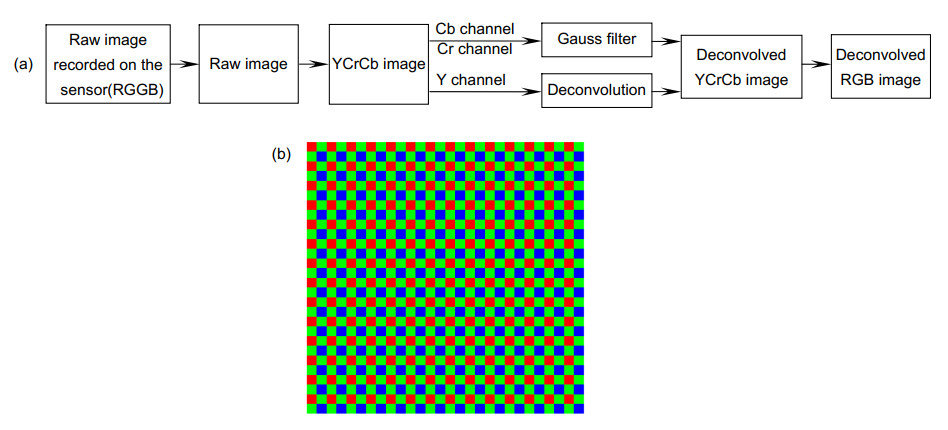
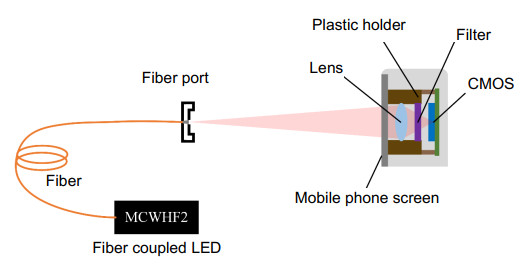
-
摘要:
随着全面屏手机的发展,手机屏下成像的研究应运而生。但由于手机屏幕存在电路走线和其他不透明部分,光通过屏幕会产生衍射,降低成像结果的图像质量,本文从图像复原的角度,对屏下相机拍摄的图像进行恢复。通过测量得到手机成像系统的点扩散函数(PSF),利用测得的PSF,对图像进行反卷积处理。本文改进了传统的反卷积方法,对原始图像进行颜色空间转换,然后对不同的通道分别处理。相较于传统反卷积方法,改进后的反卷积方法得到的处理结果在结构相似度(SSIM)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)等指标上都有提高,运行时间更短。在分通道反卷积之后,使用非局部平均算法进行去噪处理,进一步提高了屏下图像的质量。
 Abstract:
Abstract:With the development of full-screen mobile phones, the need for under-screen imaging of mobile phones has emerged. However, the diffraction caused by the wiring and other opaque parts will affect the image quality of the under-screen image. In this article, under-screen image is restored from the perspective of image restoration. The point spread function (PSF) of the mobile phone imaging system is obtained through actual measurement, and the image is deconvolved using the measured PSF. In this article, traditional deconvolution method has been improved, in which the color space of the image is converted and different channels are processed separately. Compared with the traditional deconvolution method, the results of the sub-channel deconvolution method have improved structural similarity (SSIM), peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and other indicators, and the required running time is shorter. After sub-channel deconvolution, the non-local averaging algorithm is used for denoising, which further improves the quality of the under-screen image.
-
Key words:
- deconvolution /
- denoising /
- under-screen imaging /
- image restoration
-

Overview: With the development of full-screen mobile phones, the need for under-screen imaging of mobile phones has emerged. However, the diffraction caused by the wiring and other opaque parts will affect the image quality of the under-screen image. In this article, under-screen image is restored from the perspective of image restoration. The point spread function (PSF) of the mobile phone imaging system is obtained through actual measurement, and the image is deconvolved using the measured PSF. Traditional deconvolution method has been improved in this article. In deconvolution process, the traditional and common way is to divide the image into different color channels, use the PSF of the corresponding channel to deconvolve each channel, and finally synthesize the color image. Because the high noise of the image sensor of the mobile phone has a destructive effect on the deconvolution algorithm, one need to reduce the noise of the image. The traditional denoising method will destroy the high-frequency information and cause serious ringing effect on the image restored by deconvolution. In this article, we propose a new solution to this problem: convert the blurred image from RGB color space to YCrCb space, where Y represents brightness information; Cr and Cb represent hue and saturation, respectively. Image clarity is mainly affected by brightness information, so only the Y channel needs to be deconvolved, whose noise level is lower than any of the RGB channels. In order to further reduce the influence of noise, Cr and Cb channels are processed by Gaussian filtering to reduce noise. Finally, the processed image is converted back to RGB color space to form a traditional color image. Compared with traditional deconvolution method, the results of the sub-channel deconvolution method have improved structural similarity (SSIM), peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and other indicators, and the required running time is shortened by almost three times. After sub-channel deconvolution, the sharpness of the image has been greatly improved. In order to further improve the quality of under-screen image, the non-local averaging algorithm is used to denoise the image after the sub-channel deconvolution, which finds similar image blocks in the same image to average, and redundant information in the image is used to remove noise. Furthermore, the integral image method is used to shorten the running time to meet the real-time requirements in mobile phone photography. The visual perception of the image has been better improved, and both PSNR and SSIM have been further improved after denoising.
-

-
图 3 不同噪声水平图像分别使用传统反卷积和分通道反卷积的处理结果。(a) 参考图像;(b) 参考图(a) 与测得PSF卷积后加入标准差为0.03高斯噪声后的退化模糊图像;(c) 图(b)经过传统反卷积方法恢复后的结果;(d) 图(b)经过分通道反卷积方法恢复后的结果;(e) 参考图(a)与测得PSF卷积后再加入标准差为0.06高斯噪声后的退化模糊图像;(f) 图(e)经过传统反卷积方法恢复后的结果;(g) 图(e)经过分通道反卷积方法恢复后的结果;(h) 图像峰值信噪比随着加入噪声标准差增加变化曲线;(i) 图像的结构相似性随着加入噪声标准差增加变化曲线
Figure 3. Simulation results of images with different noise levels using traditional and sub-channel deconvolution, respectively. (a) Reference images; (b) Blurred images after convolved with measured PSF and adding Gaussian noise with standard deviation of 0.03; (c) Restored results of (b) with traditional deconvolution; (d) Restored results of (b) with proposed sub-channel deconvolution; (e) Blurred images after convolved with measured PSF and adding Gaussian noise with standard deviation of 0.06; (f) Restored results of (e) with traditional deconvolution; (g) Restored results of (e) with proposed sub-channel deconvolution; (h) Curves of image peak signal-to-noise ratio with image standard deviation; (i) Curves of structure similarity with image standard deviation
图 4 仿真处理结果。第一列为参考图像;第二列为退化后的模糊图像;第三列为传统反卷积方法恢复结果;第四列为本文中提出的分通道反卷积方法处理结果;第五列为分通道反卷积之后去噪结果
Figure 4. Simulation results. First row, reference images; Sencond row, blurred images after degradation; Third row, restored results of traditional deconvolution; Fourth row, restored results of proposed sub-channel deconvolution; Fifth row, denoising results of the sub-channel deconvolved image
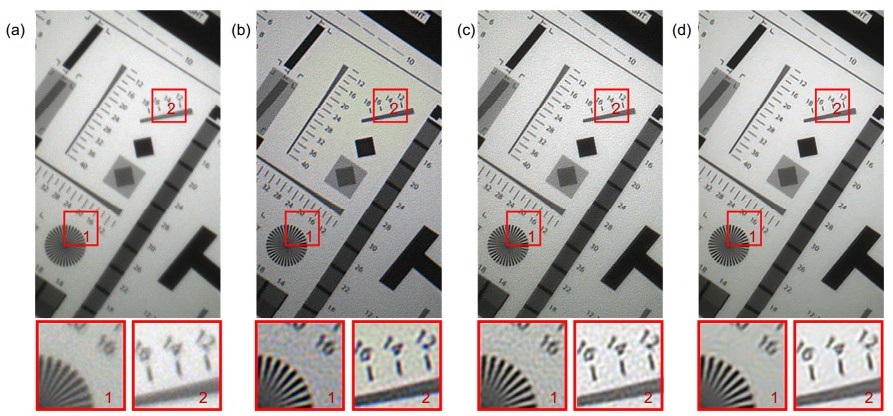
图 5 分辨率板的处理结果。(a) 屏下原始图像;(b) 传统反卷积处理后结果;(c) 本文的分通道反卷积之后清晰度提高的图像;(d) 对分通道反卷积结果去噪后的图像
Figure 5. Resolution board processing results. (a) Under-screen original image; (b) Restored image after traditional deconvolution; (c) Restored image with improved resolution after proposed sub-channel deconvolution; (d) Denoising image after sub-channel deconvolution
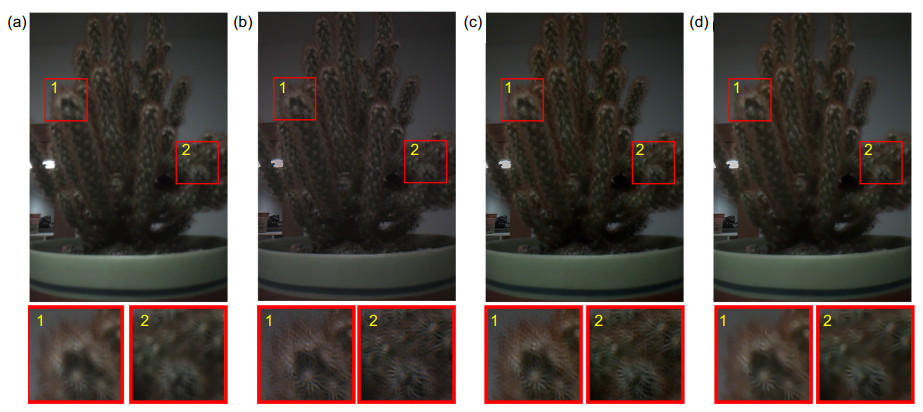
图 6 盆景的处理结果。(a) 屏下原始图像;(b) 传统反卷积处理后结果;(c) 本文的分通道反卷积之后清晰度提高的图像;(d) 对分通道反卷积结果去噪后的图像
Figure 6. Bonsai processing results. (a) Under-screen original image; (b) Restored image after traditional deconvolution; (c) Restored image with improved resolution after proposed sub-channel deconvolution; (d) Denoising image after sub-channel deconvolution
表 1 仿真图像的处理结果比较
Table 1. Result comparison of simulation images
Image name SSIM PSNR/dB Running time/s Blur T-dec S-dec Denoise Blur T-dec S-dec Denoise T-dec S-dec Image 1 0.32 0.59 0.56 0.60 20.59 23.95 24.66 24.70 0.52 0.17 Image 2 0.54 0.58 0.74 0.76 21.41 20.04 22.24 22.30 0.52 0.17 Image 3 0.73 0.74 0.83 0.84 22.76 18.87 24.12 24.46 0.49 0.17 Image 4 0.32 0.48 0.53 0.55 21.60 21.21 24.13 24.22 0.49 0.17 Image 5 0.47 0.69 0.79 0.86 25.33 26.46 27.93 28.26 0.48 0.16 Image 6 0.46 0.50 0.53 0.53 16.83 16.75 17.04 17.11 0.48 0.15 Image 7 0.62 0.75 0.89 0.92 24.27 26.41 29.02 30.06 0.55 0.18 -
[1] Holmes T J. Blind deconvolution of quantum-limited incoherent imagery: maximum-likelihood approach[J]. J Opt Soc Am A, 1992, 9(7): 1052-1061. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.9.001052
[2] Fish D A, Brinicombe A M, Pike E R, et al. Blind deconvolution by means of the Richardson-Lucy algorithm[J]. J Opt Soc Am A, 1995, 12(1): 58-65. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.12.000058
[3] Tugnait J K. Identification and deconvolution of multichannel linear non-Gaussian processes using higher order statistics and inverse filter criteria[J]. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 1997, 45(3): 658-672. doi: 10.1109/78.558482
[4] Wiener N. Extrapolation, Interpolation, and Smoothing of Stationary Time Series: with Engineering Applications[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 1964: 1043-1054.
[5] Richardson W H. Bayesian-based iterative method of image restoration[J]. J Opt Soc Am, 1972, 62(1): 55-59. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.62.000055
[6] Lucy L B. An iterative technique for the rectification of observed distributions[J]. Astron J, 1974, 79: 745. doi: 10.1086/111605
[7] Bayes. An essay towards solving a problem in the doctrine of chances[J]. Resonance, 2003, 8(4): 80-88. doi: 10.1007/BF02883540
[8] Ingaramo M, York A G, Hoogendoorn E, et al. Richardson-lucy deconvolution as a general tool for combining images with complementary strengths[J]. ChemPhysChem, 2014, 15(4): 794-800. doi: 10.1002/cphc.201300831
[9] Preibisch S, Amat F, Stamataki E, et al. Efficient bayesian-based multiview deconvolution[J]. Nat Methods, 2014, 11(6): 645-648. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2929
[10] Guo M, Li Y, Su Y J, et al. Rapid image deconvolution and multiview fusion for optical microscopy[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2020, 38(11): 1337-1346. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0560-x
[11] Dines K, Kak A. Constrained least squares filtering[J]. IEEE Trans Acoust, Speech, Signal Process, 1977, 25(4): 346-350. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1977.1162965
[12] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234-241.
[13] Dong C, Loy C C, He K M, et al. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 184-199.
[14] Dong C, Loy C C, He K M, et al. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2016, 38(2): 295-307. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2439281
[15] Goodfellow I J, Pouget-abadie J, Mirza M, et al. Generative adversarial networks[EB/OL]. (2014-06-10)[2020-08-07]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.2661.
[16] Ledig C, Theis L, Huszár F, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 105-114.
[17] Peng Y F, Sun Q L, Dun X, et al. Learned large field-of-view imaging with thin-plate optics[J]. ACM Trans Graph, 2019, 38(6): 219.
[18] Dabov K, Foi A, Katkovnik V, et al. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2007, 16(8): 2080-2095. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.901238
[19] Buades A, Coll B, Morel J M. A non-local algorithm for image denoising[C]//Proceedings of 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, USA, 2005.
[20] 冈萨雷斯R C, 伍兹R E, 艾丁斯S L. 数字图像处理[M]. 阮秋琦, 阮宇智, 译. 2版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2003: 42-46.
Gonzalez R C, Woods R E, Eddins S L. Digital Image Processing[M]. Ruan Q Q, Ruan Y Z, trans. 2nd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2003: 42-46.
[21] Wang J, Guo Y W, Ying W T, et al. Fast non-local algorithm for image denoising[C]//Proceedings of 2006 International Conference on Image Processing, Atlanta, USA, 2016: 1429-1432.
[22] Froment J. Parameter-free fast pixelwise non-local means denoising[J]. Image Process Line, 2014, 4: 300-326 doi: 10.5201/ipol.2014.120
[23] Lin Z, Song E M. A fast non-local means algorithm based on integral image and reconstructed similar kernel[J]. Proc SPIE, 2018, 10609: 106091L.
[24] Wang Z, Bovik A C, Sheikh H R, et al. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2004, 13(4): 600-612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861
[25] Jiang J, Huang J N, Zhang G J. An accelerated motion blurred star restoration based on single image[J]. IEEE Sens J, 2017, 17(5): 1306-1315. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2016.2645861
[26] He T, Hu J, Huang H Q. Hybrid high-order nonlocal gradient sparsity regularization for Poisson image deconvolution[J]. Appl Opt, 2018, 57(35): 10243-10256. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.010243
[27] MacAdam D L. Projective transformations of I. C. I. color specifications[J]. J Opt Soc Am, 1937, 27(8): 294-299. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.27.000294
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: