-
摘要:
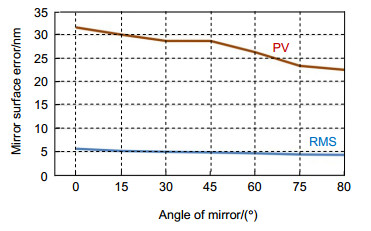
激光通信大口径地面光端机的主要作用是与卫星建立通信链路,实现卫星与地面站之间的数据传输。某激光通信车载地面光端机600 mm主镜采用微晶材料,重量较大且工作角度不断发生变化。为保证镜面变形精度,该主镜在采用轴向背部9点支撑的基础之上,需同时采用径向支撑结构平衡主镜在其工作角度下重力的径向分力。本文根据主镜工作角度变化,针对传统多点径向支撑结构尺寸大并易造成应力集中等问题,为平衡主镜径向重力分量,减小径向支撑结构尺寸,设计了中心轴与水银带相结合的径向支撑方案,采用有限元分析方法得出水银带参数对主镜面形的影响,优化了支撑参数并设计了支撑结构。主镜面形测试结果表明,采用本文提出的径向支撑结构后,主镜面形达到了预期效果,面形PV值优于λ/5,RMS值优于λ/37,完全满足设计要求。
 Abstract:
Abstract:The main function of the laser communication large-caliber ground optical transceiver is to establish a communication link with the satellite to realize data transmission between the satellite and the ground station. The 600 mm microcrystalline primary mirror of one laser communication station is heavy, and its working angle changes constantly. In order to decrease the mirror surface error, the support system not only has a 9-pose axial support structure but also simultaneously balances the radial component of gravity of the primary mirror at its working angle by using a radial support structure. Flexible lateral support structures have large size and stress, so it is not suit for the mirror that works in a wide range of rotation. The paper researches the lateral support structure with a mercury band and central shaft, and analyses the impact of mercury band parameters on the surface error. The designed lateral structure has small size and improves the surface quality of the mirror. The measured values of PV and RMS are smaller than λ/5 and λ/37, respectively. These result shows that the designed lateral support structure reaches the design purpose and satisfies the requirements.
-
Key words:
- laser communication /
- mercury band /
- lateral support /
- center support /
- surface error
-

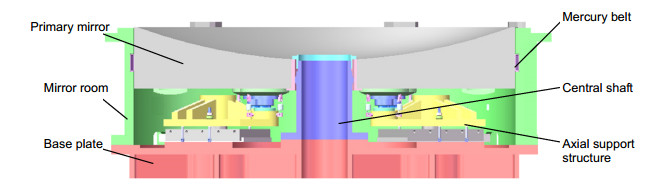
Overview: Laser communication has the advantages of high communication rate, good confidentiality, and strong anti-interference ability, and it has become a rapidly developing new mode of communication. The satellite-ground laser communication link mainly realizes the high-speed transmission of satellite massive data. Large-caliber laser communication optical terminal is an important terminal to ensure the link performance in the satellite-ground link, and directly impacts on link communication performances. As the core component of the optical antenna of the ground station. The primary mirror surface shape accuracy directly determines the optical quality of the system. The main mirror lateral support plays a decisive role in the mirror surface shape accuracy.
The primary mirror of the laser communication vehicle ground optical terminal uses microcrystalline materials. Consideration of costs, the primary mirror lightweight design is not necessary, because the optical terminal has no strict requirements for quality. The primary mirror of laser communication stations is heavy, and its working angle changes constantly. In order to decrease the mirror surface figure, the support structure needs to meet both axial and radial gravity unloading requirements.
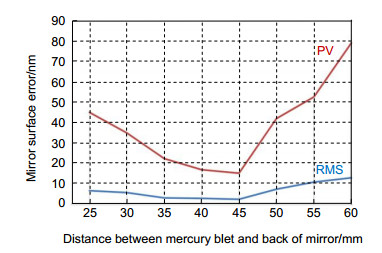
In order to ensure the accuracy of the surface shape, the support system not only has a 9-pose axial support structure but also simultaneously balances the radial component of gravity of the primary mirror. Flexible lateral support structures have large size and stress, so it is not suit for the mirror that works a in wide range of rotation. In this paper, in order to balance the radial gravity component of the primary mirror and reduce the size of the radial support structure, a combination of the central axis and the mercury belt is designed to balance the radial gravity component of the primary mirror. In the radial support scheme, the finite element analysis was used to analyze the influence of mercury belt parameters on the surface shape accuracy of the primary mirror. The support parameters were optimized, and the support structure was designed.
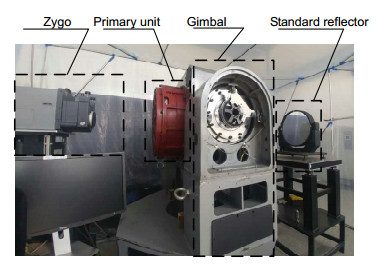
For the 600 mm microcrystalline primary mirror of the laser communication station, a composite radial support structure is designed, in which the method of combining the mercury band with the central support is adopted on the basis of the back 9-point support. The support position and structure parameters of mercury band were analyzed and optimized. After the actual application to the optical antenna primary mirror support of the laser communication ground station, the actual measurement results of the primary mirror assembly show that the designed support structure enables a surface shape error and RMS value of the primary mirror smaller than λ/5 and λ/37, respectively. The radial support fully achieves the design goal, satisfying the surface error requirements of the laser communication primary mirror.
-

-
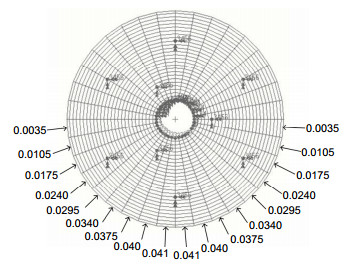
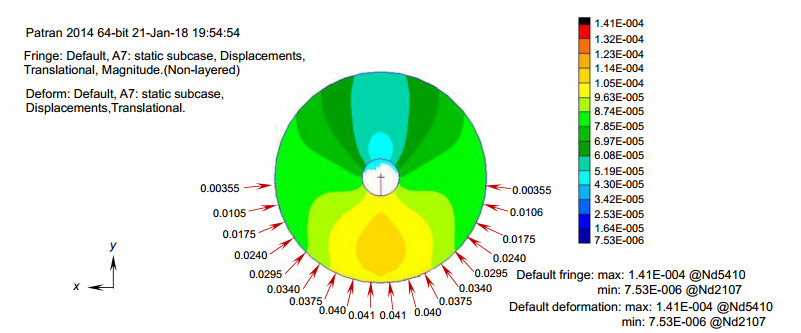
表 1 不同卸载比例下的主镜面形精度
Table 1. Precision of the main mirror shape under different unloading ratios
水银承担重力比例/% 主镜面形误差RMS/nm 90 3.55 85 3.12 80 2.85 75 3.44 70 4.44 -
[1] 刘博, 张景旭, 王富国, 等. 2m SiC主镜Kinematic侧支撑方法设计与优化[J].光电工程, 2016, 43(12): 46–51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.12.008
Liu B, Zhang J X, Wang F G, et al. Design and optimization of kinematic lateral support on 2m SiC primary mirror[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2016, 43(12): 46–51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.12.008
[2] 包奇红, 沙巍, 陈长征, 等.空间SiC反射镜背部中心支撑特性[J].光子学报, 2017, 46(2): 0222003. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gzxb201702003
Bao Q H, Sha W, Chen C Z, et al. Characteristics of rear support in centre for space SiC mirror[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2017, 46(2): 0222003. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gzxb201702003
[3] 张博文, 王小勇, 赵野, 等.天基大口径反射镜支撑技术的发展[J].红外与激光工程, 2018, 47(11): 1113001. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc201811045
Zhang B W, Wang X Y, Zhao Y, et al. Progress of support technique of space-based large aperture mirror[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(11): 1113001. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc201811045
[4] 杜俊峰, 张林波, 任戈. 1.3m主镜的支承设计[J].光学 精密工程, 2007, 15(10): 1483–1488. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxjmgc200710005
Du J F, Zhang L B, Ren G. Mounting system design for 1.3 m primary mirror[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2007, 15(10): 1483–1488. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxjmgc200710005
[5] 高明辉, 王忠素, 杨劲松, 等.大口径反射镜水银带支撑结构物理参数分析[J].光学 精密工程, 2004, 12(4): 18–20. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92835A/2004z2/1000139661.html
Gao M H, Wang Z S, Yang J S, et al. Physical parameter analysis of mercury tube mounting structure for large-aperture mirror[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2004, 12(4): 18–20. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92835A/2004z2/1000139661.html
[6] 刘国庆, 马文礼.大口径轻质镜支撑的有限元分析[J].光电工程, 2001, 28(5): 14–17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2001.05.004
Liu G Q, Ma W L. The finite element analysis for large-aperture lightweight mirror mount[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2001, 28(5): 14–17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2001.05.004
[7] 周宇翔, 沈霞.空间反射镜背部双脚架柔性支撑结构设计[J].激光技术, 2017, 41(1): 141–145. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jgjs201701029
Zhou Y X, Shen X. Structure design of backside bipod flexure mount for space reflector[J]. Laser Technology, 2017, 41(1): 141–145. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jgjs201701029
[8] 王克军, 董吉洪, 宣明, 等.空间遥感器大口径反射镜的复合支撑结构[J].光学 精密工程, 2016, 24(7): 1719–1730. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxjmgc201607023
Wang K J, Dong J H, Xuan M, et al. Compound support structure for large aperture mirror of space remote sensor[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(7): 1719–1730. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxjmgc201607023
[9] 李慎华, 关英俊, 辛宏伟, 等.大口径空间反射镜轻量化设计及其柔性支撑[J].激光与红外, 2017, 47(11): 1422–1427. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jgyhw201711017
Li S H, Guan Y J, Xin H W, et al. Lightweight design and flexible support of large diameter mirror in space camera[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2017, 47(11): 1422–1427. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jgyhw201711017
[10] 约德.光机系统设计[M]. 3版.周海宪, 程云芳, 译.北京: 机械工业出版社, 2008.
Yoder R R Jr. Opto-Mechaoical Systems Design[M]. 3rd ed. Zhou H X, Cheng Y F, trans. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2008.
[11] 张珑, 叶璐, 张金平, 等. 1.2m轻量化空间反射镜的重力支撑变形分离[J].光子学报, 2018, 47(7): 0722002. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gzxb201807010
Zhang L, Ye L, Zhang J P, et al. Gravity and support error separation of 1.2 m lightweight space mirror[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2018, 47(7): 0722002. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gzxb201807010
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: