Broadband cross-slots fractal nano-antenna and its extraordinary optical transmission characteristics
-
摘要:
针对传统纳米天线结构存在频段窄、透射率低的问题,设计了十字缝隙分形纳米天线结构。采用时域有限差分法计算了十字缝隙分形纳米天线结构的异常透射特性,分析了均匀十字缝隙结构与其之间的透射特性差异,并讨论了物理参数对十字缝隙分形纳米天线异常透射特性的影响及分形尺寸与非分形尺寸下的纳米天线透射谱变化关系。结果表明,较于均匀十字缝隙结构,十字缝隙分形结构实现了光的异常透射及全2π透射光束相位调控,尺寸更小型化,半波宽(FWHM)更宽,透射率更高,最高可达99.51%;通过调整物理参数,透射谱呈现出红移或蓝移的特性,实现了透射谱的可控性;同时,当h=50 nm时,FWHM约为356 nm,透射率仍高达95.66%,普遍高于传统结构;并且在大入射角度(70°)下,峰值透射率仍旧大于74%。总之,较于其他纳米天线结构,十字缝隙分形纳米天线具有宽频、可控可调、结构更微型化等特点,且实现了光的异常透射。

-
关键词:
- 纳米天线设计 /
- 十字缝隙分形纳米天线 /
- 表面等离激元共振 /
- 时域有限差分法 /
- 光学异常透射
Abstract:To overcome the disadvantages of narrow frequency band and low transmittance for traditional nano-antenna, a nano-antenna structure based on cross-slots fractal was designed. The extraordinary optical transmission characteristics of the cross-slots fractal nano-antenna and the differences between the cross-slots fractal nano-antenna and the uniform cross-slots nano-antenna were analyzed by the finite difference time domain method. Meanwhile, the influence of physical parameters on the extraordinary optical transmission characteristics of the cross-slots fractal nano-antenna and the relationship of transmission spectrum of the nano-antenna between the fractal size and the non-fractal size were discussed. The results show that the fractal cross-slots structure is more miniaturized, and realizes extraordinary optical transmission and full 2π phase control of transmission beam, and the transmittance is higher than the uniform cross-slots structure, the full width at half maximum (FWHM) is wider, and the highest transmittance is up to 99.51%. By adjusting the physical parameters, the transmission spectrum exhibits red-shift or blue-shift characteristics, achieving controllability of the transmission spectrum. When h=50 nm, the full width at half maximum is about 356 nm, and the transmittance is still as high as 95.66%, which is generally higher than traditional structures, and the peak transmittance is still greater than 74% at large incident angles (70 degrees). In short, the cross-slots fractal nano-antenna has the characteristics of wide frequency, controllable and adjustable, and more miniaturized structure compared with other nano-antenna structures, and realizes extraordinary optical transmission.
-

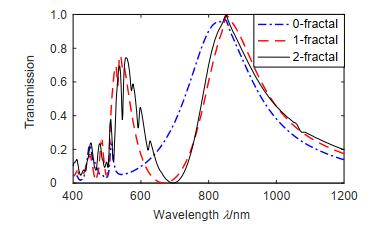
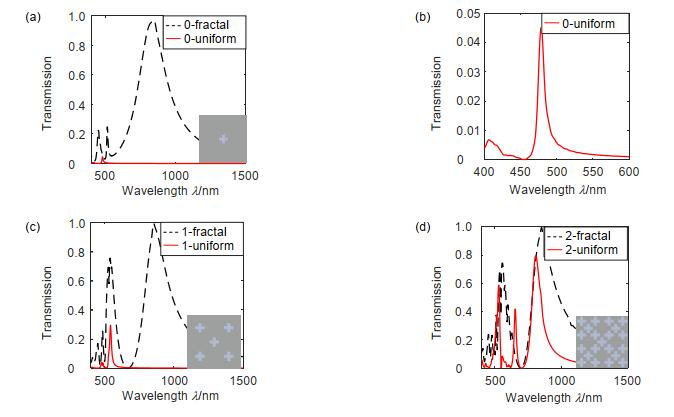
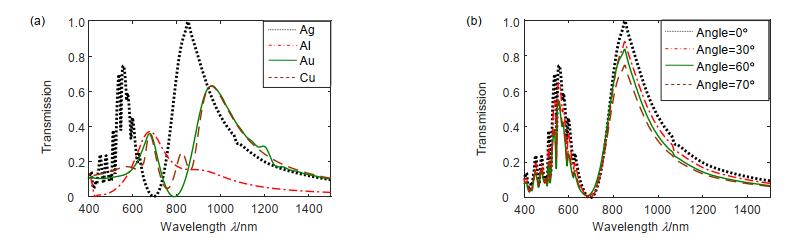
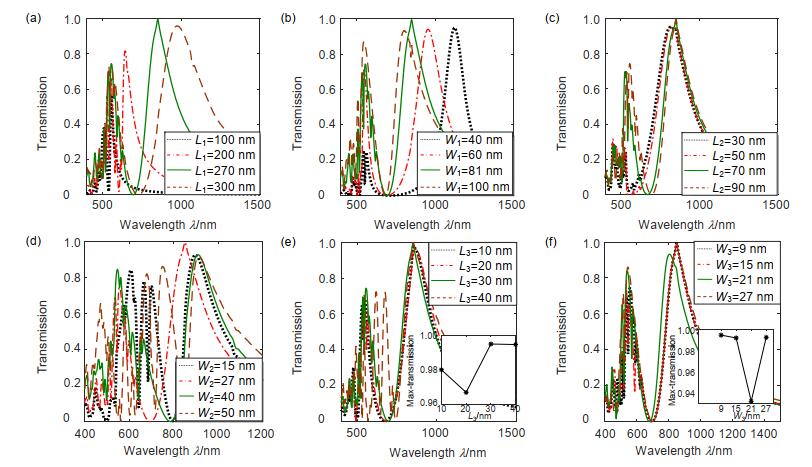
Overview: The nano-antenna structure can break through the optical diffraction limit and achieve efficient transmission of light. For nano-antennas with specific wavelengths of radiation, transmission characteristics are an important characteristic of effective light transmission. Ebbesen et al. found optical extraordinary transmission phenomena when analyzing the transmission characteristics of metal film sub-wavelength aperture arrays. When light is incident on a sub-wavelength aperture array, the light transmission is higher than the ratio of the aperture area to the total area of the film at a particular wavelength, and the transmission is 1 to 2 orders of magnitude higher than the classical aperture transmission theory. Study has shown that the generation of extraordinary optical transmission is generally attributed to the mutual coupling of light waves with free electron oscillations at the surface of metal holes or slots structures, and localized surface plasmons at the edges of apertures or slots also have a non-negligible effect on extraordinary transmission. The coupling efficiency of the plasmon polarization of the upper and lower surfaces of the structure can be improved, thereby enhancing the transmission of light. In order to achieve wide-band extraordinary transmission and the purposes of controllable and adjustable, we introduce fractal theory, and utilize the properties of self-similarity and fractal dimension to propose an extraordinary transmitted cross-slots fractal nano-antenna. Furthermore, the finite-time-difference method is used to calculate the extraordinary transmission characteristics and surface electric field distribution of the cross-slots fractal nano-antenna structure, and the transmission characteristics mechanism is systematically analyzed and compared in detail. The results show that the cross-slots fractal structure is smaller in size, wider in the full width at half maximum (FWHM), and higher in transmittance, up to 99.51%. At 851.536 nm, the light transmittance is much higher than that of the uniform cross-slots structure. The ratio of the hole area to the Ag material area realizes the extraordinary optical transmission. By adjusting the physical parameters, the transmission spectrum exhibits a red-shift or blue-shift characteristic, and achieves the controllability of the transmission spectrum. Meanwhile, when h=50 nm, the FWHM is about 356 nm, the transmittance is still as high as 95.66%, which is generally higher than the traditional structures; At a large incident angle (70 degrees), the peak transmittance is still greater than 74%. In short, the cross-slots fractal nano-antenna has the characteristics of wide frequency, controllable and adjustable, and more miniaturized structure compared with other nano-antenna structures, and realizes the extraordinary transmission of light and full 2π phase transmission control. In addition, the nano-antenna produces a significant resonance in the short-band, which further enhances the transmission of light.
-

-
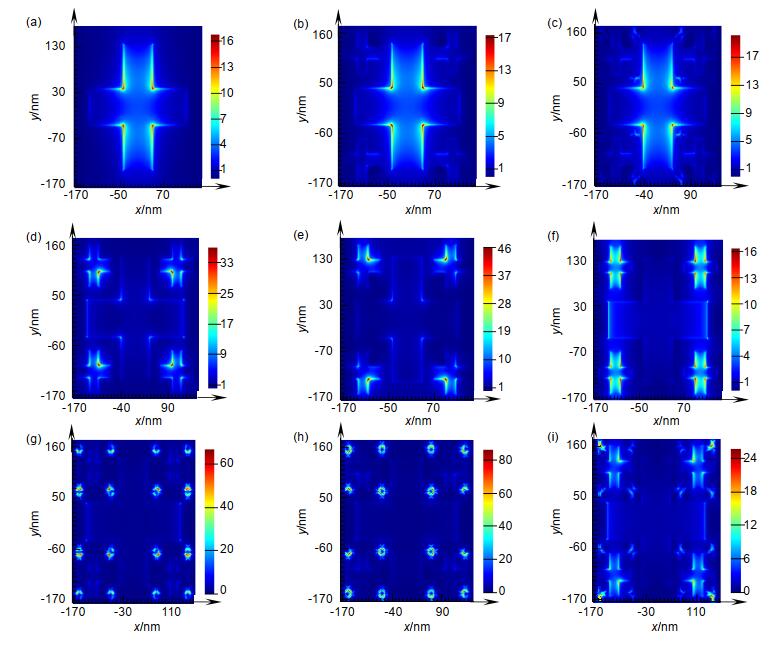
图 4 十字缝隙分形纳米天线表面的电场分布|E|。(a) 0分形:848.495 nm; (b) 1分形:854.598 nm; (c) 2分形:851.536 nm; (d) 1分形:449.995 nm;(e) 1分形:484.89 nm;(f) 1分形:537.542 nm;(g) 2分形:451.706 nm;(h) 2分形:478.061 nm;(i) 2分形:555.123 nm
Figure 4. The electric field distribution |E| on the surface of the cross-slots fractal nano-antenna. (a) 0-fractal: 848.495 nm; (b) 1-fractal: 854.598 nm; (c) 2-fractal: 851.536 nm; (d) 1-fractal: 449.995 nm; (e) 1-fractal: 484.89 nm; (f) 1-fractal: 537.542 nm; (g) 2-fractal: 451.706 nm; (h) 2-fractal: 478.061 nm; (i) 2-fractal: 555.123 nm
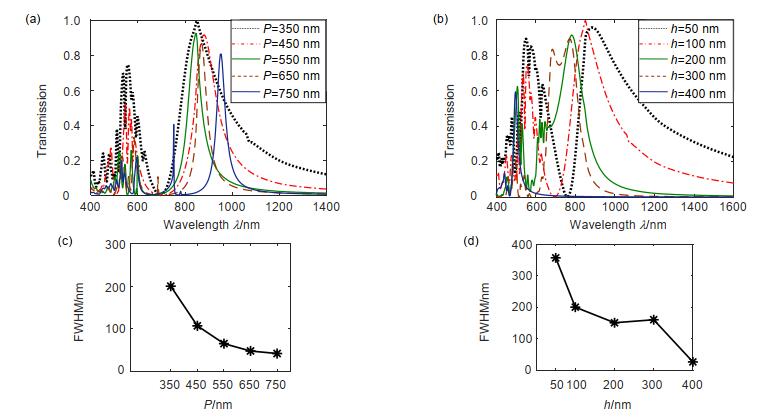
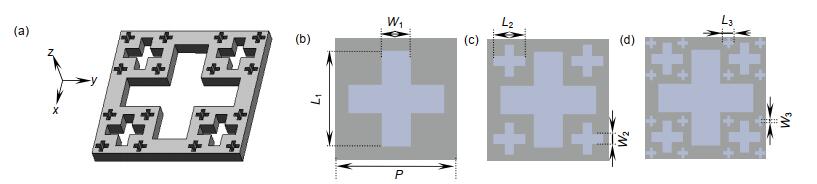
图 6 不同结构参数下的纳米天线结构透射谱及其半波宽。(a)不同边长P下的透射谱;(b)不同厚度h下的透射谱;(c)不同边长P下的半波宽;(d)不同厚度h下的半波宽
Figure 6. Transmission spectrum and FWHM of nano-antenna structure under different structural parameters.(a) Transmission spectrum with different lengths P; (b) Transmission spectrum with different thickness h; (c) FWHM with different lengths P; (d) FWHM with different thickness h
表 1 分形纳米天线实验数据
Table 1. The experimental data of fractal nano-antenna
Fractal nano-structure Peak wavelength/nm Highest peak Slots area/nm2 Total area/nm2 The area ratio 0-fractal 848.495 0.9701 37179 0.3035 1-fractal 854.598 0.9937 53703 122500 0.4384 2-fractal 851.536 0.9951 61047 0.4983 -
[1] Ebbesen T W, Lezec H J, Ghaemi H F, et al. Extraordinary optical transmission through sub-wavelength hole arrays[J]. Nature, 1998, 391(6668): 667–669. doi: 10.1038/35570
[2] Bethe H A. Theory of diffraction by small holes[J]. Physical Review, 1944, 66(7–8): 163–182. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.66.163
[3] 何嵩磊.基于分形图案的频率选择表面的仿真设计[D].武汉: 华中科技大学, 2015.
He S L. The simulation and design of frequency selective surface with fractal pattern[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science & Technology, 2015.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10487-1015906409.htm [4] 郭团.等离子体共振光纤光栅生物传感器综述[J].光学学报, 2018, 38(3): 0328006. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201803006
Guo T. Review on plasmonic optical fiber grating biosensors[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(3): 0328006. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201803006
[5] 王俊林, 张斌珍, 段俊萍, 等.柔性双阻带太赫兹超材料滤波器[J].光学学报, 2017, 37(10): 1016001. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201710032
Wang J L, Zhang B Z, Duan J P, et al. Flexible dual-stopband terahertz metamaterial filter[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(10): 1016001. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxxb201710032
[6] 祁云平, 张雪伟, 周培阳, 等.基于十字连通形环形谐振腔金属-介质-金属波导的折射率传感器和滤波器[J].物理学报, 2018, 67(19): 197301. doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20180758
Qi Y P, Zhang X W, Zhou P Y, et al. Refractive index sensor and filter of metal-insulator-metal waveguide based on ring resonator emb edded by cross structure[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2018, 67(19): 197301. doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20180758
[7] Ghaemi H F, Thio T, Grupp D E, et al. Surface plasmons enhance optical transmission through subwavelength holes[J]. Physical Review B, 1998, 58(11): 6779–6782. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.58.6779
[8] Van Der Molen K L, Koerkamp K J K, Enoch S, et al. Role of shape and localized resonances in extraordinary transmission through periodic arrays of subwavelength holes: Experiment and theory[J]. Physical Review B, 2005, 72(4): 045421. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.72.045421
[9] Degiron A, Ebbesen T W. The role of localized surface plasmon modes in the enhanced transmission of periodic subwavelength apertures[J]. Journal of Optics A: Pure and Applied Optics, 2005, 7(2): S90–S96. doi: 10.1088/1464-4258/7/2/012
[10] Zhang X N, Liu G Q, Liu Z Q, et al. Near-field plasmon effects in extraordinary optical transmission through periodic triangular hole arrays[J]. Optical Engineering, 2014, 53(10): 107108. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.53.10.107108
[11] Zhang X N, Liu G Q, Liu Z Q, et al. Effects of compound rectangular subwavelength hole arrays on enhancing optical transmission[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2015, 7(1): 4500408. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273491405_Effects_of_Compound_Rectangular_Subwavelength_Hole_Arrays_on_Enhancing_Optical_Transmission
[12] Zhang W, Wang Y K, Luo L N, et al. Extraordinary optical transmission of broadband through tapered multilayer slits[J]. Plasmonics, 2015, 10(3): 547–551. doi: 10.1007/s11468-014-9839-4
[13] 赵波, 杨建军, 黄振芬.基于表面等离激元交叉耦合作用的纳米金属双缝异常透射现象[J].光子学报, 2018, 47(3): 0324005. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzxb201803005
Zhao B, Yang J J, Huang Z F. Anomalous transmission properties of two integrated metallic nanoslits under plasmonic cross talking coupling[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2018, 47(3): 0324005. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzxb201803005
[14] 肖花.基于分形结构的多频与宽带天线研究[D].成都: 电子科技大学, 2018.
Xiao H. The research of multi-band and broadband antenna based on fractal structure[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2018.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10614-1018990761.htm [15] De Nicola F, Purayil N S P, Spirito D, et al. Multiband plasmonic sierpinski carpet fractal antennas[J]. ACS Photonics, 2018, 5(6): 2418–2425. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.8b00186
[16] Puente-Baliarda C, Romeu J, Pous A, et al. On the behavior of the sierpinski multiband fractal antenna[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1998, 46(4): 517–524. doi: 10.1109/8.664115
[17] Cakmakyapan S, Cinel N A, Cakmak A O, et al. Validation of electromagnetic field enhancement in near-infrared through sierpinski fractal nanoantennas[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(16): 19504–19512. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25321033
[18] Sivia J S, Kaur G, Sarao A K. A modified sierpinski carpet fractal antenna for multiband applications[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2017, 95(4): 4269–4279. doi: 10.1007/s11277-017-4079-5
[19] Johnson P B, Christy R W. Optical constants of the noble metals[J]. Physical Review B, 1972, 6(12): 4370–4379. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.6.4370
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: