-
摘要
在光伏发电系统中,经常存在电池板局部被遮挡的情况,造成电池板出现多峰极值的现象。传统的最大功率点(MPPT)搜索方法常常会陷入局部极值,从而错过或丢失系统的全局最大功率点,甚至产生振荡导致系统输出不稳定。提出一种改进的蝙蝠算法(IBA),并应用到太阳能阵列存在局部阴影条件下的最大功率点寻优控制中。通过混沌初始化,对群体的初始位置进行更新,增加种群的均匀性和遍历性;引入自适应惯性权重,使算法在优化前期具有较强的全局搜索能力,后期有较强的局部收缩能力,同时引入Levy飞行来产生跳跃速度,跳出局部极值;引入动态收缩区间,有效地减小算法的搜索范围。以上改进,避免了种群受到局部极值的影响而过早收敛。光伏发电系统的仿真表明:在其受到局部遮挡而出现多峰极值的情况下,改进的蝙蝠算法能够快速找到全局最优点,并且精度高。

Abstract
In photovoltaic systems, the output power curve of solar battery has multiple peaks, under the partially shaded condition. Traditional maximum power point tracking (MPPT) search method often traps in local extremum, which causes the loss of the global maximum power point even generates oscillation and leads to instability of output. An improved bat algorithm (IBA) is proposed and used to find global optimal point, by introducing chaos search strategy in initial arrangement which can improve the uniformity and ergodicity. The self-adapting weight is introduced to enhance the global searching ability of previous processing and the local searching ability of late processing, and Levy flight is introduced in the same time to create the saltation velocity to jump out the local extremum. Dynamic contraction is also used to decrease the search section more effectively, so as to avoid premature convergence of the population affected by the local extremum. The simulation shows that modified bat algorithm can find the global optimal point fast, with high precision, under the partially shaded condition.
-
Overview

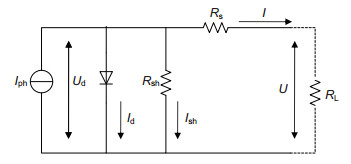
Overview: The photovoltaic system is familiar to people as the new energy. Because Photovoltaic components consist of silicon, it can be considered as a constant current source, with an anti parallel diode. And output voltage and output current can be measured by instruments, and then output power can be calculated. When the sun light is balance, characteristic of the output of PV arrays is the same as one PV component. When under the partially shaded condition, there are heat spots in PV arrays, which causes problems. Such as the output curve of solar battery will has multiple peaks. Under the partially shaded condition, traditional MPPT search methods often trap in local extremum or lose the maximum power point, and they have oscillation and instability. So intelligent algorithms are used to track the maximum power point to avoid the disadvantages that traditional methods have.
Many intelligent algorithms such as partial swarm optimization, genetic algorithm, fish algorithm and so on are used to track the maximum power point. Bat algorithm is considered to track the maximum power point of PV output curves, but there are many shortcomings in bat algorithm. So an improved bat algorithm is proposed and used to find global optimal point, by introducing chaos search strategy in initial arrangement which can improve the uniformity and ergodicity. The self-adapting weight is introduced to enhance the global searching ability of previous processing and the local searching ability of late processing, and Levy flight is introduced in the same time to create the saltation velocity to out of the local extremum and to jump out the local extremum. Dynamic contraction is also used to decrease the search section more effectively, so as to avoid premature convergence of the population affected by the local extremum.
To proof the efficiency of the improved algorithm, IBA is compared with PSO, BA and ABC. Results show that all of PSO, BA and ABC have disadvantages such as instability, large amplitude and easily to precocious, and optimization mechanism of IBA algorithm can avoid trapping in local extremum and enhance the stability. To realize the tracking of maximum power point of output curve, the improved algorithm is introduced into the Boost system, and simulation results are shown as statistical data in charts. The simulation results show that modified bat algorithm can find the global optimal point fast, with high precision, under the partially shaded condition.
-

-
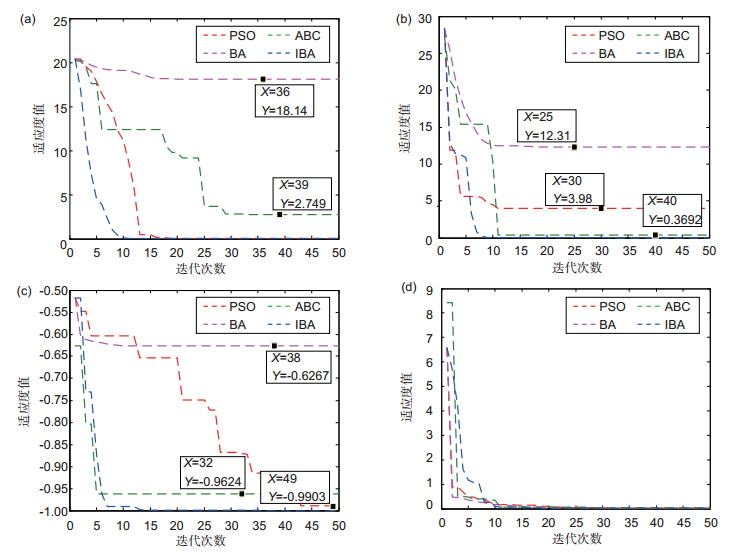
图 5 (a) Ackley函数测试寻优曲线;(b) Rastrigin函数测试寻优曲线;(c) Schaffer F6函数测试寻优曲线;(d) Ros-enbrock函数测试寻优曲线
Figure 5. (a) Testing optimization curves of Ackley function; (b) Testing optimization curves of Rastrigin function; (c) Testing optimization curves of Schaffer F6 function; (d) Test optimization curves of Rosenbrock function
表 1 标准测试函数
Table 1. Standard test functions
函数名 函数表达式 搜索空间 理论最优值 Ackley ${{f}_{1}}(x)=20+e-20\exp \left( -\frac{1}{5}\sqrt{\frac{1}{2}\sum\limits_{i=1}^{2}{x_{i}^{2}}} \right)-\exp \left( \frac{1}{2}\sum\limits_{i=1}^{2}{\cos (2\pi {{x}_{i}})} \right)$ [-30, 30] ${{f}_{1}}({{x}^{*}})=0$ Rastrigin ${{f}_{2}}(x)=\sum\limits_{i=1}^{2}{\left[ x_{i}^{2}-10\cos (2\pi {{x}_{i}})+10 \right]}$ [-5.12, 5.12] ${{f}_{2}}({{x}^{*}})=0 $ Schaffer F6 ${{f}_{3}}(x)=\left( {}^{{{\sin }^{2}}\left( \sqrt{x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}} \right)-0.5}\!\!\diagup\!\!{}_{{{\left[ 1+0.001(x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}) \right]}^{2}}}\; \right)-0.5$ [-100, 100] ${{f}_{3}}({{x}^{*}})=-1$ Rosenbrock ${{f}_{4}}(x)=\sum\limits_{i=1}^{2}{\left[100{{({{x}_{i+1}}-x_{i}^{2})}^{2}}+{{({{x}_{i}}-1)}^{2}} \right]}$ [-2.048, 2.048] ${{f}_{4}}({{x}^{*}})=0$ 表 2 算法条件
Table 2. Conditions of algorithms
函数 搜索范围 种群数 维数 迭代次数 循环次数 Ackley [-30, 30] 10 2 50 20 30 50 Rastrigin [-5.12, 5.12] 10 2 50 20 30 50 Schaffer F6 [-100, 100] 10 2 50 20 30 50 Rosenbrock [-2.048, 2.048] 10 2 50 20 30 50 表 3 算法的寻优性能测试结果
Table 3. The effort of algorithms
算法 种群数 Ackley Rastrigin Schaffer F6 Rosenbrock Qavebest Qaveds tave/s Qavebest Qaveds tave/s Qavebest Qaveds tave/s Qavebest Qaveds tave/s PSO 10 0.0012 0 0.0283 0.3553 0.3202 0.0125 -0.9149 0.0006 0.0275 0 0 0.0121 30 0.0002 0 0.0967 0.2986 0.208 0.0501 -0.9869 0.0001 0.095 0 0 0.0477 50 0.0001 0 0.0173 0.2985 0.3069 0.0986 -0.987 0.0001 0.1752 0 0 0.0957 BA 10 19.7052 0.8723 0.0163 2.5702 0.8996 0.006 -0.6681 0.0217 0.0163 0.0003 0 0.0049 30 6.8531 0.5988 0.0468 3.7291 0.5846 0.0137 -0.8987 0.0073 0.049 0.0001 0 0.0147 50 2.7509 0.8247 0.079 4.8305 0.5868 0.0247 -0.923 0.0001 0.0815 0 0 0.0221 ABC 10 0.0797 0.0082 0.0161 1.7355 0.9859 0.0114 -0.9569 0.0004 0.0238 0.2395 0.1757 0.0107 30 0.0126 0.0002 0.0358 0.2261 0.0818 0.0193 -0.9623 0.0008 0.052 0.061 0.0017 0.0213 50 0.0119 0.0001 0.055 0.1743 0.0595 0.0286 -0.968 0.0004 0.0827 0.0111 0.0001 0.036 IBA 10 0 0 0.0396 0 0 0.0189 -1 0 0.0369 0.0001 0 0.0165 30 0 0 0.1107 0 0 0.0585 -1 0 0.111 0 0 0.0499 50 0 0 0.2046 0 0 0.1052 -1 0 0.2004 0 0 0.1012 表 4 算法效果
Table 4. The effect of algorithms
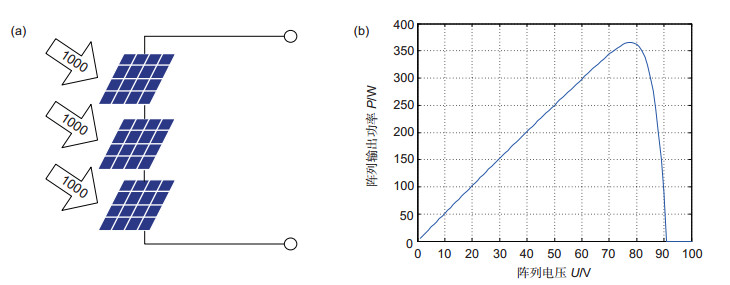
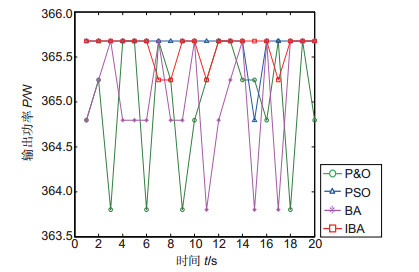
算法 循环次数 迭代次数 Qavebest tave/s P & O 20 50 364.9467 0.0034 PSO 365.4425 0.0273 BA 363.0174 0.0403 IBA 365.5899 0.0357 表 5 算法效果
Table 5. The effect of algorithms
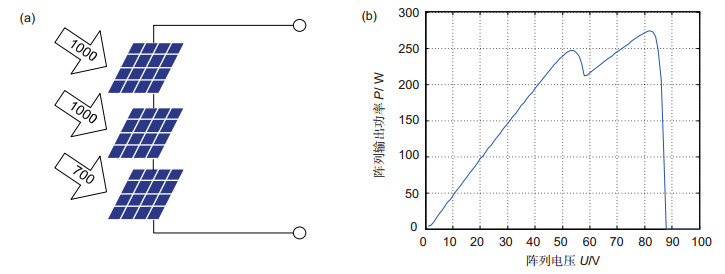
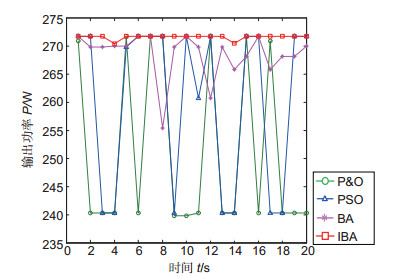
算法 循环次数 迭代次数 Qavebest tave/s P & O 20 50 252.6573 0.0077 PSO 254.2823 0.1038 BA 268.5534 0.6915 IBA 271.6769 0.2988 表 6 算法效果
Table 6. The effect of algorithms
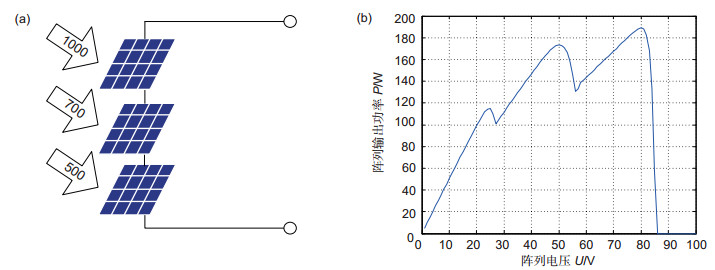
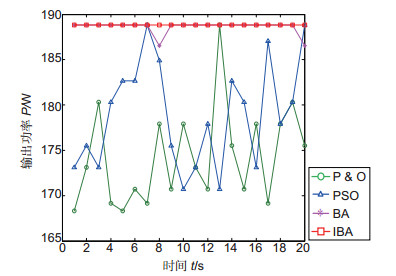
算法 循环次数 迭代次数 Qavebest tave/s P & O 20 50 174.2537 0.0486 PSO 178.9537 0.7891 BA 188.5719 0.8690 IBA 188.7997 2.0275 -
参考文献
[1] 李琦, 辛恩成, 徐睿, 等.常规太阳能电池低倍聚光条件下的特性研究与应用[J].智能电网, 2016, 4(7): 669-673. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zndw201607008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Li Q, Xin E C, Xu R, et al. Characteristic research and application of conventional solar cells under low concentration conditions[J]. Smart Grid, 2016, 4(7): 669-673. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zndw201607008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[2] 徐瑞东. 光伏发电系统运行理论与关键技术研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2012.
Xu R D. Study on theory and key technology of photovoltaic system operation[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2012.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10290-1013008801.htm [3] Liu L Q, Meng X L, Liu C X. A review of maximum power point tracking methods of PV power system at uniform and partial shading[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 53: 1500-1507. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.09.065
[4] 姬伟超, 殷时蓉, 刘朝涛.基于Buck-Boost拓扑的新量子遗传算法在MPPT技术中的应用[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2016, 44(1): 92-96. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jdqw201601014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Ji W C, Yin S R, Liu C T. Maximum power point tracking based on Buck-Boost topology with new quantum genetic algorithm[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2016, 44(1): 92-96. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jdqw201601014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[5] 郑方昊.改进遗传算法在MPPT中的应用研究[J].机械制造与自动化, 2013, 41(2): 185-187. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zzhd201302061&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Zheng F H. Research on aMaximum power point tracking with DRP based on improved genetic algorithm[J]. Machine Building & Automation, 2013, 41(2): 185-187. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zzhd201302061&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[6] 朱艳伟, 石春新, 但扬清, 等.粒子群优化算法在光伏阵列多峰最大功率点跟踪中的应用[J].中国电机工程学报, 2012, 32(4): 42-48. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zgdc201204007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Zhu Y W, Shi C X, Dan Y Q, et al. Application of PSO algorithm in global MPPT for PV array[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2012, 32(4): 42-48. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zgdc201204007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[7] 段其昌, 唐若笠, 隆霞.粒子群优化鱼群算法及其在光伏系统最大功率点跟踪中的应用[J].计算机应用, 2012, 32(12): 3299-3302. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jsjy201212010&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Duan Q C, Tang R L, Long X. Fish swarm algorithm optimized by PSO applied in maximum power point tracking of photovoltaic power system[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2012, 32(12): 3299-3302. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jsjy201212010&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[8] Shi J Y, Xue F, Qin Z J, et al. Tracking the global maximum power point of a photovoltaic system under partial shading conditions using a modified firefly algorithm[J]. Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, 2016, 8: 033501. doi: 10.1063/1.4948524
[9] Sudhakar Babu T, Rajasekar N, Sangeetha K. Modified particle swarm optimization technique based maximum power point tracking for uniform and under partial shading condition[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 34: 613-624. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2015.05.029
[10] Chen Y T, Jhang Y C, Kuo T H, Jumping maximum power point tracking method for PV array under partially shaded conditions[J]. Solar Energy, 2016, 132: 617-627. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2016.03.020
[11] Tang R L, Wu Z, Fang Y J. Maximum power point tracking of large-scale photovoltaic array[J]. Solar Energy, 2016, 134: 503-514. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2016.05.026
[12] Seyedmahmoudian M, Mekhilef S, Rahmani R, et al. Maximum power point tracking of partial shaded photovoltaic array using an evolutionary algorithm: A particle swarm optimization technique[J]. Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, 2014, 6: 023102. doi: 10.1063/1.4868025
[13] Rezk H, Eltamaly A M. A comprehensive comparison of different MPPT techniques for photovoltaic systems[J]. Solar Energy, 2015, 112: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2014.11.010
[14] Shi J Y, Zhang W, Zhang Y G, et al. MPPT for PV systems based on a dormant PSO algorithm[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2015, 123: 100-107. doi: 10.1016/j.epsr.2015.02.001
[15] 马迎东, 王文栋, 温强.基于混沌搜索策略蝙蝠算法的输电网规划[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2015, 43(15): 17-21. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jdqw201515003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Ma Y D, Wang W D, Wen Q. Transmission network planning based on bat algorithm with chaotic search strategy[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2015, 43(15): 17-21. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jdqw201515003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[16] Osaba E, Yang X S, Diaz F, et al. An improved discrete bat algorithm for symmetric and asymmetric traveling salesman problems[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2016, 48: 59-71. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2015.10.006
[17] 刘长平, 叶春明.具有混沌搜索策略的蝙蝠优化算法及性能仿真[J].系统仿真学报, 2013, 25(6): 1183-1188, 1195. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=xtfz201306007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Liu C P, Ye C M. Bat algorithm with chaotic search strategy and analysis of its property[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2013, 25(6): 1183-1188, 1195. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=xtfz201306007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[18] 严小飞, 叶东毅.基于Levy飞行的改进菌群觅食算法[J].计算机系统应用, 2015, 24(3): 124-132. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=xtyy201503021&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Yan X F, Ye D Y. Improved bacterial foraging optimization algorithm based on Levy flight[J]. Computer System & Applications, 2015, 24(3): 124-132. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=xtyy201503021&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[19] Benyoucef A S, Chouder A, Kara K, et al. Artificial bee colony based algorithm for maximum power point tracking (MPPT) for PV systems operating under partial shaded conditions[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 32: 38-48. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2015.03.047
-
访问统计


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: