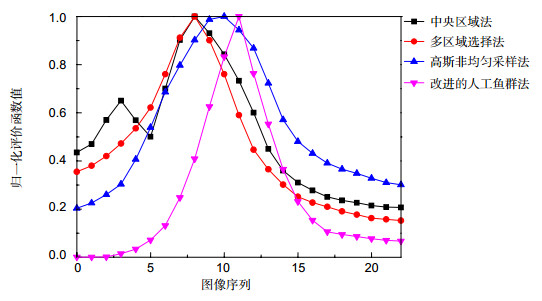
图 3 四种方法的效果图。(a1)~(a2)中央选择法;(b1)~(b2)多区域选择法;(c1)~(c2)高斯非均匀采样法;(d1)~(d2)改进的人工鱼群对焦窗口法
Figure 3. The result of 4 methods. (a1)~(a2) Central selection method; (b1)~(b2) Multi-areas selection method; (c1)~(c2) Gaussian non-uniform sampling method; (d1)~(d2) Improved artificial fish swarm focus window selection algorithm
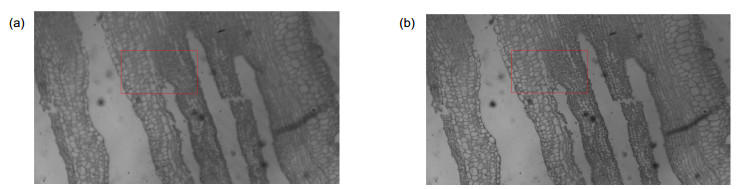
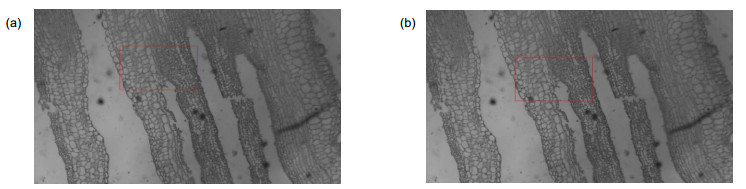
图 7 改进的人工鱼群对焦窗口法与传统人工鱼群法的实验结果图。(a)改进的人工鱼群对焦窗口法;(b)传统人工鱼群法
Figure 7. The result of improved artificial fish swarm focus window selection algorithm and traditional artificial fish swarm algorithm. (a) Improved artificial fish swarm focus window selection algorithm; (b) Traditional artificial fish swarm algorithm
表 1 不同对焦程度图像的窗口构建结果
Table 1. The position of focusing window with different levels of focus images
离焦图像/像素 正焦图像/像素 重叠率/(%) (841, 381) (827, 366) 91.90 表 2 改进的人工鱼群对焦窗口法与传统人工鱼群算法的仿真结果
Table 2. Simulation results of improved artificial fish swarm algorithm and traditional artificial fish swarm algorithm
算法 改进的人工鱼群对焦窗口法 传统的人工鱼群对焦窗口法 时间/ms 426.823 703.584 -
参考文献
[1] Sun Y, Duthaler S, Nelson B J. Autofocusing in computer microscopy: Selecting the optimal focus algorithm[J]. Microscopy Research & Technique, 2004, 65(3): 139-149. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1002-jemt.20118/
[2] Apolinar J, Rodríguez M. Three-dimensional microscope vision system based on micro laser line scanning and adaptive genetic algorithms[J]. Optics Communications, 2017, 385: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2016.09.025
[3] 江旻珊, 张楠楠, 张学典, 等.混合搜索法在显微镜自动对焦中的应用[J].光电工程, 2017, 44(7): 685-694. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.07.004
Jiang M S, Zhang N N, Zhang X D, et al. Applications of hybrid search strategy in microscope autofocus[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017, 44(7): 685-694. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.07.004
[4] 李惠光, 王帅, 沙晓鹏, 等.显微视觉系统中自动聚焦技术的研究[J].光电工程, 2014, 41(8): 1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2014.08.001
Li H G, Wang S, Sha X P, et al. Study of auto focusing technique of micro-vision system[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2014, 41(8): 1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2014.08.001
[5] 姜志国, 韩冬兵, 袁天云, 等.基于全自动控制显微镜的自动聚焦算法研究[J].中国图象图形学报, 2004, 9(4): 396-401. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8961.2004.04.003
Jiang Z G, Han D B, Yuan T Y, et al. Study on auto focusing algorithm for automatic microscope[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2004, 9(4): 396-401. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8961.2004.04.003
[6] 蒋婷.基于图像处理的自动对焦理论和技术研究[D].武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2008: 10-12.
Jiang T. Research on auto-focusing theory and technology based on image processing[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2008: 10-12.
https://wenku.baidu.com/view/32bc7f16f11dc281e53a580216fc700abb6852fd.html [7] 李奇, 徐之海, 冯华君, 等.数字成象系统自动对焦区域设计[J].光子学报, 2002, 31(1): 63-66. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzxb200201015
Li Q, Xu Z H, Feng H J, et al. Autofocus area design of digital imaging system[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2002, 31(1): 63-66. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzxb200201015
[8] Won C S, Pyun K, Gray R M. Automatic object segmentation in images with low depth of field[C]//Proceedings. International Conference on Image Processing, Rochester, NY, USA, 2002, 3: 805-808.
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1039094 [9] 樊攀.基于数字图像处理的自动聚焦系统算法研究[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2009: 20-28.
Fan P. Research on algorithm for auto-focus system based on digital image processing[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2009: 20-28.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10213-2010064298.htm [10] 朱孔凤, 姜威, 高赞, 等.自动聚焦系统中聚焦窗口的选择及参量的确定[J].光学学报, 2006, 26(6): 836-840. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2006.06.008
Zhu K F, Jiang W, Gao Z, et al. Focusing window choice and parameters determination in automatic focusing system[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2006, 26(6): 836-840. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2006.06.008
[11] 李奇, 冯华君, 徐之海.自动对焦系统中图像非均匀采样的实验研究[J].光子学报, 2003, 32(12): 1499-1501. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzxb200312023
Li Q, Feng H J, Xu Z H. Autofocus system experiment study using variational image-sampling[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2003, 32(12): 1499-1501. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzxb200312023
[12] 王彦芳, 姜威.应用于聚焦窗口自适应选择的人工鱼群算法改进[J].计算机工程与应用, 2011, 47(14): 180-182. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2011.14.052
Wang Y F, Jiang W. Application of artificial fish swarm algorithm on adaptive auto-focusing window selection[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2011, 47(14): 180-182. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2011.14.052
[13] 张学典, 汪泓, 江旻珊, 等.显著性分析在对焦图像融合方面的应用[J].光电工程, 2017, 44(4): 435-441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.04.008
Zhang X D, Wang h, Jiang M S, et al. Applications of saliency analysis in focus image fusion[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017, 44(4): 435-441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.04.008
[14] 胡涛, 陈世哲, 刘国栋, 等.图像法自动调焦的最佳调焦区域选取算法[J].光学技术, 2006, 32(6): 851-854. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.2006.06.007
Hu T, Chen S Z, Liu G D, et al. Algorithm of selecting the optimal focusing region[J]. Optical Technique, 2006, 32(6): 851-854. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.2006.06.007
[15] Gu C C, Wu K J, Hu J, et al. Region sampling for robust and rapid autofocus in microscope[J]. Microscopy Research & Technique, 2015, 78(5): 382-390. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cbcf93346f15be4c15a036d80e6ac445
[16] 黄德天.基于图像技术的自动调焦方法研究[D].长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2013: 76-78.
Huang D T. Study on anto-focusing method using image techology[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013: 76-78.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80139-1013293679.htm [17] Zhang F S, Li S W, Hu Z G, et al. Fish swarm window selection algorithm based on cell microscopic automatic focus[J]. Cluster Computing, 2017, 20(1): 485-495. doi: 10.1007/s10586-017-0752-4
[18] Neshat M, Sepidnam G, Sargolzaei M, et al. Artificial fish swarm algorithm: a survey of the state-of-the-art, hybridization, combinatorial and indicative applications[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2014, 42(4): 965-997. doi: 10.1007/s10462-012-9342-2
[19] Yu L, Li C. A global artificial fish swarm algorithm for structural damage detection[J]. Advances in Structural Engineering, 2016, 17(3): 331-346. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e2c236f9578efa3ef5529ba36f150ced
[20] Groen F C A, Young I T, Ligthart G. A comparison of different focus functions for use in autofocus algorithms[J]. Cytometry, 1985, 6(2): 81-91. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0320
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: